Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.surface.SurfaceImage¶
- class nilearn.surface.SurfaceImage(mesh, data, dtype=None)[source]¶
Surface image containing meshes & data for both hemispheres.
Added in Nilearn 0.11.0.
- Parameters:
- mesh
nilearn.surface.PolyMesh, ordictofnilearn.surface.SurfaceMesh,str,pathlib.Path Meshes for the both hemispheres.
- data
nilearn.surface.PolyData, ordictofnumpy.ndarray,str,pathlib.Path Data for the both hemispheres.
- dtypeDTypeLike object, default=None
dtype to enforce on the data. If
Nonethe original dtype is used.Added in Nilearn 0.12.1.
- mesh
- Attributes:
shape(int, int)Shape of the data.
- classmethod from_volume(mesh, volume_img, inner_mesh=None, **vol_to_surf_kwargs)[source]¶
Create surface image from volume image.
- Parameters:
- mesh
nilearn.surface.PolyMeshordictofnilearn.surface.SurfaceMesh,str,pathlib.Path Surface mesh.
- volume_imgNiimg-like object
3D or 4D volume image to project to the surface mesh.
- inner_mesh
nilearn.surface.PolyMeshordictofnilearn.surface.SurfaceMesh,str,pathlib.Path, default=None Inner mesh to pass to
nilearn.surface.vol_to_surf.- vol_to_surf_kwargs
dict[str, Any] Dictionary of extra key-words arguments to pass to
nilearn.surface.vol_to_surf.
- mesh
Examples
>>> from nilearn.surface import SurfaceImage >>> from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage >>> from nilearn.datasets import load_sample_motor_activation_image
>>> fsavg = load_fsaverage() >>> vol_img = load_sample_motor_activation_image() >>> img = SurfaceImage.from_volume(fsavg["white_matter"], vol_img) >>> img <SurfaceImage (20484,)> >>> img = SurfaceImage.from_volume( ... fsavg["white_matter"], vol_img, inner_mesh=fsavg["pial"] ... ) >>> img <SurfaceImage (20484,)>
- property shape¶
Shape of the data.
Examples using nilearn.surface.SurfaceImage¶
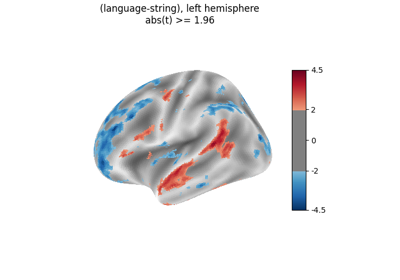
Surface-based dataset first and second level analysis of a dataset
Surface-based dataset first and second level analysis of a dataset