Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Extracting signals from a brain parcellation¶
Here we show how to extract signals from a brain parcellation and compute a correlation matrix.
We also show the importance of defining good confounds signals: the
first correlation matrix is computed after regressing out simple
confounds signals: movement regressors, white matter and CSF signals, …
The second one is without any confounds: all regions are connected to each
other. Finally we demonstrated the functionality of
load_confounds to flexibly select confound
variables from fMRIPrep outputs while following some implementation
guideline of fMRIPrep confounds documentation
https://fmriprep.org/en/stable/outputs.html#confounds.
One reference that discusses the importance of confounds is Varoquaux and Craddock[1].
This is just a code example, see the corresponding section in the documentation for more.
Retrieve the atlas and the data¶
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_atlas_harvard_oxford, fetch_development_fmri
dataset = fetch_atlas_harvard_oxford("cort-maxprob-thr25-2mm")
atlas_filename = dataset.maps
labels = dataset.labels
look_up_table = dataset.lut
print(f"Atlas ROIs are located in nifti image (4D) at: {atlas_filename}")
# One subject of brain development fMRI data
data = fetch_development_fmri(n_subjects=1, reduce_confounds=True)
fmri_filenames = data.func[0]
reduced_confounds = data.confounds[0] # This is a preselected set of confounds
[fetch_atlas_harvard_oxford] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/fsl
Atlas ROIs are located in nifti image (4D) at:
<class 'nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image'>
data shape (91, 109, 91)
affine:
[[ 2. 0. 0. -90.]
[ 0. 2. 0. -126.]
[ 0. 0. 2. -72.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
metadata:
<class 'nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Header'> object, endian='<'
sizeof_hdr : 348
data_type : np.bytes_(b'')
db_name : np.bytes_(b'')
extents : 0
session_error : 0
regular : np.bytes_(b'r')
dim_info : 0
dim : [ 3 91 109 91 1 1 1 1]
intent_p1 : 0.0
intent_p2 : 0.0
intent_p3 : 0.0
intent_code : none
datatype : uint8
bitpix : 8
slice_start : 0
pixdim : [1. 2. 2. 2. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
vox_offset : 0.0
scl_slope : nan
scl_inter : nan
slice_end : 0
slice_code : unknown
xyzt_units : 10
cal_max : 48.0
cal_min : 0.0
slice_duration : 0.0
toffset : 0.0
glmax : 0
glmin : 0
descrip : np.bytes_(b'FSL3.3')
aux_file : np.bytes_(b'MGH-Cortical')
qform_code : unknown
sform_code : aligned
quatern_b : 0.0
quatern_c : 0.0
quatern_d : 0.0
qoffset_x : -90.0
qoffset_y : -126.0
qoffset_z : -72.0
srow_x : [ 2. 0. 0. -90.]
srow_y : [ 0. 2. 0. -126.]
srow_z : [ 0. 0. 2. -72.]
intent_name : np.bytes_(b'')
magic : np.bytes_(b'n+1')
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
Extract signals on a parcellation defined by labels¶
Using the NiftiLabelsMasker
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiLabelsMasker
masker = NiftiLabelsMasker(
labels_img=atlas_filename,
lut=look_up_table,
standardize_confounds=True,
memory="nilearn_cache",
verbose=1,
)
# Here we go from nifti files to the signal time series in a numpy
# array. Note how we give confounds to be regressed out during signal
# extraction
time_series = masker.fit_transform(fmri_filenames, confounds=reduced_confounds)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:60: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_labels_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f3288515ff0>,
{ 'background_label': 0,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'CMRmap_r',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'keep_masked_labels': False,
'labels': None,
'labels_img': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>,
'low_pass': None,
'lut': index name
0 0 Background
1 1 Frontal Pole
2 2 Insular Cortex
3 3 Superior Frontal Gyrus
4 4 Middle Frontal Gyrus
..., confounds=[ '/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_desc-reducedConfounds_regressors.tsv'], sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:60: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 0.4s, 0.0min
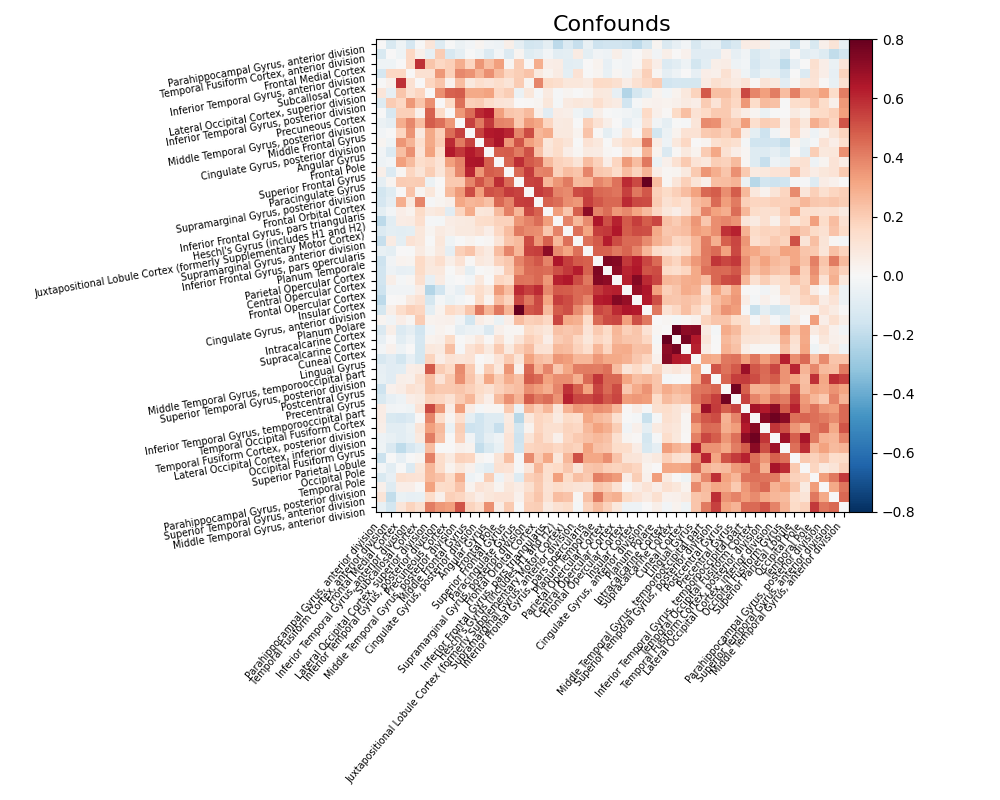
Compute and display a correlation matrix¶
from nilearn.connectome import ConnectivityMeasure
correlation_measure = ConnectivityMeasure(kind="correlation", verbose=1)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
# Plot the correlation matrix
import numpy as np
from nilearn.plotting import plot_matrix, show
# Make a large figure
# Mask the main diagonal for visualization:
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
# The labels we have start with the background (0), hence we skip the
# first label
# matrices are ordered for block-like representation
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="Confounds",
reorder=True,
)
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f3288017940>
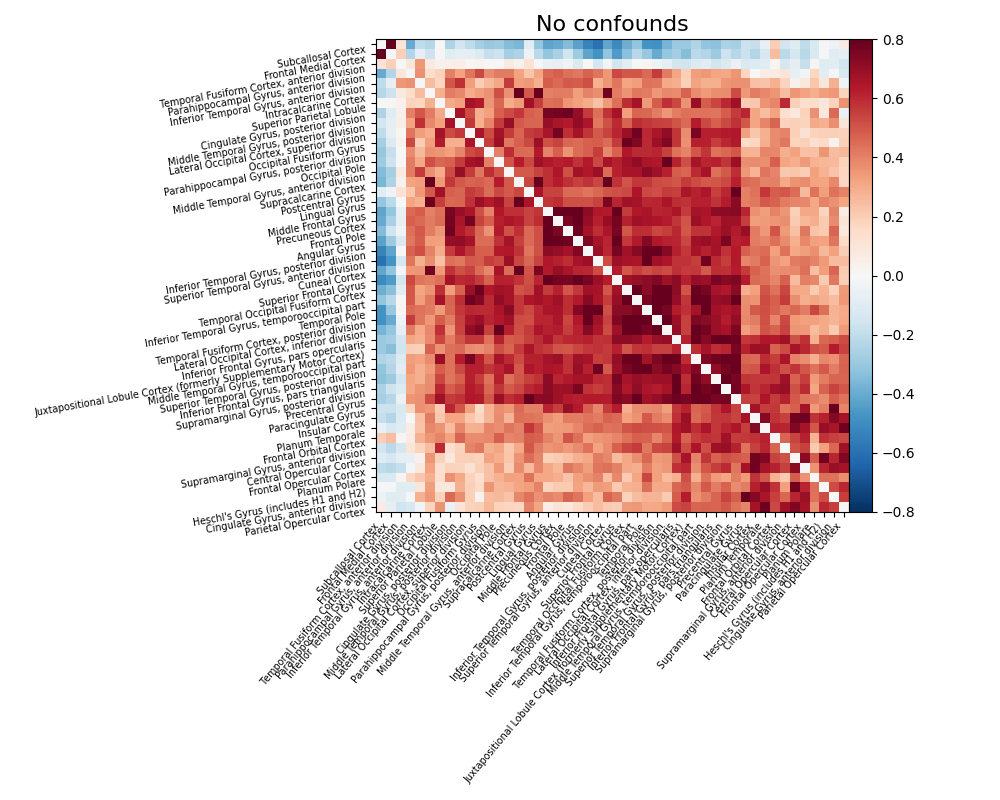
Extract signals and compute a connectivity matrix without confounds removal¶
After covering the basic of signal extraction and functional connectivity matrix presentation, let’s look into the impact of confounds to fMRI signal and functional connectivity. Firstly let’s find out what a functional connectivity matrix looks like without confound removal.
time_series = masker.fit_transform(fmri_filenames)
# Note how we did not specify confounds above. This is bad!
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="No confounds",
reorder=True,
)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:99: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_labels_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f32a8998bb0>,
{ 'background_label': 0,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'CMRmap_r',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'keep_masked_labels': False,
'labels': None,
'labels_img': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>,
'low_pass': None,
'lut': index name
0 0 Background
1 1 Frontal Pole
2 2 Insular Cortex
3 3 Superior Frontal Gyrus
4 4 Middle Frontal Gyrus
..., confounds=None, sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:99: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 0.4s, 0.0min
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f32a7f91750>
Load confounds from file using a flexible strategy with fmriprep interface¶
The load_confounds function provides
flexible parameters to retrieve the relevant columns from the TSV file
generated by fMRIPrep.
load_confounds ensures two things:
The correct regressors are selected with provided strategy, and
Volumes such as non-steady-state and/or high motion volumes are masked out correctly.
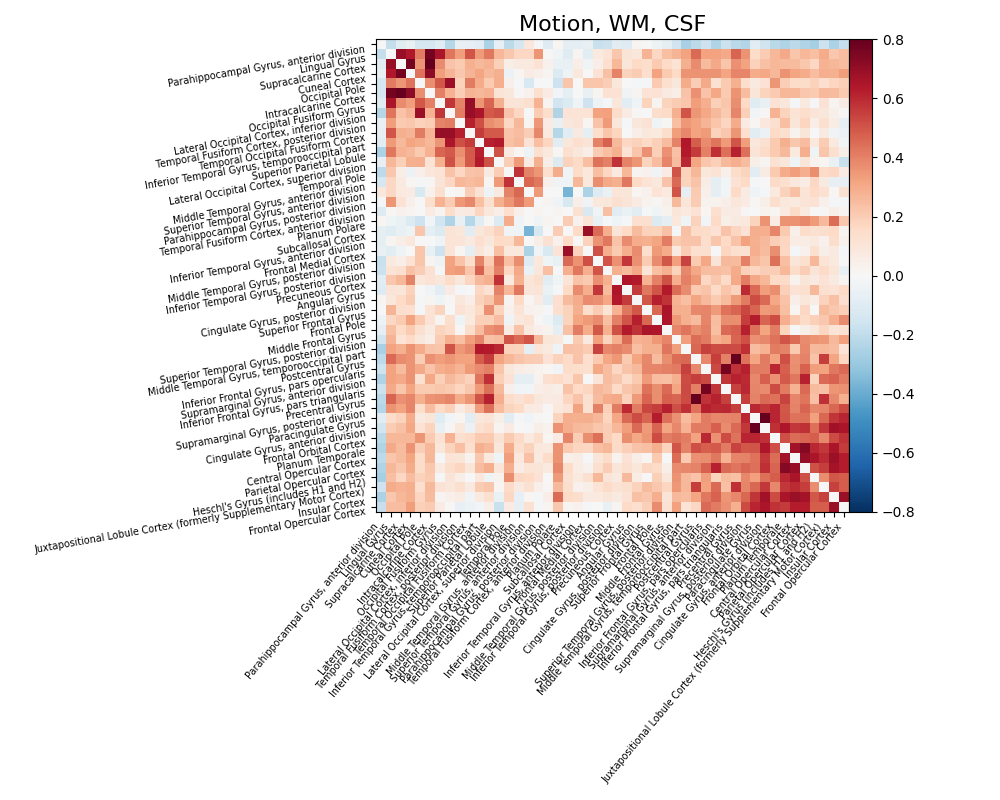
Let’s try a simple strategy removing motion, white matter signal, cerebrospinal fluid signal with high-pass filtering.
from nilearn.interfaces.fmriprep import load_confounds
confounds_simple, sample_mask = load_confounds(
fmri_filenames,
strategy=["high_pass", "motion", "wm_csf"],
motion="basic",
wm_csf="basic",
)
print("The shape of the confounds matrix is:", confounds_simple.shape)
print(confounds_simple.columns)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
fmri_filenames, confounds=confounds_simple, sample_mask=sample_mask
)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="Motion, WM, CSF",
reorder=True,
)
The shape of the confounds matrix is: (168, 12)
Index(['cosine00', 'cosine01', 'cosine02', 'cosine03', 'csf', 'rot_x', 'rot_y',
'rot_z', 'trans_x', 'trans_y', 'trans_z', 'white_matter'],
dtype='object')
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:144: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_labels_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f32a8998d60>,
{ 'background_label': 0,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'CMRmap_r',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'keep_masked_labels': False,
'labels': None,
'labels_img': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>,
'low_pass': None,
'lut': index name
0 0 Background
1 1 Frontal Pole
2 2 Insular Cortex
3 3 Superior Frontal Gyrus
4 4 Middle Frontal Gyrus
..., confounds=[ cosine00 cosine01 cosine02 ... trans_y trans_z white_matter
0 0.109104 0.109090 0.109066 ... -0.026078 0.055006 -0.876886
1 0.109066 0.108937 0.108723 ... -0.027587 0.049458 -1.418909
2 0.108990 0.108632 0.108038 ... -0.019085 0.075787 -1.540842
3 0.108875 0.108176 0.107012 ... -0.023900 0.053022 -1.922085
4 0.108723 0.107567 0.105651 ... -0.033396 0.077764 -1.843388
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
163 -0.108723 0.107567 -0.105651 ... 0.064873 -0.022169 1.221217
164 -0.108875 0.108176 -0.107012 ... -0.064266 -0.042248 1.237783
165 -0.108990 0.108632 -0.108038 ... 0.053241 -0.029500 1.590905
166 -0.109066 0.108937 -0.108723 ... -0.081559 -0.034236 1.122246
167 -0.109104 0.109090 -0.109066 ... 0.069287 -0.007294 1.000828
[168 rows x 12 columns]], sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:144: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 0.4s, 0.0min
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f32a7468e50>
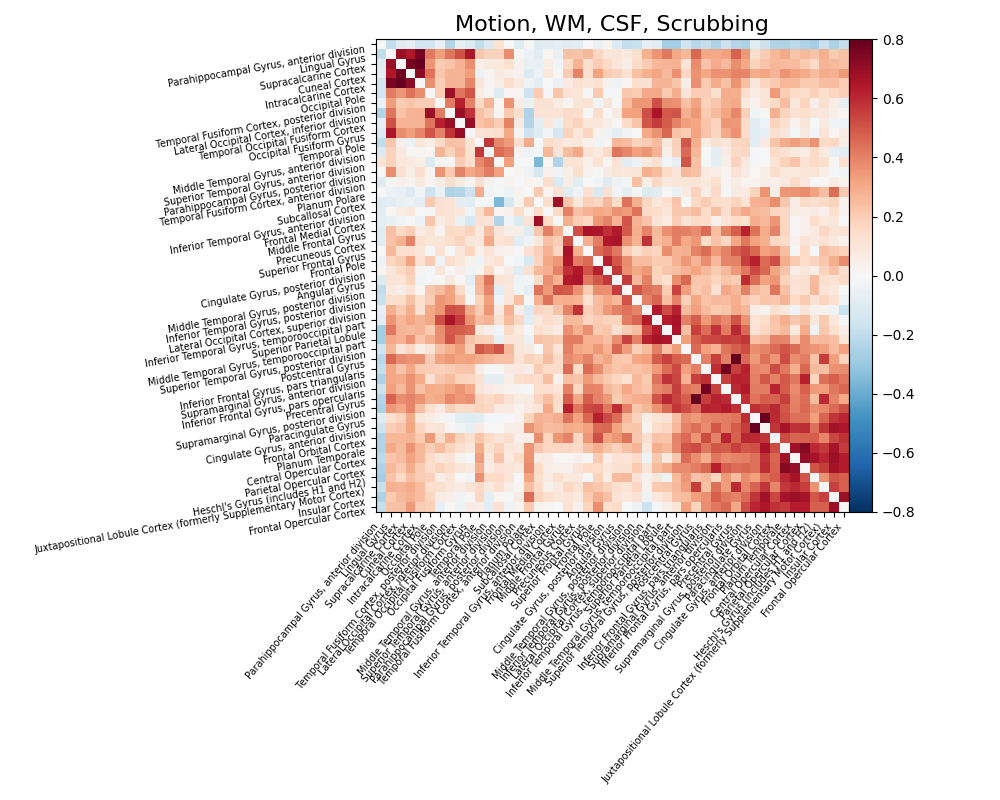
Motion-based scrubbing¶
With a scrubbing-based strategy,
load_confounds returns a sample_mask
that removes the index of volumes exceeding the framewise displacement and
standardized DVARS threshold, and all the continuous segment with less than
five volumes. Before applying scrubbing, it’s important to access the
percentage of volumns scrubbed. Scrubbing is not a suitable strategy for
datasets with too many high motion subjects.
On top of the simple strategy above, let’s add scrubbing to our
strategy.
confounds_scrub, sample_mask = load_confounds(
fmri_filenames,
strategy=["high_pass", "motion", "wm_csf", "scrub"],
motion="basic",
wm_csf="basic",
)
print(
f"After scrubbing, {sample_mask.shape[0]} "
f"out of {confounds_scrub.shape[0]} volumes remains"
)
print("The shape of the confounds matrix is:", confounds_simple.shape)
print(confounds_scrub.columns)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
fmri_filenames, confounds=confounds_scrub, sample_mask=sample_mask
)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="Motion, WM, CSF, Scrubbing",
reorder=True,
)
After scrubbing, 164 out of 168 volumes remains
The shape of the confounds matrix is: (168, 12)
Index(['cosine00', 'cosine01', 'cosine02', 'cosine03', 'csf', 'rot_x', 'rot_y',
'rot_z', 'trans_x', 'trans_y', 'trans_z', 'white_matter'],
dtype='object')
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:189: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_labels_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f32a0d20970>,
{ 'background_label': 0,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'CMRmap_r',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'keep_masked_labels': False,
'labels': None,
'labels_img': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>,
'low_pass': None,
'lut': index name
0 0 Background
1 1 Frontal Pole
2 2 Insular Cortex
3 3 Superior Frontal Gyrus
4 4 Middle Frontal Gyrus
..., confounds=[ cosine00 cosine01 cosine02 ... trans_y trans_z white_matter
0 0.108440 0.106895 0.110644 ... -0.026366 0.054759 -0.878390
1 0.108401 0.106742 0.110301 ... -0.027876 0.049211 -1.420413
2 0.108325 0.106438 0.109616 ... -0.019374 0.075540 -1.542346
3 0.108211 0.105981 0.108591 ... -0.024188 0.052775 -1.923589
4 0.108058 0.105373 0.107229 ... -0.033685 0.077517 -1.844892
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
163 -0.109387 0.105373 -0.104073 ... 0.064585 -0.022416 1.219713
164 -0.109540 0.105981 -0.105434 ... -0.064554 -0.042495 1.236279
165 -0.109654 0.106438 -0.106460 ... 0.052952 -0.029747 1.589401
166 -0.109731 0.106742 -0.107145 ... -0.081847 -0.034483 1.120742
167 -0.109769 0.106895 -0.107488 ... 0.068998 -0.007541 0.999324
[168 rows x 12 columns]], sample_mask=array([ 0, ..., 167], shape=(164,)), dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:189: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 0.4s, 0.0min
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f32a7f92050>
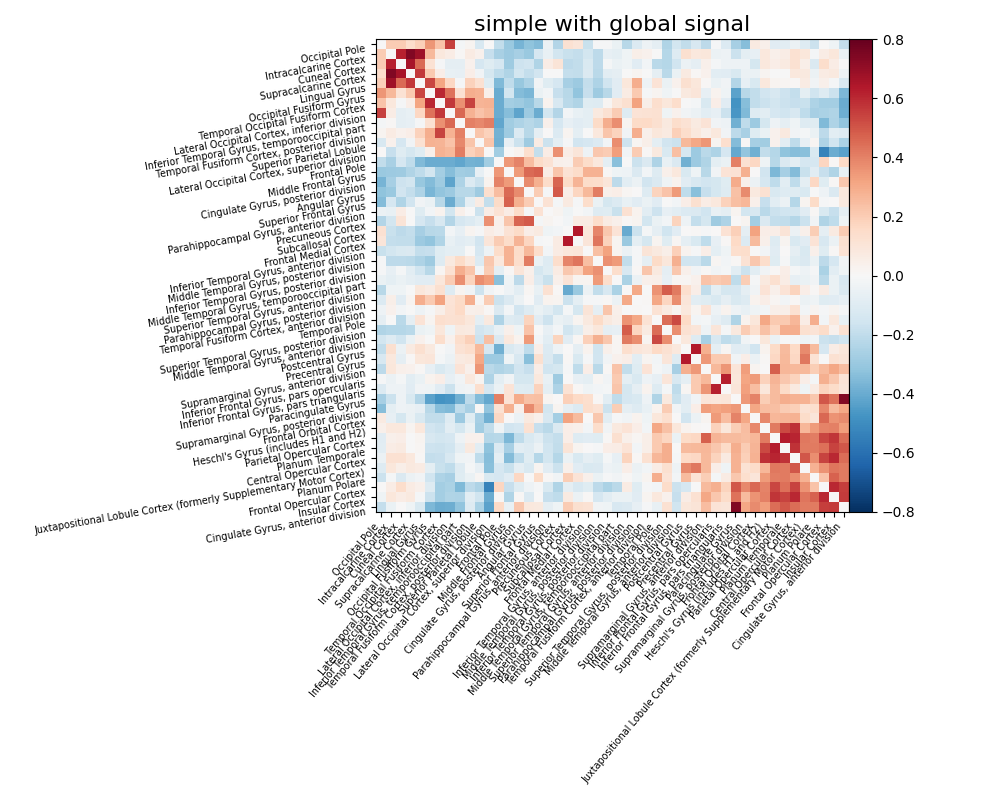
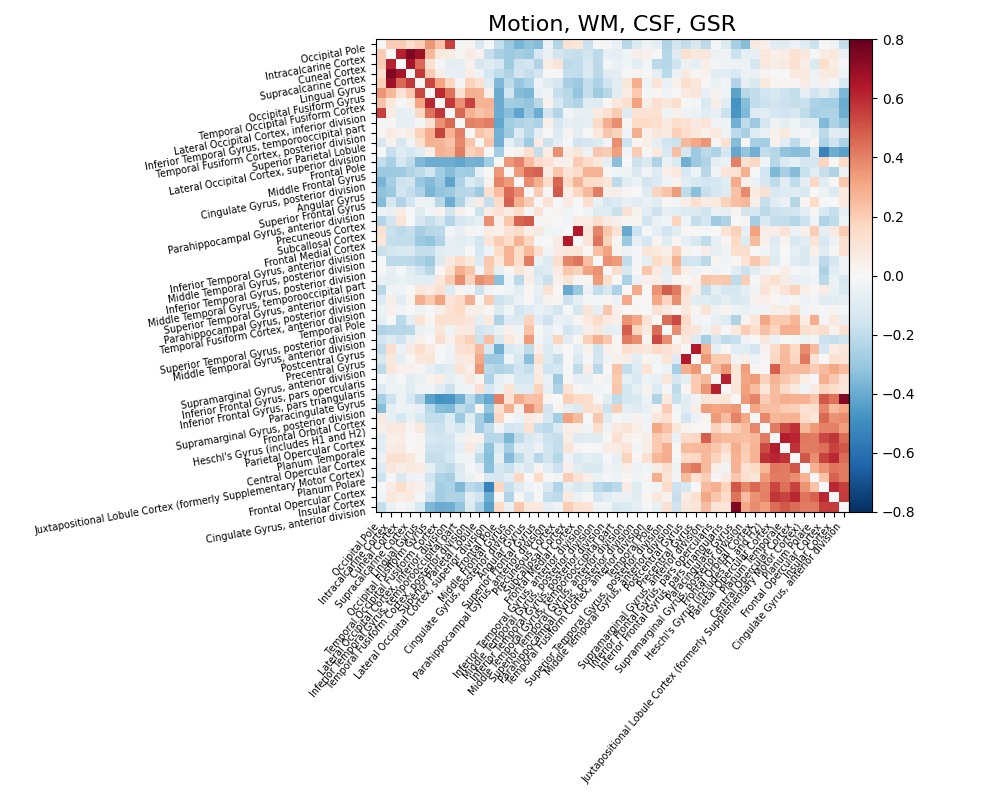
The impact of global signal removal¶
Global signal removes the grand mean from your signal. The benefit is that it can remove impacts of physiological artifacts with minimal impact on the degrees of freedom. The downside is that one cannot get insight into variance explained by certain sources of noise. Now let’s add global signal to the simple strategy and see its impact.
confounds_minimal_no_gsr, sample_mask = load_confounds(
fmri_filenames,
strategy=["high_pass", "motion", "wm_csf", "global_signal"],
motion="basic",
wm_csf="basic",
global_signal="basic",
)
print("The shape of the confounds matrix is:", confounds_minimal_no_gsr.shape)
print(confounds_minimal_no_gsr.columns)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
fmri_filenames, confounds=confounds_minimal_no_gsr, sample_mask=sample_mask
)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="Motion, WM, CSF, GSR",
reorder=True,
)
The shape of the confounds matrix is: (168, 13)
Index(['cosine00', 'cosine01', 'cosine02', 'cosine03', 'csf', 'global_signal',
'rot_x', 'rot_y', 'rot_z', 'trans_x', 'trans_y', 'trans_z',
'white_matter'],
dtype='object')
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:226: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_labels_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f3288015c00>,
{ 'background_label': 0,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'CMRmap_r',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'keep_masked_labels': False,
'labels': None,
'labels_img': <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>,
'low_pass': None,
'lut': index name
0 0 Background
1 1 Frontal Pole
2 2 Insular Cortex
3 3 Superior Frontal Gyrus
4 4 Middle Frontal Gyrus
..., confounds=[ cosine00 cosine01 cosine02 ... trans_y trans_z white_matter
0 0.109104 0.109090 0.109066 ... -0.026078 0.055006 -0.876886
1 0.109066 0.108937 0.108723 ... -0.027587 0.049458 -1.418909
2 0.108990 0.108632 0.108038 ... -0.019085 0.075787 -1.540842
3 0.108875 0.108176 0.107012 ... -0.023900 0.053022 -1.922085
4 0.108723 0.107567 0.105651 ... -0.033396 0.077764 -1.843388
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
163 -0.108723 0.107567 -0.105651 ... 0.064873 -0.022169 1.221217
164 -0.108875 0.108176 -0.107012 ... -0.064266 -0.042248 1.237783
165 -0.108990 0.108632 -0.108038 ... 0.053241 -0.029500 1.590905
166 -0.109066 0.108937 -0.108723 ... -0.081559 -0.034236 1.122246
167 -0.109104 0.109090 -0.109066 ... 0.069287 -0.007294 1.000828
[168 rows x 13 columns]], sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:226: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 0.4s, 0.0min
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7f32c4e46500>
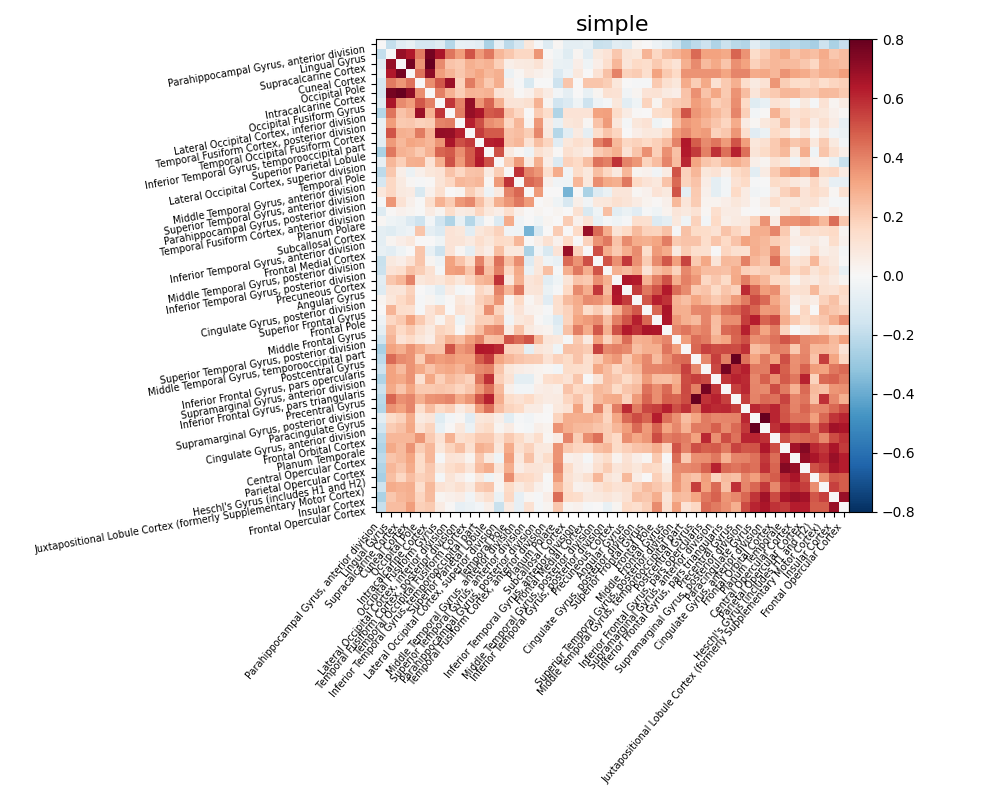
Using predefined strategies¶
Instead of customizing the strategy through
load_confounds, one can use a predefined
strategy with load_confounds_strategy.
Based on the confound variables generated through fMRIPrep, and past
benchmarks studies (Ciric et al.[2], Parkes et al.[3]):
simple, scrubbing, compcor, ica_aroma.
The following examples shows how to use the simple strategy and overwrite
the motion default to basic.
from nilearn.interfaces.fmriprep import load_confounds_strategy
# use default parameters
confounds, sample_mask = load_confounds_strategy(
fmri_filenames, denoise_strategy="simple", motion="basic"
)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
fmri_filenames, confounds=confounds, sample_mask=sample_mask
)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="simple",
reorder=True,
)
# add optional parameter global signal
confounds, sample_mask = load_confounds_strategy(
fmri_filenames,
denoise_strategy="simple",
motion="basic",
global_signal="basic",
)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
fmri_filenames, confounds=confounds, sample_mask=sample_mask
)
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[0]
np.fill_diagonal(correlation_matrix, 0)
plot_matrix(
correlation_matrix,
figure=(10, 8),
labels=labels[1:],
vmax=0.8,
vmin=-0.8,
title="simple with global signal",
reorder=True,
)
show()
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:262: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Loading regions from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
object at 0x7f32a8fafa00>
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Resampling regions
[NiftiLabelsMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_signal_extraction.py:287: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.090 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 481 MB