Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Extract signals on spheres and plot a connectome¶
This example shows how to extract signals from spherical regions. We show how to build spheres around user-defined coordinates, as well as centered on coordinates from the Power-264 atlas (Power et al.[1]), and the Dosenbach-160 atlas (Dosenbach et al.[2]).
We estimate connectomes using two different methods: sparse inverse covariance and partial_correlation, to recover the functional brain networks structure.
We’ll start by extracting signals from Default Mode Network regions and computing a connectome from them.
Retrieve the brain development fMRI dataset¶
We are going to use a subject from the development functional connectivity dataset.
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_development_fmri
dataset = fetch_development_fmri(n_subjects=10)
# print basic information on the dataset
print(f"First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: {dataset.func[0]}")
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz
Coordinates of Default Mode Network¶
dmn_coords = [(0, -52, 18), (-46, -68, 32), (46, -68, 32), (1, 50, -5)]
labels = [
"Posterior Cingulate Cortex",
"Left Temporoparietal junction",
"Right Temporoparietal junction",
"Medial prefrontal cortex",
]
Extracts signal from sphere around DMN seeds¶
We can compute the mean signal within spheres of a fixed radius
around a sequence of (x, y, z) coordinates with the object
NiftiSpheresMasker.
The resulting signal is then prepared by the masker object: Detrended,
band-pass filtered and standardized to 1 variance.
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiSpheresMasker
masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
dmn_coords,
radius=8,
detrend=True,
standardize_confounds=True,
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=dataset.t_r,
memory="nilearn_cache",
memory_level=1,
verbose=1,
clean_args={
"butterworth__padtype": "even"
}, # kwarg to modify Butterworth filter
)
# Additionally, we pass confound information to ensure our extracted
# signal is cleaned from confounds.
func_filename = dataset.func[0]
confounds_filename = dataset.confounds[0]
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=[confounds_filename]
)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:76: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_spheres_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f32a0dafe80>,
{ 'allow_overlap': False,
'clean_args': {'butterworth__padtype': 'even'},
'clean_kwargs': {'butterworth__padtype': 'even'},
'detrend': True,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': 0.01,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'low_pass': 0.1,
'mask_img': None,
'radius': 8,
'reports': True,
'seeds': [(0, -52, 18), (-46, -68, 32), (46, -68, 32), (1, 50, -5)],
'smoothing_fwhm': None,
'standardize': False,
'standardize_confounds': True,
't_r': 2}, confounds=[ '/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_desc-reducedConfounds_regressors.tsv'], sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:76: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 1.5s, 0.0min
Display spheres summary report¶
By default all spheres are displayed.
This can be tweaked by passing an integer or list/array of indices
to the displayed_spheres argument of generate_report.
Display time series¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(constrained_layout=True)
for time_serie, label in zip(time_series.T, labels, strict=False):
plt.plot(time_serie, label=label)
plt.title("Default Mode Network Time Series")
plt.xlabel("Scan number")
plt.ylabel("Normalized signal")
plt.legend()
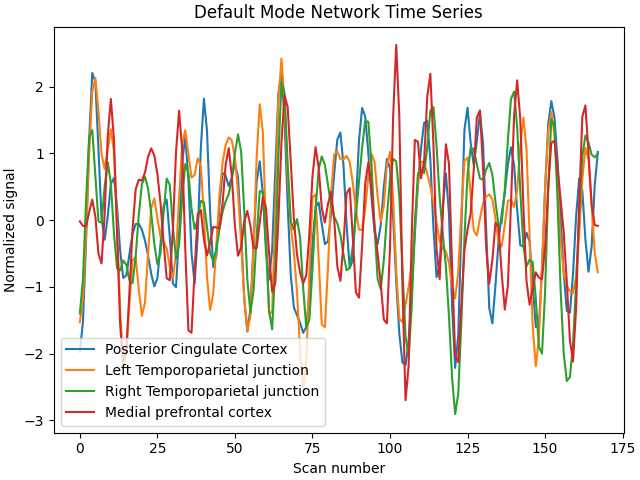
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f32a07b2e90>
Compute partial correlation matrix¶
Using object ConnectivityMeasure:
its default covariance estimator is Ledoit-Wolf,
allowing to obtain accurate partial correlations.
from nilearn.connectome import ConnectivityMeasure
connectivity_measure = ConnectivityMeasure(
kind="partial correlation", verbose=1
)
partial_correlation_matrix = connectivity_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[
0
]
[ConnectivityMeasure.wrapped] Finished fit
Display connectome¶
We display the graph of connections with :func: nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome.
from nilearn.plotting import plot_connectome, show
plot_connectome(
partial_correlation_matrix,
dmn_coords,
title="Default Mode Network Connectivity",
)
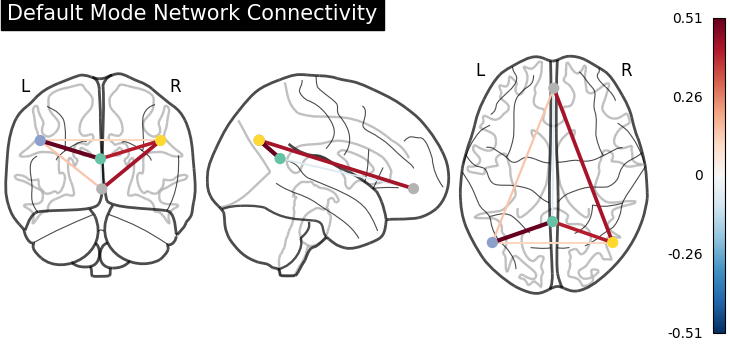
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7f32c4db6440>
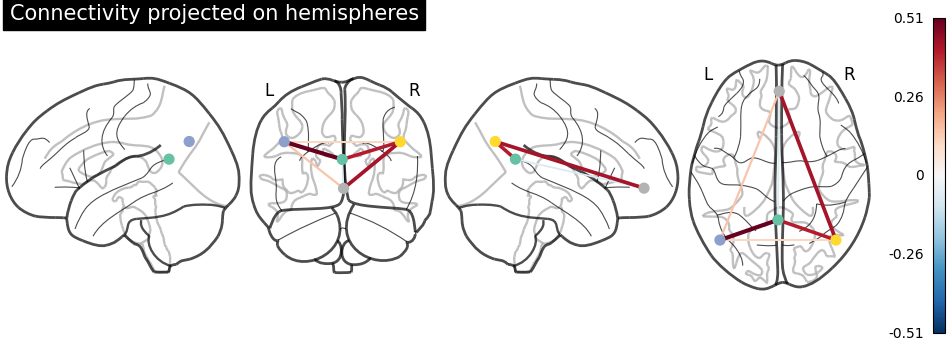
Display connectome with hemispheric projections. Notice (0, -52, 18) is included in both hemispheres since x == 0.
plot_connectome(
partial_correlation_matrix,
dmn_coords,
title="Connectivity projected on hemispheres",
display_mode="lyrz",
)
show()
3D visualization in a web browser¶
An alternative to plot_connectome is to use
view_connectome, which gives more interactive
visualizations in a web browser. See 3D Plots of connectomes
for more details.
from nilearn.plotting import view_connectome
view = view_connectome(partial_correlation_matrix, dmn_coords)
# In a notebook, if ``view`` is the output of a cell, it will
# be displayed below the cell
view
# uncomment this to open the plot in a web browser:
# view.open_in_browser()
Extract signals on spheres from an atlas¶
Next, instead of supplying our own coordinates, we will use coordinates generated at the center of mass of regions from two different atlases. This time, we’ll use a different correlation measure.
First we fetch the coordinates of the Power atlas
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_coords_power_2011
power = fetch_coords_power_2011()
print(f"Power atlas comes with {power.keys()}.")
Power atlas comes with dict_keys(['rois', 'description']).
Note
You can retrieve the coordinates for any atlas, including atlases
not included in nilearn, using
find_parcellation_cut_coords.
Compute within spheres averaged time-series¶
We collect the regions coordinates in a numpy array
import numpy as np
coords = np.vstack((power.rois["x"], power.rois["y"], power.rois["z"])).T
print(f"Stacked power coordinates in array of shape {coords.shape}.")
Stacked power coordinates in array of shape (264, 3).
and define spheres masker, with small enough radius to avoid regions overlap.
spheres_masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
seeds=coords,
smoothing_fwhm=6,
radius=5.0,
detrend=True,
standardize_confounds=True,
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=dataset.t_r,
verbose=1,
)
timeseries = spheres_masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=confounds_filename
)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:213: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Smoothing images
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:213: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
Estimate correlations¶
We start by estimating the signal covariance matrix. Here the number of ROIs exceeds the number of samples,
print(f"time series has {timeseries.shape[0]} samples")
time series has 168 samples
in which situation the graphical lasso sparse inverse covariance estimator captures well the covariance structure.
from sklearn.covariance import GraphicalLassoCV
covariance_estimator = GraphicalLassoCV(cv=3, verbose=1)
We just fit our regions signals into the GraphicalLassoCV object
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 3.6s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 1 out of 4: 3s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 5.8s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 2 out of 4: 9s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 4.8s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 3 out of 4: 14s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 3.8s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 4 out of 4: 17s
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/numpy/_core/_methods.py:191: RuntimeWarning:
invalid value encountered in subtract
and get the ROI-to-ROI covariance matrix.
matrix = covariance_estimator.covariance_
print(f"Covariance matrix has shape {matrix.shape}.")
Covariance matrix has shape (264, 264).
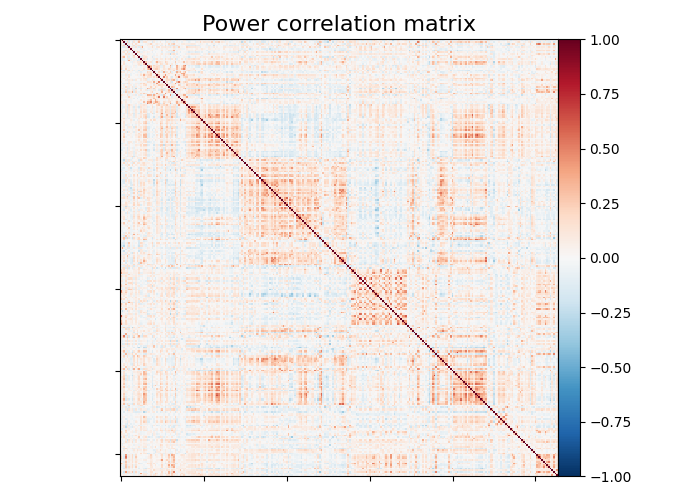
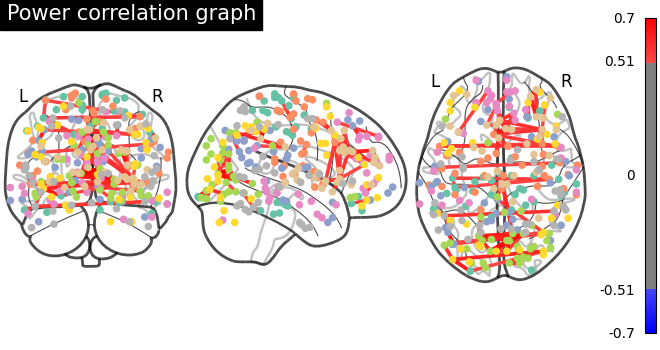
Plot matrix, graph, and strength¶
We use :func: nilearn.plotting.plot_matrix to visualize our correlation matrix and display the graph of connections with nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome.
from nilearn.plotting import plot_matrix
plot_matrix(
matrix,
vmin=-1.0,
vmax=1.0,
title="Power correlation matrix",
)
# Tweak edge_threshold to keep only the strongest connections.
plot_connectome(
matrix,
coords,
title="Power correlation graph",
edge_threshold="99.8%",
node_size=20,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7f32a77f7220>
Note
Note the 1. on the matrix diagonal: These are the signals variances, set to 1. by the spheres_masker. Hence the covariance of the signal is a correlation matrix.
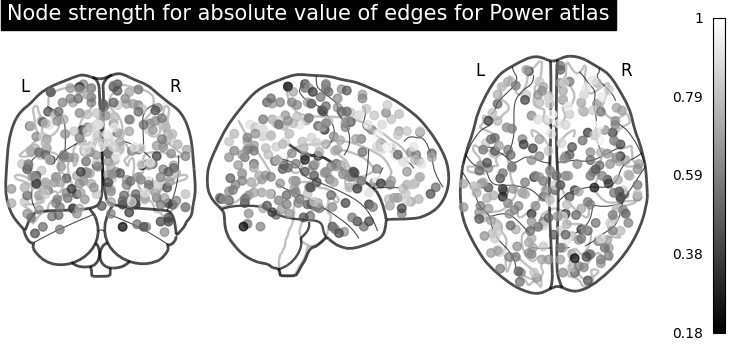
Sometimes, the information in the correlation matrix is overwhelming and aggregating edge strength from the graph would help. Use the function nilearn.plotting.plot_markers to visualize this information.
from nilearn.plotting import plot_markers
# calculate normalized, absolute strength for each node
node_strength = np.sum(np.abs(matrix), axis=0)
node_strength /= np.max(node_strength)
plot_markers(
node_strength,
coords,
title="Node strength for absolute value of edges for Power atlas",
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7f32a7fe23e0>
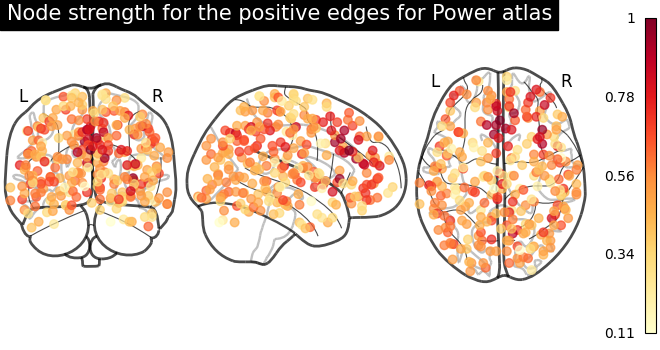
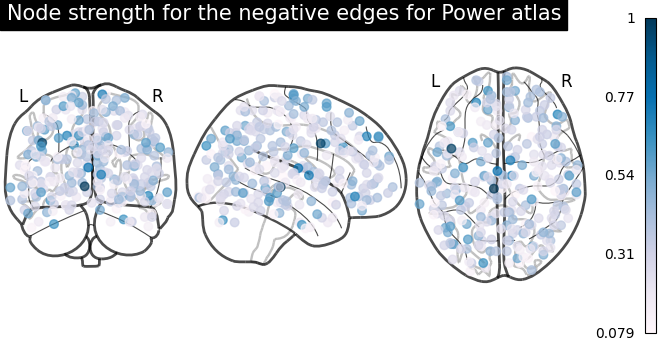
From the correlation matrix, we observe that there is a positive and negative structure. We could make two different plots, one for the positive and one for the negative structure.
from matplotlib.pyplot import cm
# clip connectivity matrix to preserve positive and negative edges
positive_edges = np.clip(matrix, 0, matrix.max())
negative_edges = np.clip(matrix, matrix.min(), 0)
# calculate strength for positive edges
node_strength_positive = np.sum(np.abs(positive_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_positive /= np.max(node_strength_positive)
# calculate strength for negative edges
node_strength_negative = np.sum(np.abs(negative_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_negative /= np.max(node_strength_negative)
# plot nodes' strength for positive edges
plot_markers(
node_strength_positive,
coords,
title="Node strength for the positive edges for Power atlas",
node_cmap=cm.YlOrRd,
)
# plot nodes' strength for negative edges
plot_markers(
node_strength_negative,
coords,
title="Node strength for the negative edges for Power atlas",
node_cmap=cm.PuBu,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7f32a8d93910>
Connectome extracted from Dosenbach’s atlas¶
We repeat the same steps for Dosenbach’s atlas.
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_coords_dosenbach_2010
dosenbach = fetch_coords_dosenbach_2010()
coords = np.vstack(
(
dosenbach.rois["x"],
dosenbach.rois["y"],
dosenbach.rois["z"],
)
).T
spheres_masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
seeds=coords,
smoothing_fwhm=6,
radius=4.5,
detrend=True,
standardize_confounds=True,
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=dataset.t_r,
verbose=1,
)
timeseries = spheres_masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=confounds_filename
)
covariance_estimator = GraphicalLassoCV(verbose=True)
covariance_estimator.fit(timeseries)
matrix = covariance_estimator.covariance_
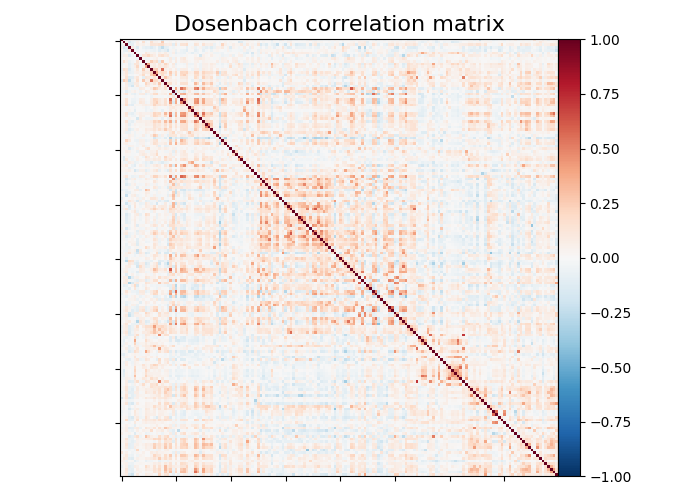
plot_matrix(
matrix,
vmin=-1.0,
vmax=1.0,
title="Dosenbach correlation matrix",
)
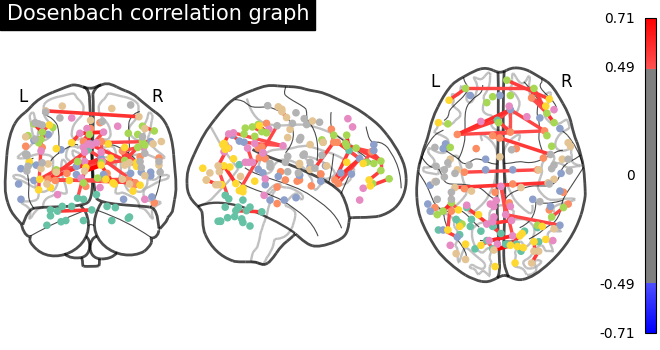
plot_connectome(
matrix,
coords,
title="Dosenbach correlation graph",
edge_threshold="99.7%",
node_size=20,
)
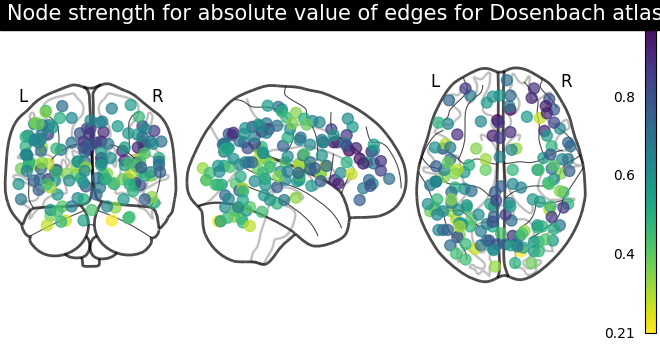
# calculate average strength for each node
node_strength = np.sum(np.abs(matrix), axis=0)
node_strength /= np.max(node_strength)
plot_markers(
node_strength,
coords,
title="Node strength for absolute value of edges for Dosenbach atlas",
)
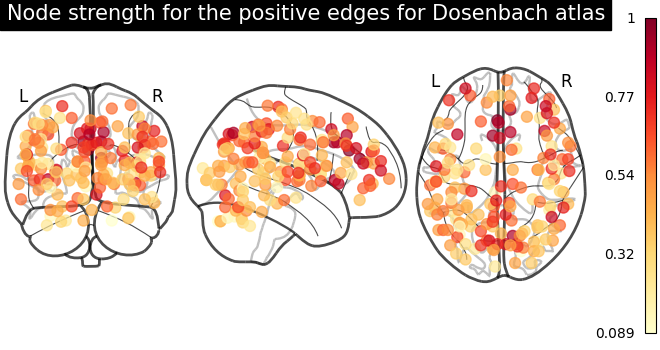
# clip connectivity matrix to preserve positive and negative edges
positive_edges = np.clip(matrix, 0, matrix.max())
negative_edges = np.clip(matrix, matrix.min(), 0)
# calculate strength for positive and edges
node_strength_positive = np.sum(np.abs(positive_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_positive /= np.max(node_strength_positive)
node_strength_negative = np.sum(np.abs(negative_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_negative /= np.max(node_strength_negative)
# plot nodes' strength for positive edges
plot_markers(
node_strength_positive,
coords,
title="Node strength for the positive edges for Dosenbach atlas",
node_cmap=cm.YlOrRd,
)
# plot nodes' strength for negative edges
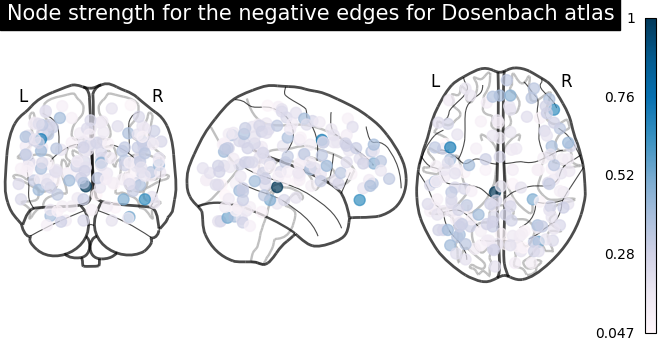
plot_markers(
node_strength_negative,
coords,
title="Node strength for the negative edges for Dosenbach atlas",
node_cmap=cm.PuBu,
)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:353: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Smoothing images
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/03_connectivity/plot_sphere_based_connectome.py:353: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 5 out of 5 | elapsed: 2.9s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 1 out of 4: 2s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 5 out of 5 | elapsed: 3.7s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 2 out of 4: 6s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 5 out of 5 | elapsed: 4.1s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 3 out of 4: 10s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 5 out of 5 | elapsed: 3.7s finished
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 4 out of 4: 14s
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/numpy/_core/_methods.py:191: RuntimeWarning:
invalid value encountered in subtract
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7f32880165f0>
We can easily identify the Dosenbach’s networks from the matrix blocks.
print(f"Dosenbach networks names are {np.unique(dosenbach.networks)}")
show()
Dosenbach networks names are ['cerebellum' 'cingulo-opercular' 'default' 'fronto-parietal' 'occipital'
'sensorimotor']
References¶
See also
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 57.049 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 485 MB