Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Visualizing global patterns with a carpet plot¶
A common quality control step for functional MRI data is to visualize the data over time in a carpet plot (also known as a Power plot or a grayplot).
The plot_carpet function generates a carpet plot
from a 4D functional image.
Fetching data from ADHD dataset¶
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_adhd
from nilearn.plotting import plot_carpet
adhd_dataset = fetch_adhd(n_subjects=1)
# Print basic information on the dataset
print(
f"First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: {adhd_dataset.func[0]}"
)
[fetch_adhd] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd
First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd/data/0010042/0010042_rest_tshift_RPI_voreg_mni.nii.gz
Deriving a mask¶
from nilearn import masking
# Build an EPI-based mask because we have no anatomical data
mask_img = masking.compute_epi_mask(adhd_dataset.func[0])
Visualizing global patterns over time¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
display = plot_carpet(
adhd_dataset.func[0],
mask_img,
t_r=adhd_dataset.t_r,
title="global patterns over time",
)
display.show()

/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_carpet.py:38: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
Deriving a label-based mask¶
Create a gray matter/white matter/cerebrospinal fluid mask from ICBM152 tissue probability maps.
import numpy as np
from nilearn import image
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_icbm152_2009
atlas = fetch_icbm152_2009()
atlas_img = image.concat_imgs((atlas["gm"], atlas["wm"], atlas["csf"]))
map_labels = {"Gray Matter": 1, "White Matter": 2, "Cerebrospinal Fluid": 3}
atlas_data = atlas_img.get_fdata()
discrete_version = np.argmax(atlas_data, axis=3) + 1
discrete_version[np.max(atlas_data, axis=3) == 0] = 0
discrete_atlas_img = image.new_img_like(
atlas_img, discrete_version.astype(np.float32)
)
[fetch_icbm152_2009] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/icbm152_2009
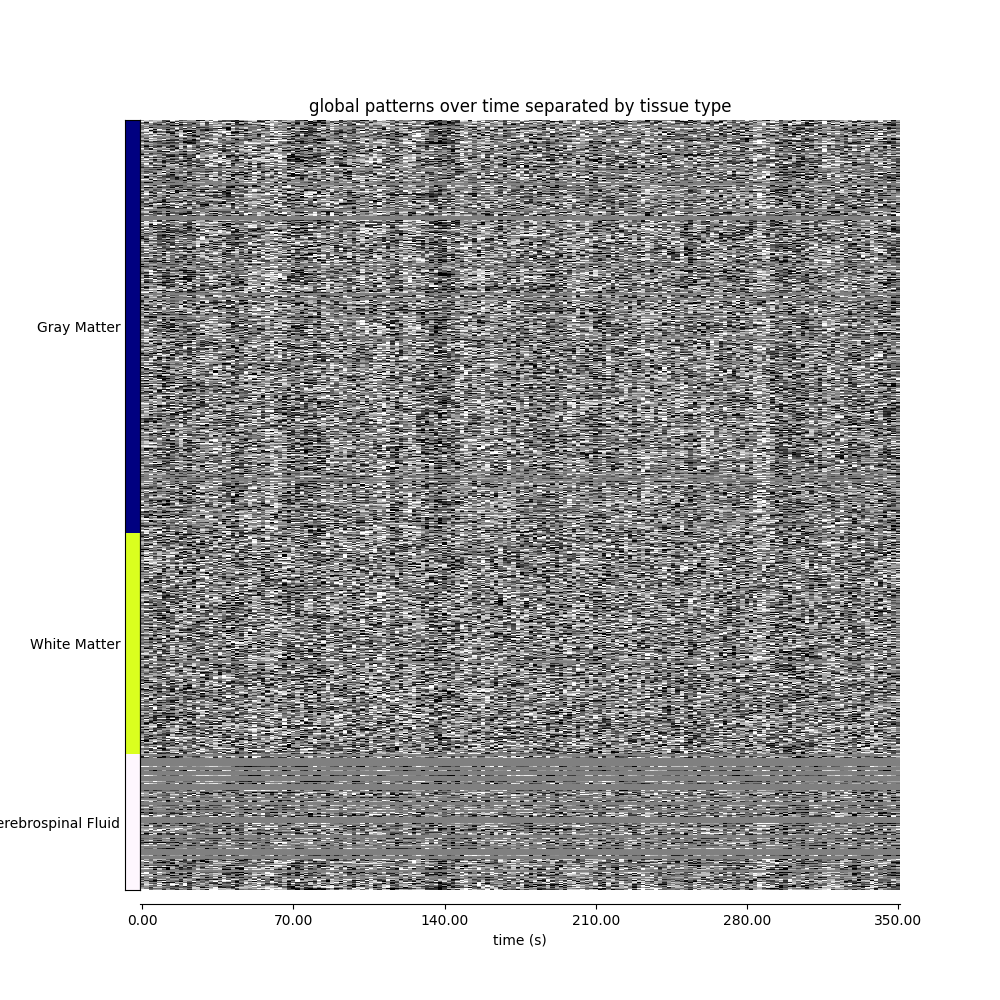
Visualizing global patterns, separated by tissue type¶
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
display = plot_carpet(
adhd_dataset.func[0],
discrete_atlas_img,
t_r=adhd_dataset.t_r,
mask_labels=map_labels,
axes=ax,
title="global patterns over time separated by tissue type",
)
plt.show()
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_carpet.py:74: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_carpet.py:74: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_carpet.py:74: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_carpet.py:74: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
[plot_carpet] Coercing atlas_values to int
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 22.186 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 990 MB