Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.glm.second_level.SecondLevelModel¶
- class nilearn.glm.second_level.SecondLevelModel(mask_img=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, memory=None, memory_level=1, verbose=0, n_jobs=1, minimize_memory=True)[source]¶
Implement the General Linear Model for multiple subject fMRI data.
- Parameters:
- mask_imgNiimg-like,
NiftiMaskerorMultiNiftiMaskerorSurfaceMaskerobject or None, default=None Mask to be used on data. If an instance of masker is passed, then its mask will be used. If no mask is given, it will be computed automatically by a
NiftiMasker, or aSurfaceMasker(depending on the type passed at fit time) with default parameters. Automatic mask computation assumes first level imgs have already been masked.- target_affine3x3 or a 4x4 array-like, or None, default=None
If specified, the image is resampled corresponding to this new affine.
Note
This parameter is passed to
nilearn.image.resample_img.Note
This parameter is ignored when fitting surface images.
- target_shape
tupleorlistor None, default=None If specified, the image will be resized to match this new shape. len(target_shape) must be equal to 3.
Note
If target_shape is specified, a target_affine of shape (4, 4) must also be given.
Note
This parameter is passed to
nilearn.image.resample_img.Note
This parameter is ignored when fitting surface images.
- smoothing_fwhm
floatorintor None, optional. If smoothing_fwhm is not None, it gives the full-width at half maximum in millimeters of the spatial smoothing to apply to the signal.
Note
This parameter is ignored when fitting surface images.
- memoryNone, instance of
joblib.Memory,str, orpathlib.Path, default=None Used to cache the masking process. By default, no caching is done. If a
stris given, it is the path to the caching directory.- memory_level
int, default=1 Rough estimator of the amount of memory used by caching. Higher value means more memory for caching. Zero means no caching.
- verbose
boolorint, default=0 Verbosity level (
0orFalsemeans no message). If 0, prints nothing. If 1, prints final computation time. If 2, prints masker computation details.- n_jobs
int, default=1 The number of CPUs to use to do the computation. -1 means ‘all CPUs’.
- minimize_memory
bool, default=True Gets rid of some variables on the model fit results that are not necessary for contrast computation and would only be useful for further inspection of model details. This has an important impact on memory consumption.
- mask_imgNiimg-like,
- Attributes:
- confounds_
pandas.DataFrameor None Confounds used to fit the GLM.
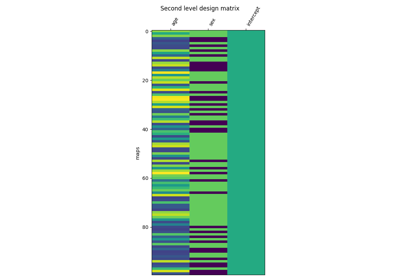
- design_matrix_
pandas.DataFrame Design matrix used to fit the GLM.
- labels_array of shape
(n_elements_,) a map of values on voxels / vertices used to identify the corresponding model
- masker_
NiftiMaskerorSurfaceMasker Masker used to filter and mask data during fit. If
NiftiMaskerorSurfaceMaskeris given inmask_imgparameter, this is a copy of it. Otherwise, a masker is created using the value ofmask_imgand other NiftiMasker/SurfaceMasker related parameters as initialization.- memory_joblib memory cache
- n_elements_
int The number of voxels or vertices in the mask.
Added in Nilearn 0.12.1.
- results_
dict, with keys corresponding to the different labels values. Values are SimpleRegressionResults corresponding to the voxels or vertices, if minimize_memory is True, RegressionResults if minimize_memory is False
- second_level_input_
listofFirstLevelModelobjects orpandas.DataFrameorlistof 3D Niimg-like objects orlistofSurfaceImageobjects orpandas.Seriesof Niimg-like objects. Input used to fit the GLM.
- confounds_
- __init__(mask_img=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, memory=None, memory_level=1, verbose=0, n_jobs=1, minimize_memory=True)[source]¶
- compute_contrast(second_level_contrast=None, first_level_contrast=None, second_level_stat_type=None, output_type='z_score')[source]¶
Generate different outputs corresponding to the contrasts provided e.g. z_map, t_map, effects and variance.
- Parameters:
- second_level_contrast
strornumpy.ndarrayof shape(n_col), optional Where n_col is the number of columns of the design matrix. The string can be a formula compatible with
pandas.DataFrame.eval. Basically one can use the name of the conditions as they appear in the design matrix of the fitted model combined with operators +- and combined with numbers with operators +-*/. The default None is accepted if the design matrix has a single column, in which case the only possible contrast array((1)) is applied; when the design matrix has multiple columns, an error is raised.- first_level_contrast
strornumpy.ndarrayof shape (n_col) with respect toFirstLevelModelor None, default=None When the model is a
SecondLevelModel:in case a
listofFirstLevelModelwas provided assecond_level_input, we have to provide a contrast to apply to the first level models to get the corresponding list of images desired, that would be tested at the second level,in case a
DataFramewas provided assecond_level_inputthis is the map name to extract from theDataFramemap_namecolumn. (it has to be a ‘t’ contrast).
When the model is a
FirstLevelModel: This parameter is ignored.- second_level_stat_type{‘t’, ‘F’} or None, default=None
Type of the second level contrast.
- output_type{‘z_score’, ‘stat’, ‘p_value’, ‘effect_size’, ‘effect_variance’, ‘all’}, default=’z_score’
Type of the output map.
- second_level_contrast
- Returns:
- output_image
Nifti1Image The desired output image(s). If
output_type == 'all', then the output is a dictionary of images, keyed by the type of image.
- output_image
- fit(second_level_input, confounds=None, design_matrix=None)[source]¶
Fit the second-level GLM.
create design matrix
do a masker job: fMRI_data -> Y
fit regression to (Y, X)
- Parameters:
- second_level_input
listofFirstLevelModelobjects orpandas.DataFrameorlistof 3D Niimg-like objects or 4D Niimg-like objects orlistofSurfaceImageobjects orpandas.Seriesof Niimg-like objects. Giving
FirstLevelModelobjects will allow to easily compute the second level contrast of arbitrary first level contrasts thanks to the first_level_contrast argument ofcompute_contrast. Effect size images will be computed for each model to contrast at the second level.If a
DataFrame, then it has to contain subject_label, map_name and effects_map_path. It can contain multiple maps that would be selected during contrast estimation with the argument first_level_contrast ofcompute_contrast. TheDataFramewill be sorted based on the subject_label column to avoid order inconsistencies when extracting the maps. So the rows of the automatically computed design matrix, if not provided, will correspond to the sorted subject_label column.If a
listof Niimg-like objects orSurfaceImageobjects then this is taken literally as Y for the model fit and design_matrix must be provided.
- confounds
pandas.DataFrameor None, Default=None Must contain a
subject_labelcolumn. All other columns are considered as confounds and included in the model. Ifdesign_matrixis provided then this argument is ignored. The resulting second level design matrix uses the same column names as in the givenDataFramefor confounds. At least two columns are expected,subject_labeland at least one confound.- design_matrix
pandas.DataFrame,stror orpathlib.Pathto a CSV or TSV file, or None, Default=None Design matrix to fit the GLM. The number of rows in the design matrix must agree with the number of maps derived from
second_level_input. Ensure that the order of maps given by asecond_level_inputlist of Niimgs matches the order of the rows in the design matrix.
- second_level_input
- generate_report(contrasts=None, first_level_contrast=None, title=None, bg_img='MNI152TEMPLATE', threshold=None, alpha=0.001, cluster_threshold=0, height_control='fpr', two_sided=False, min_distance=8.0, plot_type='slice', cut_coords=None, display_mode=None, report_dims=(1600, 800))[source]¶
Return a
HTMLReportwhich shows all important aspects of a fitted GLM.The
HTMLReportcan be opened in a browser, displayed in a notebook, or saved to disk as a standalone HTML file.The GLM must be fitted and have the computed design matrix(ces).
- Parameters:
- contrasts
dictwithstr- ndarray key-value pairs orstrorlistofstror ndarray orlistof ndarray, Default=None Contrasts information for a first or second level model.
Example:
Contrasts are passed to
contrast_deffor FirstLevelModel (nilearn.glm.first_level.FirstLevelModel.compute_contrast) & second_level_contrast for SecondLevelModel (nilearn.glm.second_level.SecondLevelModel.compute_contrast)- first_level_contrast
strornumpy.ndarrayof shape (n_col) with respect toFirstLevelModelor None, default=None When the model is a
SecondLevelModel:in case a
listofFirstLevelModelwas provided assecond_level_input, we have to provide a contrast to apply to the first level models to get the corresponding list of images desired, that would be tested at the second level,in case a
DataFramewas provided assecond_level_inputthis is the map name to extract from theDataFramemap_namecolumn. (it has to be a ‘t’ contrast).
When the model is a
FirstLevelModel: This parameter is ignored.Added in Nilearn 0.12.0.
- title
stror None, default=None If string, represents the web page’s title and primary heading, model type is sub-heading. If None, page titles and headings are autogenerated using contrast names.
- bg_imgNiimg-like object, default=’MNI152TEMPLATE’
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. The background image for mask and stat maps to be plotted on upon. To turn off background image, just pass “bg_img=None”.
- threshold
floatorintor None, default=None Cluster forming threshold in same scale as stat_img (either a t-scale or z-scale value). Used only if height_control is None. If
thresholdis set to None whenheight_controlis None,thresholdwill be set to 3.09.Note
When
two_sidedis True:'threshold'cannot be negative.The given value should be within the range of minimum and maximum intensity of the input image. All intensities in the interval
[-threshold, threshold]will be set to zero.When
two_sidedis False:If the threshold is negative:
It should be greater than the minimum intensity of the input data. All intensities greater than or equal to the specified threshold will be set to zero. All other intensities keep their original values.
If the threshold is positive:
It should be less than the maximum intensity of the input data. All intensities less than or equal to the specified threshold will be set to zero. All other intensities keep their original values.
- alpha
float, default=0.001 Number controlling the thresholding (either a p-value or q-value). Its actual meaning depends on the height_control parameter. This function translates alpha to a z-scale threshold.
- cluster_threshold
int, default=0 Cluster size threshold. Sets of connected voxels / vertices (clusters) with size smaller than this number will be removed.
- cluster_threshold
- height_control
stror None, default=’fpr’ false positive control meaning of cluster forming threshold: ‘fpr’ or ‘fdr’ or ‘bonferroni’ or None.
- two_sided
bool, default=False Whether to employ two-sided thresholding or to evaluate positive values only.
- min_distance
float, default=8.0 For display purposes only. Minimum distance between subpeaks in mm.
- plot_type
str, {‘slice’, ‘glass’}, default=’slice’ Specifies the type of plot to be drawn for the statistical maps.
- cut_coordsNone, allowed types depend on the
display_mode, optional The world coordinates of the point where the cut is performed.
If
display_modeis'ortho'or'tiled', this must be a 3-sequence offloatorint:(x, y, z).If
display_modeis'xz','yz'or'yx', this must be a 2-sequence offloatorint:(x, z),(y, z)or(x, y).If
display_modeis"x","y", or"z", this can be:If
display_modeis'mosaic', this can be:an
intin which case it specifies the number of cuts to perform in each direction"x","y","z".a 3-sequence of
floatorintin which case it specifies the number of cuts to perform in each direction"x","y","z"separately.dict<str: 1Dndarray> in which case keys are the directions (‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’) and the values are sequences holding the cut coordinates.
If
Noneis given, the cuts are calculated automatically.
Note
cut_coordswill not be used whenplot_type='glass'.- display_mode
str, default=None Default is ‘z’ if plot_type is ‘slice’; ‘ortho’ if plot_type is ‘glass’.
Choose the direction of the cuts: ‘x’ - sagittal, ‘y’ - coronal, ‘z’ - axial, ‘l’ - sagittal left hemisphere only, ‘r’ - sagittal right hemisphere only, ‘ortho’ - three cuts are performed in orthogonal directions.
Possible values are: ‘ortho’, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’, ‘xz’, ‘yx’, ‘yz’, ‘l’, ‘r’, ‘lr’, ‘lzr’, ‘lyr’, ‘lzry’, ‘lyrz’.
- report_dimsSequence[
int,int], default=(1600, 800) Specifies width, height (in pixels) of report window within a notebook. Only applicable when inserting the report into a Jupyter notebook. Can be set after report creation using report.width, report.height.
- contrasts
- Returns:
- report_text
HTMLReport Contains the HTML code for the GLM report.
- report_text
- get_metadata_routing()¶
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- property mask_img_¶
Return mask image using during fit.
- property predicted¶
Transform voxelwise predicted values to the same shape as the input Nifti1Image(s).
- Returns:
- outputlist
A list of Nifti1Image(s).
- property r_square¶
Transform voxelwise r-squared values to the same shape as the input Nifti1Image(s).
- Returns:
- outputlist
A list of Nifti1Image(s).
- property residuals¶
Transform voxelwise residuals to the same shape as the input Nifti1Image(s).
- Returns:
- outputlist
A list of Nifti1Image(s).
- set_fit_request(*, confounds='$UNCHANGED$', design_matrix='$UNCHANGED$', second_level_input='$UNCHANGED$')¶
Configure whether metadata should be requested to be passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant when this estimator is used as a sub-estimator within a meta-estimator and metadata routing is enabled with
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please check the User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.Added in version 1.3.
- Parameters:
- confoundsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
confoundsparameter infit.- design_matrixstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
design_matrixparameter infit.- second_level_inputstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
second_level_inputparameter infit.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_params(**params)¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
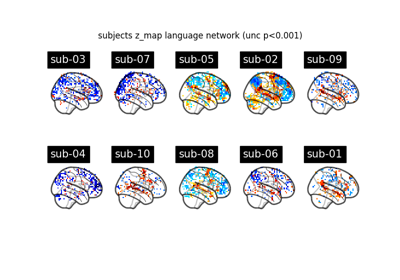
Examples using nilearn.glm.second_level.SecondLevelModel¶
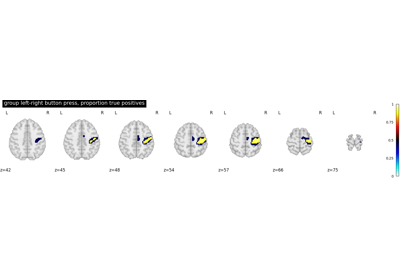
Second-level fMRI model: true positive proportion in clusters
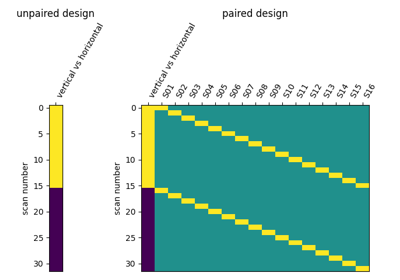
Second-level fMRI model: two-sample test, unpaired and paired
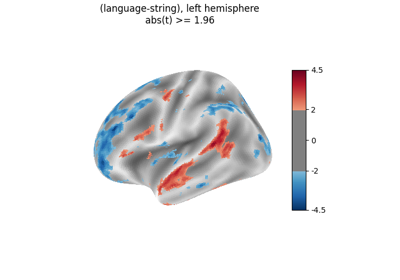
Surface-based dataset first and second level analysis of a dataset