Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.glm.ARModel¶
- class nilearn.glm.ARModel(design, rho)[source]¶
A regression model with an AR(p) covariance structure.
In terms of a LikelihoodModel, the parameters are beta, the usual regression parameters, and sigma, a scalar nuisance parameter that shows up as multiplier in front of the AR(p) covariance.
- Parameters:
- designndarray
2D array with design matrix.
- rho
intor array-like If int, gives order of model, and initializes rho to zeros. If ndarray, gives initial estimate of rho. Be careful as
ARModel(X, 1) != ARModel(X, 1.0).
- fit(Y)[source]¶
Fit model to data Y.
Full fit of the model including estimate of covariance matrix, (whitened) residuals and scale.
- Parameters:
- Yarray-like
The dependent variable for the Least Squares problem.
- Returns:
- fitRegressionResults
- logL(beta, Y, nuisance=None)[source]¶
Return the value of the loglikelihood function at beta.
Given the whitened design matrix, the loglikelihood is evaluated at the parameter vector, beta, for the dependent variable, Y and the nuisance parameter, sigma Greene[1].
- Parameters:
- betandarray
The parameter estimates. Must be of length
df_model.- Yndarray
The dependent variable
- nuisance
dict, default=None A dict with key ‘sigma’, which is an optional estimate of sigma. If None, defaults to its maximum likelihood estimate (with beta fixed) as
sum((Y - X*beta)**2) / n, where n=Y.shape[0], X=self.design.
- Returns:
- loglffloat
The value of the loglikelihood function.
Notes
The log-Likelihood Function is defined as
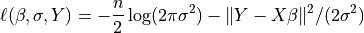
The parameter
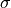 above is what is sometimes referred to
as a nuisance parameter. That is, the likelihood is considered as a
function of
above is what is sometimes referred to
as a nuisance parameter. That is, the likelihood is considered as a
function of 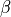 , but to evaluate it, a value of
, but to evaluate it, a value of
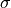 is needed.
is needed.If
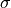 is not provided,
then its maximum likelihood estimate:
is not provided,
then its maximum likelihood estimate: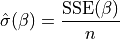
is plugged in. This likelihood is now a function of only
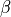 and is technically referred to as a profile-likelihood.
and is technically referred to as a profile-likelihood.References