Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.datasets.fetch_haxby¶
- nilearn.datasets.fetch_haxby(data_dir=None, subjects=(2,), fetch_stimuli=False, url=None, resume=True, verbose=1)[source]¶
Download and loads complete haxby dataset.
See Haxby et al.[1].
- Parameters:
- data_dir
pathlib.Pathorstror None, optional Path where data should be downloaded. By default, files are downloaded in a
nilearn_datafolder in the home directory of the user. See alsonilearn.datasets.utils.get_data_dirs.- subjects
listortupleorint, default=(2,) Either a list of subjects or the number of subjects to load, from 1 to 6. By default, 2nd subject will be loaded. Empty list returns no subject data.
- fetch_stimuli
bool, default=False Indicate if stimuli images must be downloaded. They will be presented as a dictionary of categories.
- url
stror None, default=None URL of file to download. Override download URL. Used for test only (or if you setup a mirror of the data).
- resume
bool, default=True Whether to resume download of a partly-downloaded file.
- verbose
boolorint, default=1 Verbosity level (
0orFalsemeans no message).
- data_dir
- Returns:
- data
sklearn.utils.Bunch Dictionary-like object, the interest attributes are :
- data
Notes
If the dataset files are already present in the user’s Nilearn data directory, this fetcher will not re-download them. To force a fresh download, you can remove the existing dataset folder from your local Nilearn data directory.
For more details on how Nilearn stores datasets.
PyMVPA provides a tutorial making use of this dataset: http://www.pymvpa.org/tutorial.html
More information about its structure: http://dev.pymvpa.org/datadb/haxby2001.html
See additional information <https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1063736>
Run 8 in subject 5 does not contain any task labels. The anatomical image for subject 6 is unavailable.
References
Examples using nilearn.datasets.fetch_haxby¶
Basic nilearn example: manipulating and looking at data
Decoding of a dataset after GLM fit for signal extraction
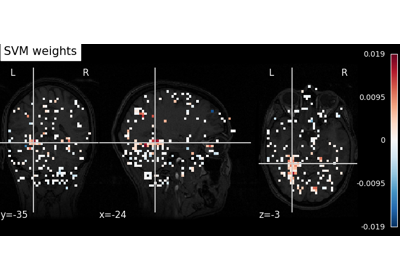
Decoding with ANOVA + SVM: face vs house in the Haxby dataset
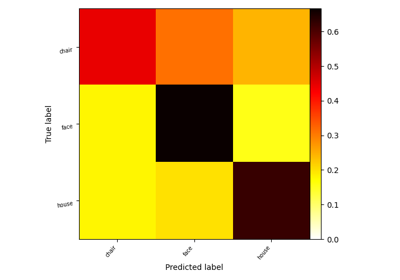
Decoding with FREM: face vs house vs chair object recognition
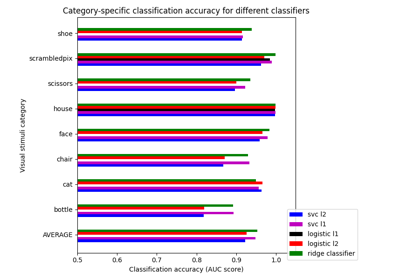
Different classifiers in decoding the Haxby dataset
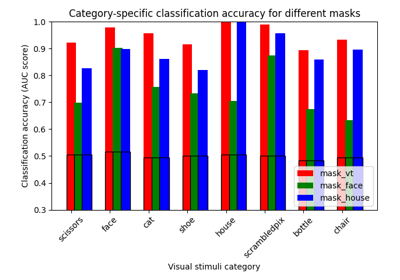
ROI-based decoding analysis in Haxby et al. dataset
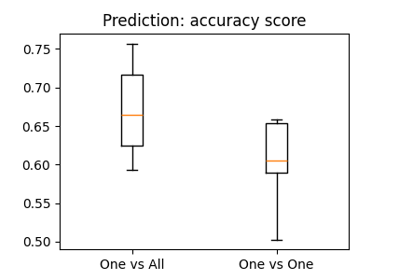
The haxby dataset: different multi-class strategies
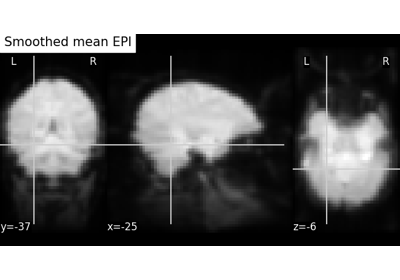
Computing a Region of Interest (ROI) mask manually
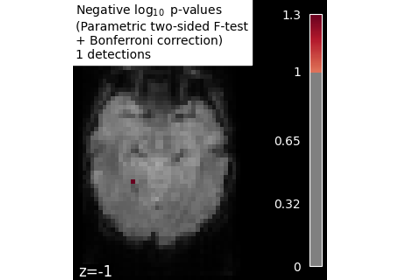
Massively univariate analysis of face vs house recognition