Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Setting a parameter by cross-validation¶
Here we set the number of features selected in an Anova-SVC approach to maximize the cross-validation score.
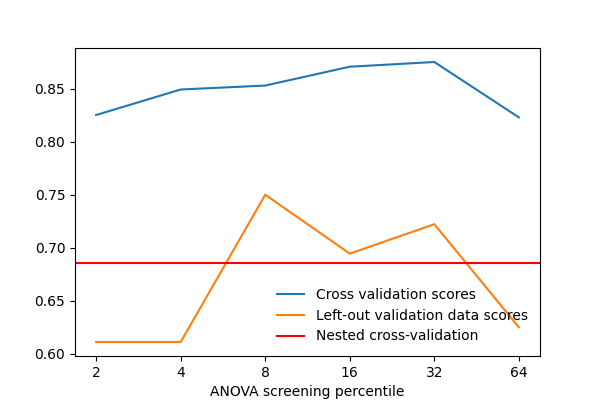
After separating 2 runs for validation, we vary that parameter and measure the cross-validation score. We also measure the prediction score on the left-out validation data. As we can see, the two scores vary by a significant amount: this is due to sampling noise in cross validation, and choosing the parameter k to maximize the cross-validation score, might not maximize the score on left-out data.
Thus using data to maximize a cross-validation score computed on that same data is likely to be too optimistic and lead to an overfit.
The proper approach is known as a “nested cross-validation”. It consists in doing cross-validation loops to set the model parameters inside the cross-validation loop used to judge the prediction performance: the parameters are set separately on each fold, never using the data used to measure performance.
For decoding tasks, in nilearn, this can be done using the
Decoder object, which will automatically select
the best parameters of an estimator from a grid of parameter values.
One difficulty is that the Decoder object is a composite estimator: a pipeline of feature selection followed by Support Vector Machine. Tuning the SVM’s parameters is already done automatically inside the Decoder, but performing cross-validation for the feature selection must be done manually.
Load the Haxby dataset¶
from nilearn import datasets
from nilearn.plotting import show
# by default 2nd subject data will be fetched on which we run our analysis
haxby_dataset = datasets.fetch_haxby()
fmri_img = haxby_dataset.func[0]
mask_img = haxby_dataset.mask
# print basic information on the dataset
print(f"Mask nifti image (3D) is located at: {haxby_dataset.mask}")
print(f"Functional nifti image (4D) are located at: {haxby_dataset.func[0]}")
# Load the behavioral data
import pandas as pd
labels = pd.read_csv(haxby_dataset.session_target[0], sep=" ")
y = labels["labels"]
# Keep only data corresponding to shoes or bottles
from nilearn.image import index_img
condition_mask = y.isin(["shoe", "bottle"])
fmri_niimgs = index_img(fmri_img, condition_mask)
y = y[condition_mask]
run = labels["chunks"][condition_mask]
[fetch_haxby] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001
Mask nifti image (3D) is located at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz
Functional nifti image (4D) are located at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/subj2/bold.nii.gz
ANOVA pipeline with Decoder object¶
Nilearn Decoder object aims to provide smooth user experience by acting as a pipeline of several tasks: preprocessing with NiftiMasker, reducing dimension by selecting only relevant features with ANOVA – a classical univariate feature selection based on F-test, and then decoding with different types of estimators (in this example is Support Vector Machine with a linear kernel) on nested cross-validation.
from nilearn.decoding import Decoder
# We provide a grid of hyperparameter values to the Decoder's internal
# cross-validation. If no param_grid is provided, the Decoder will use a
# default grid with sensible values for the chosen estimator
param_grid = [
{
"penalty": ["l2"],
"dual": [True],
"C": [100, 1000],
},
{
"penalty": ["l1"],
"dual": [False],
"C": [100, 1000],
},
]
# Here screening_percentile is set to 2 percent, meaning around 800
# features will be selected with ANOVA.
decoder = Decoder(
estimator="svc",
cv=5,
mask=mask_img,
smoothing_fwhm=4,
screening_percentile=2,
param_grid=param_grid,
verbose=1,
)
Fit the Decoder and predict the responses¶
As a complete pipeline by itself, decoder will perform cross-validation for the estimator, in this case Support Vector Machine. We can output the best parameters selected for each cross-validation fold. See https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/cross_validation.html for an excellent explanation of how cross-validation works.
# Fit the Decoder
decoder.fit(fmri_niimgs, y)
# Print the best parameters for each fold
for i, (best_c, best_penalty, best_dual, cv_score) in enumerate(
zip(
decoder.cv_params_["shoe"]["C"],
decoder.cv_params_["shoe"]["penalty"],
decoder.cv_params_["shoe"]["dual"],
decoder.cv_scores_["shoe"],
strict=False,
)
):
print(
f"Fold {i + 1} | Best SVM parameters: C={best_c}"
f", penalty={best_penalty}, dual={best_dual} with score: {cv_score}"
)
# Output the prediction with Decoder
y_pred = decoder.predict(fmri_niimgs)
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a04bd1b0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:117: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a04bd1b0>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 2
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 1.9171
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 399 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 5 out of 5 | elapsed: 2.7s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Fold 1 | Best SVM parameters: C=1000, penalty=l1, dual=False with score: 0.9256198347107438
Fold 2 | Best SVM parameters: C=1000, penalty=l2, dual=True with score: 0.9177489177489176
Fold 3 | Best SVM parameters: C=100, penalty=l1, dual=False with score: 0.8354978354978355
Fold 4 | Best SVM parameters: C=100, penalty=l1, dual=False with score: 0.8593073593073592
Fold 5 | Best SVM parameters: C=1000, penalty=l2, dual=True with score: 0.735930735930736
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a04bd1b0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Compute prediction scores with different values of screening percentile¶
import numpy as np
screening_percentile_range = [2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
cv_scores = []
val_scores = []
for sp in screening_percentile_range:
decoder = Decoder(
estimator="svc",
mask=mask_img,
smoothing_fwhm=4,
cv=3,
screening_percentile=sp,
param_grid=param_grid,
verbose=1,
)
decoder.fit(index_img(fmri_niimgs, run < 10), y[run < 10])
cv_scores.append(np.mean(decoder.cv_scores_["bottle"]))
print(f"Sreening Percentile: {sp:.3f}")
print(f"Mean CV score: {cv_scores[-1]:.4f}")
y_pred = decoder.predict(index_img(fmri_niimgs, run == 10))
val_scores.append(np.mean(y_pred == y[run == 10]))
print(f"Validation score: {val_scores[-1]:.4f}")
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26d9630>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26d9630>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 2
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 1.9171
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 399 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.0s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 2.000
Mean CV score: 0.8189
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26da020>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.5556
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a72df160>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a72df160>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 4
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 3.83419
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 1197 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.6s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 4.000
Mean CV score: 0.8493
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a72dd930>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.3889
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0a4bd00>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0a4bd00>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 8
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 7.66838
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 2793 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 2.2s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 8.000
Mean CV score: 0.8567
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c51d9720>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.6111
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5128100>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5128100>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 16
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 15.3368
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 5986 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 3.8s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 16.000
Mean CV score: 0.8667
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5128670>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.4444
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c512bf10>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c512bf10>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 32
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 30.6735
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 11973 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 5.6s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 32.000
Mean CV score: 0.8885
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c51dba30>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.5556
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0aa4df0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:156: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0aa4df0>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 64
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 61.3471
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 24346 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 10.0s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
Sreening Percentile: 64.000
Mean CV score: 0.8767
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26db880>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Validation score: 0.5556
Nested cross-validation¶
We are going to tune the parameter ‘screening_percentile’ in the pipeline.
import warnings
from sklearn.exceptions import ConvergenceWarning
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
cv = KFold(n_splits=3)
nested_cv_scores = []
for train, test in cv.split(run):
y_train = np.array(y)[train]
y_test = np.array(y)[test]
val_scores = []
for sp in screening_percentile_range:
with warnings.catch_warnings():
# silence warnings about Liblinear not converging
# increase the number of iterations.
warnings.filterwarnings(
action="ignore", category=ConvergenceWarning
)
decoder = Decoder(
estimator="svc",
mask=mask_img,
smoothing_fwhm=4,
cv=3,
screening_percentile=sp,
param_grid=param_grid,
verbose=1,
)
decoder.fit(index_img(fmri_niimgs, train), y_train)
y_pred = decoder.predict(index_img(fmri_niimgs, test))
val_scores.append(np.mean(y_pred == y_test))
nested_cv_scores.append(np.max(val_scores))
print(f"Nested CV score: {np.mean(nested_cv_scores):.4f}")
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c512ab00>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c512ab00>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 2
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 1.9171
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 399 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 0.9s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3e500>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3f790>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3f790>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 4
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 3.83419
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 1197 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.5s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3efe0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3f790>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4b3f790>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 8
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 7.66838
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 2793 features.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 2.2s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3ef50>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3f1c0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3f1c0>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 16
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 15.3368
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 5986 features.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 3.2s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a746bd00>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3e410>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3e410>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 32
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 30.6735
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 11973 features.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 4.4s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c14bfac0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3f340>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3f340>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 64
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 61.3471
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 24346 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 8.2s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4c3f340>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0aa51e0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0aa51e0>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 2
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 1.9171
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 399 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 0.6s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a746ba30>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a746b160>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a746b160>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 4
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 3.83419
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 1197 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.1s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5ebf0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5dc90>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5dc90>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 8
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 7.66838
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 2793 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.7s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f329b7c6740>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5cc10>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5cc10>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 16
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 15.3368
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 5986 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 2.3s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c500be50>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a091a9e0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a091a9e0>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 32
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 30.6735
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 11973 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 4.0s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c517bc40>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a74cdd50>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a74cdd50>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 64
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 61.3471
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 24346 features.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/.tox/doc/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/svm/_base.py:1250: ConvergenceWarning:
Liblinear failed to converge, increase the number of iterations.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 7.8s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c51dba30>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a04bfc10>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a04bfc10>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 2
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 1.9171
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 399 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 0.6s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26d8b80>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0acba90>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a0acba90>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 4
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 3.83419
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 1197 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 0.9s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c26d93f0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5009600>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5009600>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 8
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 7.66838
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 2793 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 1.5s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a746b790>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c500b850>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c500b850>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 16
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 15.3368
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 5986 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 2.3s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32a8a5c6a0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5009c60>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c5009c60>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 32
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 30.6735
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 11973 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 3.8s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c4990f70>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c500b760>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_grid_search.py:199: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[Decoder.fit] Resampling mask
[Decoder.fit] Finished fit
[Decoder.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c500b760>
[Decoder.fit] Smoothing images
[Decoder.fit] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[Decoder.fit] Mask volume = 1.96442e+06mm^3 = 1964.42cm^3
[Decoder.fit] Standard brain volume = 1.88299e+06mm^3
[Decoder.fit] Original screening-percentile: 64
[Decoder.fit] Corrected screening-percentile: 61.3471
[Decoder.fit] The decoding model will be trained on 24346 features.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 3 out of 3 | elapsed: 6.6s finished
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.fit] Computing image from signals
[Decoder.predict] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f32c50091b0>
[Decoder.predict] Smoothing images
[Decoder.predict] Extracting region signals
[Decoder.predict] Cleaning extracted signals
Nested CV score: 0.6806
Plot the prediction scores using matplotlib¶
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(cv_scores, label="Cross validation scores")
plt.plot(val_scores, label="Left-out validation data scores")
plt.xticks(
np.arange(len(screening_percentile_range)), screening_percentile_range
)
plt.axis("tight")
plt.xlabel("ANOVA screening percentile")
plt.axhline(
np.mean(nested_cv_scores), label="Nested cross-validation", color="r"
)
plt.legend(loc="best", frameon=False)
show()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 56.693 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 1177 MB