Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Simple example of NiftiMasker use¶
Here is a simple example of automatic mask computation using the nifti masker. The mask is computed and visualized.
Retrieve the brain development functional dataset¶
We fetch the dataset and print some basic information about it.
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_development_fmri
dataset = fetch_development_fmri(n_subjects=1)
func_filename = dataset.func[0]
print(f"First functional nifti image (4D) is at: {func_filename}")
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
[fetch_development_fmri] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri
First functional nifti image (4D) is at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz
Compute the mask¶
As the input image is an EPI image,
the background is noisy
and we cannot rely on the 'background' masking strategy.
We need to use the 'epi' one.
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
masker = NiftiMasker(
mask_strategy="epi",
memory="nilearn_cache",
memory_level=1,
smoothing_fwhm=8,
verbose=1,
)
Note
When viewing an Nilearn estimator in a notebook (or more generally on an HTML page like here) you get an expandable ‘Parameters’ section where the parameters that have different values from their default are highlighted in orange. If you are using a version of scikit-learn >= 1.8.0 you will also get access to the ‘docstring’ description of each parameter.
[NiftiMasker.fit] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-p
ixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz'
[NiftiMasker.fit] Computing mask
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.masking.compute_epi_mask...
compute_epi_mask('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz', verbose=0)
_________________________________________________compute_epi_mask - 0.2s, 0.0min
[NiftiMasker.fit] Resampling mask
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.image.resampling.resample_img...
resample_img(<nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f5d986013f0>, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, copy=False, interpolation='nearest')
_____________________________________________________resample_img - 0.0s, 0.0min
[NiftiMasker.fit] Finished fit
Note
You can also note that after fitting, the HTML representation of the estimator looks different than before before fitting.
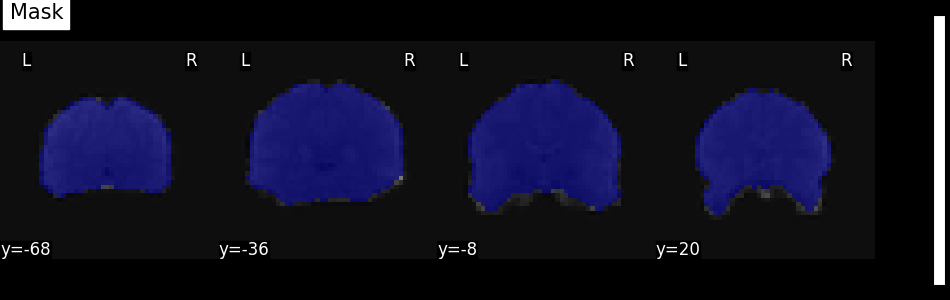
Visualize the mask¶
We can quickly get an idea about the estimated mask for this functional image by plotting the mask.
We get the estimated mask from the mask_img_ attribute of the masker:
the final _ ofd this attribute name means it was generated
by the fit method.
We can then plot it using the plot_roi function
with the mean functional image as background.
from nilearn.image.image import mean_img
from nilearn.plotting import plot_roi, show
mask_img = masker.mask_img_
mean_func_img = mean_img(func_filename)
plot_roi(mask_img, mean_func_img, display_mode="y", cut_coords=4, title="Mask")
show()
Visualize the masker report¶
More information can be obtained about the masker and its mask
by generating a masker report.
This can be done using
the generate_report method.
Note
The generated report can be:
displayed in a Notebook,
opened in a browser using the
.open_in_browser()method,or saved to a file using the
.save_as_html(output_filepath)method.
Preprocess data with the NiftiMasker¶
We extract the data from the nifti image and turn it into a numpy array.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/06_manipulating_images/plot_nifti_simple.py:106: FutureWarning: boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
fmri_masked = masker.transform(func_filename)
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.nifti_masker.filter_and_mask...
filter_and_mask('/home/runner/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f5d986013f0>, { 'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'gray',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'low_pass': None,
'reports': True,
'runs': None,
'smoothing_fwhm': 8,
'standardize': False,
'standardize_confounds': True,
't_r': None,
'target_affine': None,
'target_shape': None}, memory_level=1, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), verbose=1, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, copy=True, dtype=None, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f5d96a55d20>
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Smoothing images
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/06_manipulating_images/plot_nifti_simple.py:106: FutureWarning: boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
fmri_masked = masker.transform(func_filename)
__________________________________________________filter_and_mask - 0.8s, 0.0min
(168, 24256)
fmri_masked is now a 2D numpy array, (n_voxels x n_time_points).
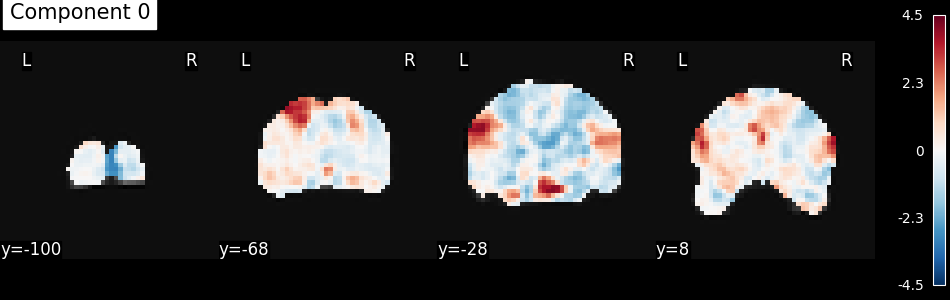
Run an algorithm and visualize the results¶
Given that we now have a numpy array,
we can then pass the data the wide range of algorithm.
Here we will just do an independent component analysis,
turned the extracted component back into images
(using inverse_transform),
then we will plot the first component.
from sklearn.decomposition import FastICA
from nilearn.image import index_img
from nilearn.plotting import plot_stat_map, show
ica = FastICA(n_components=10, random_state=42, tol=0.001, max_iter=2000)
components_masked = ica.fit_transform(fmri_masked.T).T
components = masker.inverse_transform(components_masked)
plot_stat_map(
index_img(components, 0),
mean_func_img,
display_mode="y",
cut_coords=4,
title="Component 0",
)
show()
[NiftiMasker.inverse_transform] Computing image from signals
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.masking.unmask...
unmask(array([[-1.0416 , ..., -0.558067],
...,
[ 0.574022, ..., -0.41854 ]], shape=(10, 24256)),
<nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f5d986013f0>)
___________________________________________________________unmask - 0.1s, 0.0min
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.811 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 486 MB