Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Making a surface plot of a 3D statistical map¶
In this example, we will project a 3D statistical map onto a cortical mesh
using SurfaceImage,
display a surface plot of the projected map
using plot_surf_stat_map
with different plotting engines,
and add contours of regions of interest using
plot_surf_contours.
Sample the 3D data around each node of the mesh¶
You can create a SurfaceImage object
from a nifti image by using the from_volume class method.
that will call indirectly vol_to_surf.
Get a statistical map as nifti
from nilearn.datasets import load_sample_motor_activation_image
stat_img = load_sample_motor_activation_image()
Get a cortical mesh
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage
fsaverage_meshes = load_fsaverage()
Construct a surface image from a volume.
from nilearn.surface import SurfaceImage
surface_image = SurfaceImage.from_volume(
mesh=fsaverage_meshes["pial"],
volume_img=stat_img,
)
Here, we load the curvature map to use as background map some plots. We define a surface map whose value for a given vertex is 1 if the curvature is positive, -1 if the curvature is negative.
import numpy as np
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage_data
curv_sign = load_fsaverage_data(data_type="curvature")
for hemi, data in curv_sign.data.parts.items():
curv_sign.data.parts[hemi] = np.sign(data)
Plot the surface image¶
You can visualize the surface image using the function
plot_surf_stat_map which uses matplotlib
as the default plotting engine.
from nilearn.plotting import plot_surf_stat_map
# In this example we will plot both hemispheres, but you can choose one of
# "left", "right" or "both".
hemi = "both"
fig = plot_surf_stat_map(
stat_map=surface_image,
surf_mesh=fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
hemi=hemi,
title="Surface with matplotlib",
threshold=1.0,
bg_map=curv_sign,
)
fig.show()
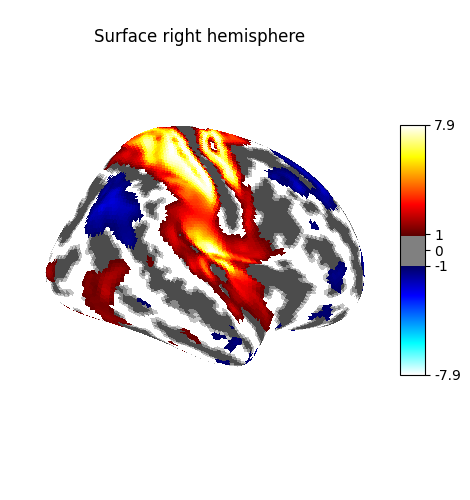
If you have a recent version of Nilearn (>=0.8.2),
and if you have plotly installed,
you can easily configure plot_surf_stat_map
to use plotly instead of matplotlib:
# If plotly is not installed, use matplotlib
from nilearn._utils.helpers import is_plotly_installed
engine = "plotly" if is_plotly_installed() else "matplotlib"
print(f"Using plotting engine {engine}.")
figure = plot_surf_stat_map(
stat_map=surface_image,
surf_mesh=fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
hemi=hemi,
title=f"Surface with {engine}",
threshold=1.0,
bg_map=curv_sign,
bg_on_data=True,
engine=engine, # Specify the plotting engine here
)
figure.show()
# Uncomment the line below to have interactive
# visualization in the browser
# figure.show(renderer="browser")
Using plotting engine plotly.
When using matplolib as the plotting engine, a standard
matplotlib.figure.Figure is returned.
With plotly as the plotting engine,
a custom PlotlySurfaceFigure
is returned which provides a similar API
to the Figure.
For example, you can save a static version of the figure to file
(this option requires to have kaleido installed):
# Save the figure as we would do with a matplotlib figure.
# Uncomment the following line to save the previous figure to file
# fig.savefig("both_hemisphere.png")
Plot 3D image for comparison¶
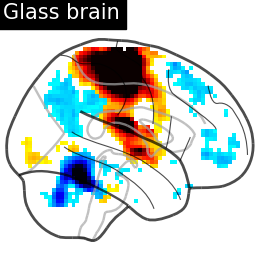
from nilearn.plotting import plot_glass_brain, plot_stat_map, show
plot_glass_brain(
stat_map_img=stat_img,
display_mode="r",
plot_abs=False,
title="Glass brain",
threshold=2.0,
)
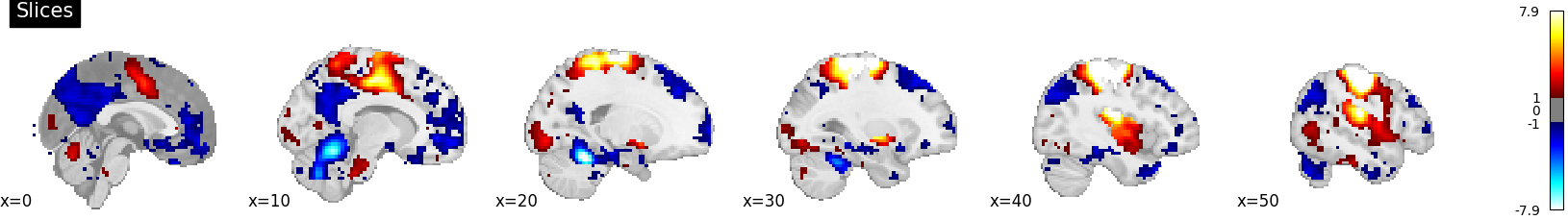
plot_stat_map(
stat_map_img=stat_img,
display_mode="x",
threshold=1.0,
cut_coords=list(range(0, 51, 10)),
title="Slices",
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._slicers.XSlicer object at 0x7f32a7483e50>
Use an atlas and choose regions to outline¶
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_atlas_surf_destrieux
fsaverage = load_fsaverage("fsaverage5")
destrieux = fetch_atlas_surf_destrieux()
destrieux_atlas = SurfaceImage(
mesh=fsaverage["inflated"],
data={
"left": destrieux["map_left"],
"right": destrieux["map_right"],
},
)
# these are the regions we want to outline
regions_dict = {
"G_postcentral": "Postcentral gyrus",
"G_precentral": "Precentral gyrus",
}
# get indices in atlas for these labels
regions_indices = [
np.where(np.array(destrieux.labels) == region)[0][0]
for region in regions_dict
]
labels = list(regions_dict.values())
[fetch_atlas_surf_destrieux] Dataset found in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/destrieux_surface
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_3d_map_to_surface_projection.py:149: UserWarning:
The following regions are present in the atlas look-up table,
but missing from the atlas image:
index name
0 Unknown
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_3d_map_to_surface_projection.py:149: UserWarning:
The following regions are present in the atlas look-up table,
but missing from the atlas image:
index name
0 Unknown
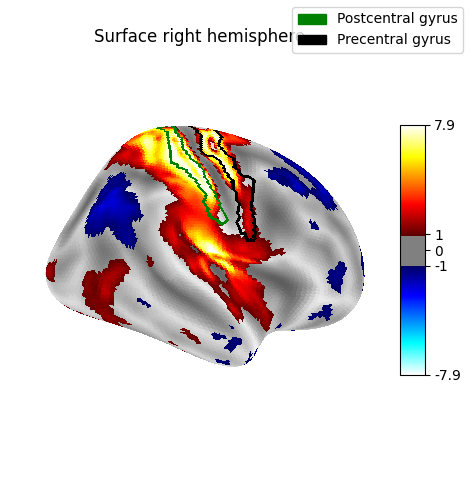
Display outlines of the regions of interest on top of a statistical map¶
from nilearn.plotting import plot_surf_contours
fsaverage_sulcal = load_fsaverage_data(data_type="sulcal", mesh_type="pial")
figure = plot_surf_stat_map(
stat_map=surface_image,
surf_mesh=fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
hemi=hemi,
title="ROI outlines on surface",
threshold=1.0,
bg_map=fsaverage_sulcal,
engine=engine,
)
if engine == "matplotlib":
figure = plot_surf_contours(
roi_map=destrieux_atlas,
hemi=hemi,
labels=labels,
levels=regions_indices,
figure=figure,
legend=True,
colors=["g", "k"],
)
elif engine == "plotly":
figure.add_contours(
roi_map=destrieux_atlas,
levels=regions_indices,
labels=labels,
lines=[{"width": 5}],
)
# Uncomment the line below to have interactive
# visualization in the browser
# figure.show(renderer="browser")
figure.show()
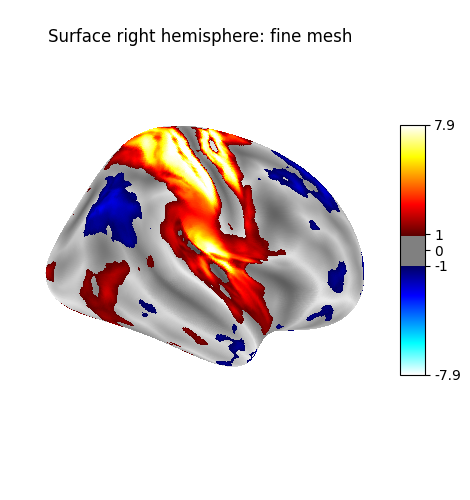
Plot with higher-resolution mesh¶
load_fsaverage
and load_fsaverage_data
take a mesh argument
which specifies whether to fetch
the low-resolution fsaverage5 mesh,
or another mesh
like the high-resolution fsaverage mesh.
Using mesh="fsaverage" will result
in more memory usage and computation time,
but finer visualizations.
big_fsaverage_meshes = load_fsaverage(mesh="fsaverage")
big_fsaverage_sulcal = load_fsaverage_data(
mesh="fsaverage",
data_type="sulcal",
mesh_type="inflated",
)
big_img = SurfaceImage.from_volume(
mesh=big_fsaverage_meshes["pial"],
volume_img=stat_img,
)
plot_surf_stat_map(
stat_map=big_img,
surf_mesh=big_fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
hemi=hemi,
title="Surface fine mesh",
threshold=1.0,
bg_map=big_fsaverage_sulcal,
)
show()
[load_fsaverage] Dataset created in /home/runner/nilearn_data/fsaverage
[load_fsaverage] Downloading data from https://osf.io/svf8k/download ...
[load_fsaverage] Downloaded 2236416 of 34242788 bytes (6.5%%, 14.3s remaining)
[load_fsaverage] Downloaded 23953408 of 34242788 bytes (70.0%%, 0.9s
remaining)
[load_fsaverage] ...done. (4 seconds, 0 min)
[load_fsaverage] Extracting data from
/home/runner/nilearn_data/fsaverage/735bf0f211246c83396b5f21f706c224/download...
[load_fsaverage] .. done.
[load_fsaverage_data] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/fsaverage
[load_fsaverage_data] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/fsaverage
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_3d_map_to_surface_projection.py:238: RuntimeWarning:
Meshes are not identical but have compatible number of vertices.
Plot multiple views of the 3D volume on a surface¶
plot_img_on_surf
takes a nifti statistical map
and projects it onto a surface.
It supports multiple choices of orientations,
and can plot either one or both hemispheres.
If no surf_mesh is given,
plot_img_on_surf projects the images onto
FreeSurfer's fsaverage5.
from nilearn.plotting import plot_img_on_surf
plot_img_on_surf(
stat_map=stat_img,
views=["lateral", "medial"],
hemispheres=["left", "right"],
title="multiple views of the 3D volume",
bg_on_data=True,
symmetric_cmap=None,
)
show()
3D visualization in a web browser¶
An alternative to plot_surf_stat_map is to use
view_surf or
view_img_on_surf that give
more interactive visualizations in a web browser.
See 3D Plots of statistical maps or atlases on the cortical surface for more details.
from nilearn.plotting import view_surf
view = view_surf(
surf_mesh=fsaverage_meshes["inflated"],
surf_map=surface_image,
threshold="90%",
bg_map=fsaverage_sulcal,
hemi=hemi,
title="3D visualization in a web browser",
)
# In a notebook, if ``view`` is the output of a cell,
# it will be displayed below the cell
view
# If plotly is not installed or the code is run in script mode,
# it is still possible to have interactive visualization in the
# browser by uncommenting the below line.
# view.open_in_browser()
We don’t need to do the projection ourselves, we can use
view_img_on_surf:
from nilearn.plotting import view_img_on_surf
view = view_img_on_surf(stat_img, threshold="90%")
view
# If plotly is not installed or the code is run in script mode,
# it is still possible to have interactive visualization in the
# browser by uncommenting the below line.
# view.open_in_browser()
Impact of plot parameters on visualization¶
You can specify arguments to be passed on to the function
vol_to_surf using vol_to_surf_kwargs
This allows fine-grained control of how the input 3D image
is resampled and interpolated -
for example if you are viewing a volumetric atlas,
you would want to avoid averaging the labels between neighboring regions.
Using nearest-neighbor interpolation with zero radius will achieve this.
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009
destrieux = fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009()
view = view_img_on_surf(
stat_map_img=destrieux.maps,
surf_mesh="fsaverage",
cmap="tab20",
vol_to_surf_kwargs={
"n_samples": 1,
"radius": 0.0,
"interpolation": "nearest_most_frequent",
},
symmetric_cmap=False,
colorbar=False,
)
view
# If plotly is not installed or the code is run in script mode,
# it is still possible to have interactive visualization in the
# browser by uncommenting the below line.
# view.open_in_browser()
[fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009] Dataset created in
/home/runner/nilearn_data/destrieux_2009
[fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009] Downloading data from
https://www.nitrc.org/frs/download.php/11942/destrieux2009.tgz ...
[fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009] ...done. (1 seconds, 0 min)
[fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009] Extracting data from
/home/runner/nilearn_data/destrieux_2009/2a2e5a5707983d509d9319c692c867ab/destri
eux2009.tgz...
[fetch_atlas_destrieux_2009] .. done.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/01_plotting/plot_3d_map_to_surface_projection.py:325: UserWarning:
The following regions are present in the atlas look-up table,
but missing from the atlas image:
index name
42 L Medial_wall
117 R Medial_wall
[view_img_on_surf] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/fsaverage
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 22.871 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 1681 MB