Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Massively univariate analysis of face vs house recognition¶
A permuted Ordinary Least Squares algorithm is run at each voxel in order to determine whether or not it behaves differently under a “face viewing” condition and a “house viewing” condition. We consider the mean image per run and per condition. Otherwise, the observations cannot be exchanged at random because a time dependence exists between observations within a same run (see Winkler et al.[1] for more detailed explanations).
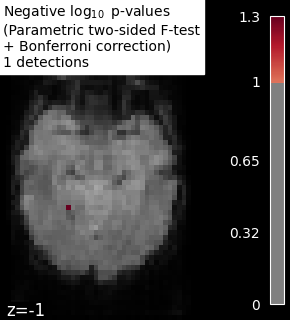
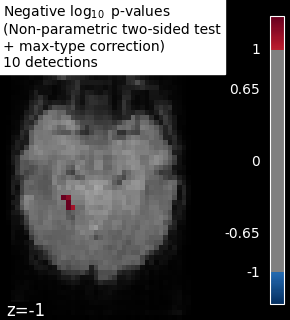
The example shows the small differences that exist between Bonferroni-corrected p-values and family-wise corrected p-values obtained from a permutation test combined with a max-type procedure (Anderson and Robinson[2]). Bonferroni correction is a bit conservative, as revealed by the presence of a few false negative.
Load Haxby dataset¶
from nilearn import datasets, image
from nilearn.plotting import plot_stat_map, show
haxby_dataset = datasets.fetch_haxby(subjects=[2])
# print basic information on the dataset
print(f"Mask nifti image (3D) is located at: {haxby_dataset.mask}")
print(f"Functional nifti image (4D) is located at: {haxby_dataset.func[0]}")
[fetch_haxby] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001
Mask nifti image (3D) is located at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz
Functional nifti image (4D) is located at: /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/subj2/bold.nii.gz
Restrict to faces and houses¶
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
labels = pd.read_csv(haxby_dataset.session_target[0], sep=" ")
conditions = labels["labels"]
categories = conditions.unique()
conditions_encoded = np.zeros_like(conditions)
for c, category in enumerate(categories):
conditions_encoded[conditions == category] = c
runs = labels["chunks"]
condition_mask = conditions.isin(["face", "house"])
conditions_encoded = conditions_encoded[condition_mask]
Mask data¶
from nilearn.image import index_img
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
mask_filename = haxby_dataset.mask
nifti_masker = NiftiMasker(
smoothing_fwhm=8,
mask_img=mask_filename,
memory="nilearn_cache", # cache options
memory_level=1,
verbose=1,
)
func_filename = haxby_dataset.func[0]
func_reduced = index_img(func_filename, condition_mask)
fmri_masked = nifti_masker.fit_transform(func_reduced)
# We consider the mean image per run and per condition.
# Otherwise, the observations cannot be exchanged at random because
# a time dependence exists between observations within a same run.
n_runs = np.unique(runs).size
conditions_per_run = 2
grouped_fmri_masked = np.empty(
(conditions_per_run * n_runs, fmri_masked.shape[1])
)
grouped_conditions_encoded = np.empty((conditions_per_run * n_runs, 1))
for s in range(n_runs):
run_mask = runs[condition_mask] == s
run_house_mask = np.logical_and(
run_mask, conditions[condition_mask] == "house"
)
run_face_mask = np.logical_and(
run_mask, conditions[condition_mask] == "face"
)
grouped_fmri_masked[2 * s] = fmri_masked[run_house_mask].mean(0)
grouped_fmri_masked[2 * s + 1] = fmri_masked[run_face_mask].mean(0)
grouped_conditions_encoded[2 * s] = conditions_encoded[run_house_mask][0]
grouped_conditions_encoded[2 * s + 1] = conditions_encoded[run_face_mask][
0
]
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Loading mask from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001/mask.nii.gz'
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f327eabece0>
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/07_advanced/plot_haxby_mass_univariate.py:66: UserWarning:
[NiftiMasker.fit] Generation of a mask has been requested (imgs != None) while a mask was given at masker creation. Given mask will be used.
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Resampling mask
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/07_advanced/plot_haxby_mass_univariate.py:66: FutureWarning:
boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.nifti_masker.filter_and_mask...
filter_and_mask(<nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f327eabece0>, <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a77dee90>, { 'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'cmap': 'gray',
'detrend': False,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': None,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'low_pass': None,
'reports': True,
'runs': None,
'smoothing_fwhm': 8,
'standardize': False,
'standardize_confounds': True,
't_r': None,
'target_affine': None,
'target_shape': None}, memory_level=1, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), verbose=1, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, copy=True, dtype=None, sklearn_output_config=None)
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f327eabece0>
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Smoothing images
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
__________________________________________________filter_and_mask - 1.3s, 0.0min
Perform massively univariate analysis with permuted OLS¶
We use a two-sided t-test to compute p-values, but we keep trace of the effect sign to add it back at the end and thus observe the signed effect
from nilearn.mass_univariate import permuted_ols
# Note that an intercept as a covariate is used by default
output = permuted_ols(
grouped_conditions_encoded,
grouped_fmri_masked,
n_perm=10000,
two_sided_test=True,
verbose=1, # display progress bar
n_jobs=2, # can be changed to use more CPUs
)
neg_log_pvals = output["logp_max_t"]
t_scores_original_data = output["t"]
signed_neg_log_pvals = neg_log_pvals * np.sign(t_scores_original_data)
signed_neg_log_pvals_unmasked = nifti_masker.inverse_transform(
signed_neg_log_pvals
)
[Parallel(n_jobs=2)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 2 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=2)]: Done 2 out of 2 | elapsed: 5.5s finished
[NiftiMasker.inverse_transform] Computing image from signals
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.masking.unmask...
unmask(array([[0., ..., 0.]], shape=(1, 39912)), <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a77dee90>)
___________________________________________________________unmask - 0.0s, 0.0min
scikit-learn F-scores for comparison
F-test does not allow to observe the effect sign (pure two-sided test)
from sklearn.feature_selection import f_regression
# f_regression implicitly adds intercept
_, pvals_bonferroni = f_regression(
grouped_fmri_masked,
grouped_conditions_encoded.ravel(),
)
pvals_bonferroni *= fmri_masked.shape[1]
pvals_bonferroni[np.isnan(pvals_bonferroni)] = 1
pvals_bonferroni[pvals_bonferroni > 1] = 1
neg_log_pvals_bonferroni = -np.log10(pvals_bonferroni)
neg_log_pvals_bonferroni_unmasked = nifti_masker.inverse_transform(
neg_log_pvals_bonferroni
)
[NiftiMasker.inverse_transform] Computing image from signals
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.masking.unmask...
unmask(array([-0., ..., -0.], shape=(39912,)), <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at 0x7f32a77dee90>)
___________________________________________________________unmask - 0.0s, 0.0min
Visualization¶
from nilearn.image import get_data
# Use the fMRI mean image as a surrogate of anatomical data
mean_fmri_img = image.mean_img(func_filename)
threshold = -np.log10(0.1) # 10% corrected
vmax = min(signed_neg_log_pvals.max(), neg_log_pvals_bonferroni.max())
# Plot thresholded p-values map corresponding to F-scores
neg_log_pvals_bonferroni_data = get_data(neg_log_pvals_bonferroni_unmasked)
n_detections = (neg_log_pvals_bonferroni_data > threshold).sum()
title = (
"Negative $\\log_{10}$ p-values"
"\n(Parametric two-sided F-test"
"\n+ Bonferroni correction)"
f"\n{n_detections} detections"
)
display = plot_stat_map(
neg_log_pvals_bonferroni_unmasked,
mean_fmri_img,
threshold=threshold,
display_mode="z",
cut_coords=[-1],
vmax=vmax,
vmin=threshold,
cmap="inferno",
)
display.title(title, size=10)
# Plot permutation p-values map
n_detections = (np.abs(signed_neg_log_pvals) > threshold).sum()
title = (
"Negative $\\log_{10}$ p-values"
"\n(Non-parametric two-sided test"
"\n+ max-type correction)"
f"\n{n_detections} detections"
)
display = plot_stat_map(
signed_neg_log_pvals_unmasked,
mean_fmri_img,
threshold=threshold,
display_mode="z",
cut_coords=[-1],
vmax=vmax,
vmin=threshold,
cmap="inferno",
)
display.title(title, size=10)
show()
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 15.862 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 1189 MB