Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Default Mode Network extraction of ADHD dataset¶
This example shows a full step-by-step workflow of fitting a GLM to signal extracted from a seed on the Posterior Cingulate Cortex and saving the results. More precisely, this example shows how to use a signal extracted from a seed region as the regressor in a GLM to determine the correlation of each region in the dataset with the seed region.
More specifically:
A sequence of fMRI volumes are loaded.
A design matrix with the Posterior Cingulate Cortex seed is defined.
A GLM is applied to the dataset (effect/covariance, then contrast estimation).
The Default Mode Network is displayed.
import numpy as np
from nilearn import plotting
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_adhd
from nilearn.glm.first_level import (
FirstLevelModel,
make_first_level_design_matrix,
)
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiSpheresMasker
Prepare data and analysis parameters¶
Prepare the data.
adhd_dataset = fetch_adhd(n_subjects=1)
# Prepare seed
pcc_coords = (0, -53, 26)
[fetch_adhd] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd
Extract the seed region’s time course¶
Extract the time course of the seed region.
seed_masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
[pcc_coords],
radius=10,
detrend=True,
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=adhd_dataset.t_r,
memory="nilearn_cache",
memory_level=1,
verbose=1,
)
seed_time_series = seed_masker.fit_transform(adhd_dataset.func[0])
n_scans = seed_time_series.shape[0]
frametimes = np.linspace(0, (n_scans - 1) * adhd_dataset.t_r, n_scans)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Finished fit
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/04_glm_first_level/plot_adhd_dmn.py:57: FutureWarning: boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
seed_time_series = seed_masker.fit_transform(adhd_dataset.func[0])
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker.filter_and_extract...
filter_and_extract('/home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd/data/0010042/0010042_rest_tshift_RPI_voreg_mni.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_spheres_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7f5dbc973a00>,
{ 'allow_overlap': False,
'clean_args': None,
'clean_kwargs': {},
'detrend': True,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': 0.01,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'low_pass': 0.1,
'mask_img': None,
'radius': 10,
'reports': True,
'seeds': [(0, -53, 26)],
'smoothing_fwhm': None,
'standardize': False,
'standardize_confounds': True,
't_r': 2.0}, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=1)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd/data/0010042/0010042_rest_tshift_RPI_voreg_mni.n
ii.gz'
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Extracting region signals
[NiftiSpheresMasker.wrapped] Cleaning extracted signals
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/04_glm_first_level/plot_adhd_dmn.py:57: FutureWarning: boolean values for 'standardize' will be deprecated in nilearn 0.15.0.
Use 'zscore_sample' instead of 'True' or use 'None' instead of 'False'.
seed_time_series = seed_masker.fit_transform(adhd_dataset.func[0])
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 3.5s, 0.1min
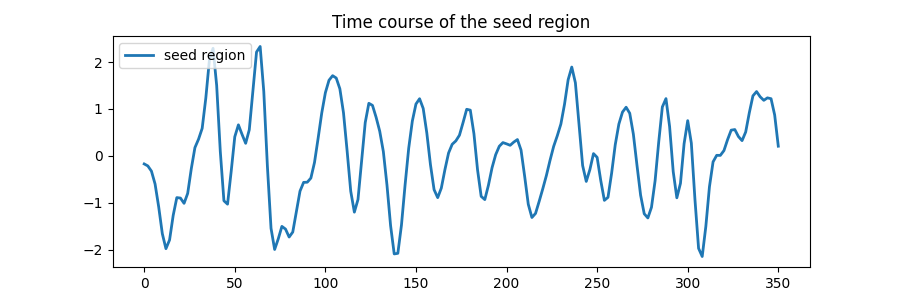
Plot the time course of the seed region.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9, 3))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(frametimes, seed_time_series, linewidth=2, label="seed region")
ax.legend(loc=2)
ax.set_title("Time course of the seed region")
plt.show()
Estimate contrasts¶
Specify the contrasts.
design_matrix = make_first_level_design_matrix(
frametimes,
hrf_model="spm",
add_regs=seed_time_series,
add_reg_names=["pcc_seed"],
)
dmn_contrast = np.array([1] + [0] * (design_matrix.shape[1] - 1))
contrasts = {"seed_based_glm": dmn_contrast}
Perform first level analysis¶
Setup and fit GLM.
first_level_model = FirstLevelModel(verbose=1)
first_level_model = first_level_model.fit(
run_imgs=adhd_dataset.func[0], design_matrices=design_matrix
)
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Loading data from
'/home/runner/nilearn_data/adhd/data/0010042/0010042_rest_tshift_RPI_voreg_mni.n
ii.gz'
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computing mask
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Resampling mask
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Finished fit
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computing run 1 out of 1 runs (go take a coffee, a big
one).
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Performing mask computation.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Loading data from <nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image object at
0x7f5dab9721d0>
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Extracting region signals
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Masking took 0 seconds.
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/04_glm_first_level/plot_adhd_dmn.py:91: UserWarning: Mean values of 0 observed. The data have probably been centered. Scaling might not work as expected.
first_level_model = first_level_model.fit(
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Performing GLM computation.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] GLM took 1 seconds.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computation of 1 runs done in 2 seconds.
Estimate the contrast.
print("Contrast seed_based_glm computed.")
z_map = first_level_model.compute_contrast(
contrasts["seed_based_glm"], output_type="z_score"
)
Contrast seed_based_glm computed.
[FirstLevelModel.compute_contrast] Computing image from signals
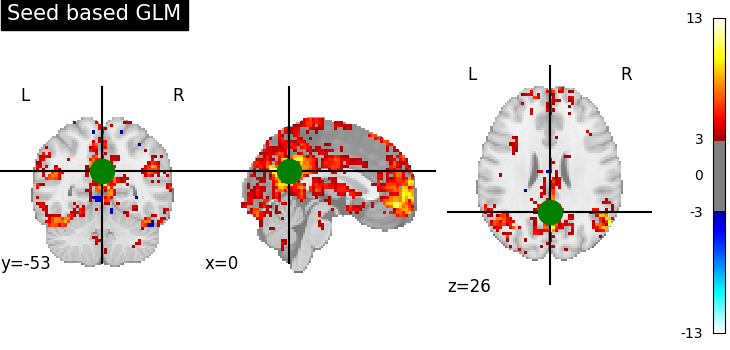
Saving snapshots of the contrasts
from pathlib import Path
display = plotting.plot_stat_map(
z_map, threshold=3.0, title="Seed based GLM", cut_coords=pcc_coords
)
display.add_markers(
marker_coords=[pcc_coords], marker_color="g", marker_size=300
)
output_dir = Path.cwd() / "results" / "plot_adhd_dmn"
output_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
filename = "dmn_z_map.png"
display.savefig(output_dir / filename)
print(f"Save z-map in '{filename}'.")
Save z-map in 'dmn_z_map.png'.
Generating a report¶
It can be useful to quickly generate a portable, ready-to-view report with most of the pertinent information. This is easy to do if you have a fitted model and the list of contrasts, which we do here.
report = first_level_model.generate_report(
contrasts=contrasts,
title="ADHD DMN Report",
cluster_threshold=15,
min_distance=8.0,
plot_type="glass",
)
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Computing image from signals
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating contrast-level figures...
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating design matrices figures...
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating contrast matrices figures...
Note
The generated report can be:
displayed in a Notebook,
opened in a browser using the
.open_in_browser()method,or saved to a file using the
.save_as_html(output_filepath)method.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 13.106 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 472 MB