Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.image.index_img¶
- nilearn.image.index_img(imgs, index)[source]¶
Indexes into a image in the last dimension.
Common use cases include extracting an image out of img or creating a 4D (or 2D for surface) image whose data is a subset of img data.
- Parameters:
- imgs4D Niimg-like object or 2D
SurfaceImage - indexAny type compatible with numpy array indexing
Used for indexing the data array in the last dimension.
- imgs4D Niimg-like object or 2D
- Returns:
Nifti1ImageorSurfaceImageIndexed image.
Examples
First we concatenate two MNI152 images to create a 4D-image:
>>> from nilearn import datasets >>> from nilearn.image import concat_imgs, index_img >>> joint_mni_image = concat_imgs([datasets.load_mni152_template(), ... datasets.load_mni152_template()]) >>> print(joint_mni_image.shape) (197, 233, 189, 2)
We can now select one slice from the last dimension of this 4D-image:
>>> single_mni_image = index_img(joint_mni_image, 1) >>> print(single_mni_image.shape) (197, 233, 189)
We can also select multiple frames using the slice constructor:
>>> five_mni_images = concat_imgs([datasets.load_mni152_template()] * 5) >>> print(five_mni_images.shape) (197, 233, 189, 5) >>> first_three_images = index_img(five_mni_images, ... slice(0, 3)) >>> print(first_three_images.shape) (197, 233, 189, 3)
Examples using nilearn.image.index_img¶
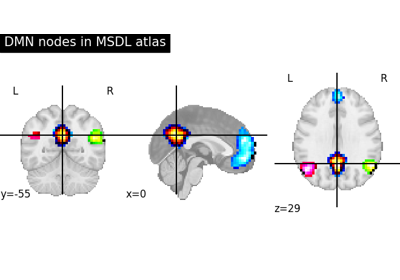
Visualizing a probabilistic atlas: the default mode in the MSDL atlas
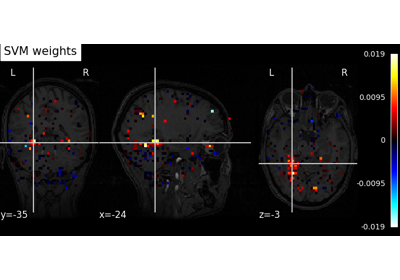
Decoding of a dataset after GLM fit for signal extraction
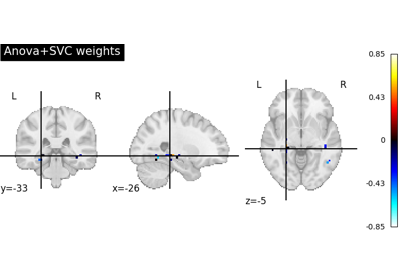
Decoding with ANOVA + SVM: face vs house in the Haxby dataset
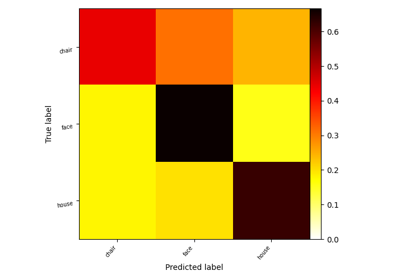
Decoding with FREM: face vs house vs chair object recognition
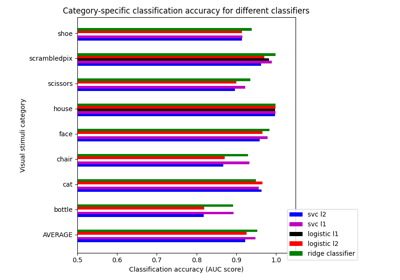
Different classifiers in decoding the Haxby dataset
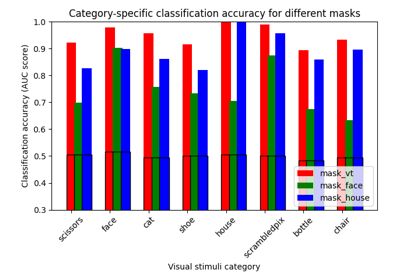
ROI-based decoding analysis in Haxby et al. dataset
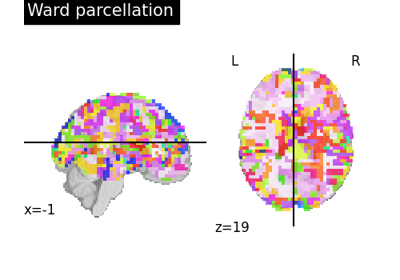
Clustering methods to learn a brain parcellation from fMRI
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes
Regions Extraction of Default Mode Networks using Smith Atlas
Massively univariate analysis of face vs house recognition
Multivariate decompositions: Independent component analysis of fMRI