Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Example of surface-based first-level analysis¶
A full step-by-step example of fitting a GLM to experimental data sampled on the cortical surface and visualizing the results.
More specifically:
A sequence of fMRI volumes is loaded.
fMRI data are projected onto a reference cortical surface (the FreeSurfer template, fsaverage).
A GLM is applied to the dataset (effect/covariance, then contrast estimation).
Inspect GLM reports and save the results to disk.
The result of the analysis are statistical maps that are defined on the brain mesh. We display them using Nilearn capabilities.
The projection of fMRI data onto a given brain mesh requires that both are initially defined in the same space.
The functional data should be coregistered to the anatomy from which the mesh was obtained.
Another possibility, used here, is to project the normalized fMRI data to an MNI-coregistered mesh, such as fsaverage.
The advantage of this second approach is that it makes it easy to run second-level analyses on the surface. On the other hand, it is obviously less accurate than using a subject-tailored mesh.
Prepare data and analysis parameters¶
Fetch the data.
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_localizer_first_level
data = fetch_localizer_first_level()
t_r = data.t_r
slice_time_ref = data.slice_time_ref
[fetch_localizer_first_level] Dataset found in /home/remi-gau/nilearn_data/localizer_first_level
Project the fMRI image to the surface¶
For this we need to get a mesh representing the geometry of the surface. We could use an individual mesh, but we first resort to a standard mesh, the so-called fsaverage5 template from the FreeSurfer software.
We use the SurfaceImage
to create an surface object instance
that contains both the mesh
(here we use the one from the fsaverage5 templates)
and the BOLD data that we project on the surface.
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage
from nilearn.surface import SurfaceImage
fsaverage5 = load_fsaverage()
surface_image = SurfaceImage.from_volume(
mesh=fsaverage5["pial"],
volume_img=data.epi_img,
)
Perform first level analysis¶
We can now simply run a GLM by directly passing
our SurfaceImage instance
as input to FirstLevelModel.fit
Here we use an HRF model containing the Glover model and its time derivative The drift model is implicitly a cosine basis with a period cutoff at 128s.
from nilearn.glm.first_level import FirstLevelModel
glm = FirstLevelModel(
t_r=t_r,
slice_time_ref=slice_time_ref,
hrf_model="glover + derivative",
minimize_memory=False,
verbose=1,
).fit(run_imgs=surface_image, events=data.events)
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computing mask
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Finished fit
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computing run 1 out of 1 runs (go take a coffee, a big one).
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Performing mask computation.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Extracting region signals
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Cleaning extracted signals
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Masking took 0 seconds.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Performing GLM computation.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] GLM took 0 seconds.
[FirstLevelModel.fit] Computation of 1 runs done in 0 seconds.
Estimate contrasts¶
Specify the contrasts.
For practical purpose, we first generate an identity matrix whose size is the number of columns of the design matrix.
import numpy as np
design_matrix = glm.design_matrices_[0]
contrast_matrix = np.eye(design_matrix.shape[1])
At first, we create basic contrasts.
basic_contrasts = {
column: contrast_matrix[i]
for i, column in enumerate(design_matrix.columns)
}
Next, we add some intermediate contrasts and one contrast adding all conditions with some auditory parts.
basic_contrasts["audio"] = (
basic_contrasts["audio_left_hand_button_press"]
+ basic_contrasts["audio_right_hand_button_press"]
+ basic_contrasts["audio_computation"]
+ basic_contrasts["sentence_listening"]
)
one contrast adding all conditions involving instructions reading
basic_contrasts["visual"] = (
basic_contrasts["visual_left_hand_button_press"]
+ basic_contrasts["visual_right_hand_button_press"]
+ basic_contrasts["visual_computation"]
+ basic_contrasts["sentence_reading"]
)
one contrast adding all conditions involving computation
basic_contrasts["computation"] = (
basic_contrasts["visual_computation"]
+ basic_contrasts["audio_computation"]
)
one contrast adding all conditions involving sentences
basic_contrasts["sentences"] = (
basic_contrasts["sentence_listening"] + basic_contrasts["sentence_reading"]
)
Finally, we create a dictionary of more relevant contrasts
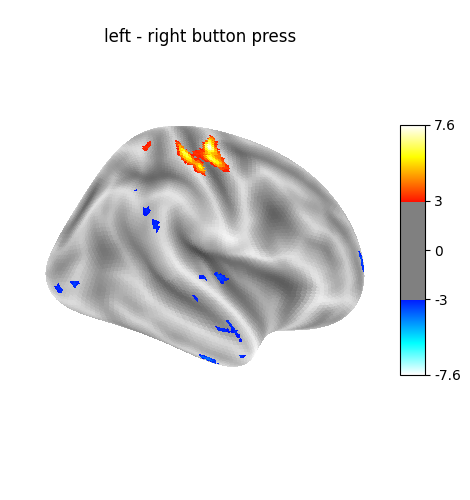
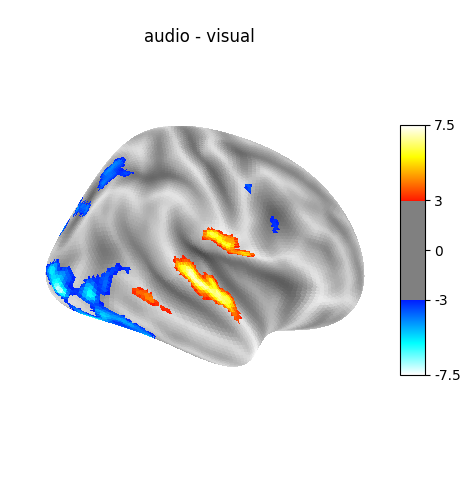
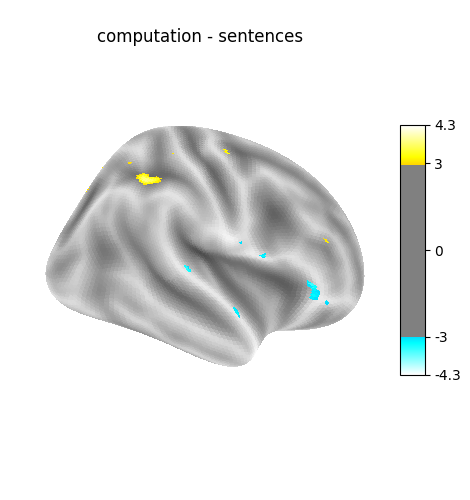
'left - right button press': probes motor activity in left versus right button presses.'audio - visual': probes the difference of activity between listening to some content or reading the same type of content (instructions, stories).'computation - sentences': looks at the activity when performing a mental computation task versus simply reading sentences.
Of course, we could define other contrasts, but we keep only 3 for simplicity.
contrasts = {
"(left - right) button press": (
basic_contrasts["audio_left_hand_button_press"]
- basic_contrasts["audio_right_hand_button_press"]
+ basic_contrasts["visual_left_hand_button_press"]
- basic_contrasts["visual_right_hand_button_press"]
),
"audio - visual": basic_contrasts["audio"] - basic_contrasts["visual"],
"computation - sentences": (
basic_contrasts["computation"] - basic_contrasts["sentences"]
),
}
Let’s estimate the t-contrasts, and extract a table of clusters that survive our thresholds.
We use the same threshold (uncorrected p < 0.001) for all contrasts.
We plot each contrast map on the inflated fsaverage mesh, together with a suitable background to give an impression of the cortex folding.
from scipy.stats import norm
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage_data
from nilearn.plotting import plot_surf_stat_map, show
from nilearn.reporting import get_clusters_table
p_val = 0.001
threshold = norm.isf(p_val)
cluster_threshold = 20
two_sided = True
fsaverage_data = load_fsaverage_data(data_type="sulcal")
results = {}
for contrast_id, contrast_val in contrasts.items():
results[contrast_id] = glm.compute_contrast(contrast_val, stat_type="t")
table = get_clusters_table(
results[contrast_id],
stat_threshold=threshold,
cluster_threshold=cluster_threshold,
two_sided=two_sided,
)
print(f"\n{contrast_id=}")
print(table)
for contrast_id, z_score in results.items():
hemi = "left"
if contrast_id == "(left - right) button press":
hemi = "both"
plot_surf_stat_map(
surf_mesh=fsaverage5["inflated"],
stat_map=z_score,
hemi=hemi,
title=contrast_id,
threshold=threshold,
bg_map=fsaverage_data,
)
show()
[FirstLevelModel.compute_contrast] Computing image from signals
contrast_id='(left - right) button press'
Cluster ID Hemisphere Peak Stat Cluster Size (vertices)
0 1 right 7.363035 133
1 2 left -3.095616 223
2 3 left -3.090853 20
3 4 left -3.157886 21
[FirstLevelModel.compute_contrast] Computing image from signals
contrast_id='audio - visual'
Cluster ID Hemisphere Peak Stat Cluster Size (vertices)
0 1 left 7.589528 188
1 2 right 7.194872 149
2 3 right 6.364164 75
3 4 right 4.300838 20
4 5 left -3.102627 239
5 6 left -3.100104 61
6 7 right -3.098115 136
7 8 right -3.200971 27
8 9 right -3.103647 270
9 10 right -3.096202 52
[FirstLevelModel.compute_contrast] Computing image from signals
contrast_id='computation - sentences'
Cluster ID Hemisphere Peak Stat Cluster Size (vertices)
0 1 right 3.803730 35
1 2 left -3.100574 47
Cluster-level inference¶
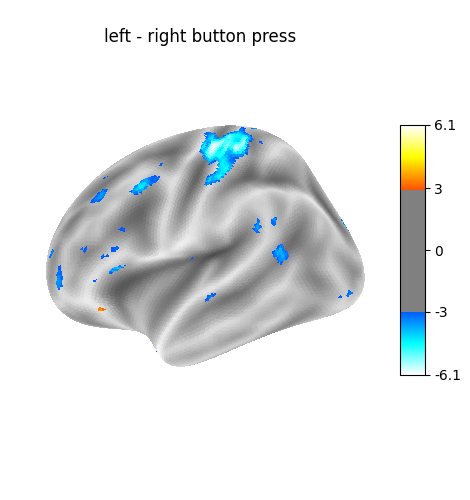
We can also perform cluster-level inference (aka “All resolution Inference”) for a given contrast. This gives a high-probability lower bound on the proportion of true discoveries in each cluster
from nilearn.glm import cluster_level_inference
from nilearn.surface.surface import get_data as get_surf_data
proportion_true_discoveries_img = cluster_level_inference(
results["audio - visual"], threshold=[2.5, 3.5, 4.5], alpha=0.05
)
data = get_surf_data(proportion_true_discoveries_img)
unique_vals = np.unique(data.ravel())
print(unique_vals)
plot_surf_stat_map(
surf_mesh=fsaverage5["inflated"],
stat_map=proportion_true_discoveries_img,
hemi="left",
cmap="inferno",
title="audio - visual, proportion true positives",
bg_map=fsaverage_data,
avg_method="max",
)
show()
[-0. 0.16666667 0.2 0.25 0.33333333 0.36363636
0.4 0.42857143 0.46153846 0.5 0.55555556 0.57142857
0.58333333 0.6 0.61538462 0.625 0.65217391 0.65384615
0.66666667 0.7 0.71428571 0.75 0.77777778 0.8
0.83333333 0.875 0.9 0.90909091 1. ]
Generate a report for the GLM¶
report = glm.generate_report(
contrasts,
threshold=threshold,
bg_img=load_fsaverage_data(data_type="sulcal", mesh_type="inflated"),
height_control=None,
cluster_threshold=cluster_threshold,
two_sided=two_sided,
)
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Computing image from signals
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Computing image from signals
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Computing image from signals
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating contrast-level figures...
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating design matrices figures...
[FirstLevelModel.generate_report] Generating contrast matrices figures...
Note
The generated report can be:
displayed in a Notebook,
opened in a browser using the
.open_in_browser()method,or saved to a file using the
.save_as_html(output_filepath)method.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 26.359 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 298 MB