Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Cortical surface-based searchlight decoding¶
This is a demo for surface-based searchlight decoding, as described in Chen et al.[1].
Warning
This example projects results from the Haxby dataset on the fsaverage surface. This is inappropriate given that the Haxby data has not been properly coregistered to allow for such projection. It is done in this example for pedagogical reasons to show “how to do it”.
Load Haxby dataset¶
import pandas as pd
from nilearn.datasets import fetch_haxby
# We fetch 2nd subject from haxby datasets (which is default)
haxby_dataset = fetch_haxby()
fmri_filename = haxby_dataset.func[0]
labels = pd.read_csv(haxby_dataset.session_target[0], sep=" ")
y = labels["labels"]
run = labels["chunks"]
[fetch_haxby] Dataset found in /home/runner/nilearn_data/haxby2001
Restrict to faces and houses¶
from nilearn.image import index_img
condition_mask = y.isin(["face", "house"])
fmri_img = index_img(fmri_filename, condition_mask)
y, run = y[condition_mask], run[condition_mask]
Surface BOLD response¶
Fetch a coarse surface of the left hemisphere only for speed and average voxels 5 mm close to the 3d pial surface.
from sklearn import neighbors
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage
from nilearn.surface import SurfaceImage
fsaverage = load_fsaverage()
fmri_img_surf = SurfaceImage.from_volume(
mesh=fsaverage["pial"], volume_img=fmri_img, radius=5
)
Searchlight computation¶
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from nilearn.decoding.searchlight import search_light
# For the sake of speed,
# we will only run the decoding on one hemisphere
# in this example.
hemispheres_to_analyze = ["left"]
# Uncomment the following line if you want to run both hemispheres.
# hemispheres_to_analyze = ["left", "right"]
# Let us initialize a result scores dictionary ,
# to be able to create a SurfaceImage from it later.
scores = {
"left": np.zeros(fmri_img_surf.mesh.parts["left"].n_vertices),
"right": np.zeros(fmri_img_surf.mesh.parts["right"].n_vertices),
}
for hemi in hemispheres_to_analyze:
print(f"Running searchlight on {hemi} hemisphere.")
# To define the BOLD responses
# to be included within each searchlight "sphere"
# we define an adjacency matrix
# based on the inflated surface vertices
# such that nearby vertices are concatenated
# within the same searchlight.
coordinates = fsaverage["inflated"].parts[hemi].coordinates
nn = neighbors.NearestNeighbors()
adjacency = nn.fit(coordinates).radius_neighbors_graph(coordinates).tolil()
# Simple linear estimator preceded by a normalization step
estimator = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), RidgeClassifier(alpha=10.0))
# Define cross-validation scheme
cv = KFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=False)
X = fmri_img_surf.data.parts[hemi].T
# Cross-validated search light
scores[hemi] = search_light(
X, y, estimator, adjacency, cv=cv, n_jobs=-1, verbose=1
)
Running searchlight on left hemisphere.
[Parallel(n_jobs=-1)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 4 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=-1)]: Done 2 out of 4 | elapsed: 55.8s remaining: 55.8s
[Parallel(n_jobs=-1)]: Done 4 out of 4 | elapsed: 56.2s finished
Visualization¶
from nilearn.datasets import load_fsaverage_data
from nilearn.plotting import plot_surf_stat_map, show
fsaverage_data = load_fsaverage_data(mesh_type="inflated", data_type="sulcal")
score_img = SurfaceImage(mesh=fsaverage["inflated"], data=scores)
chance = 0.5
for hemi in hemispheres_to_analyze:
score_img.data.parts[hemi] = score_img.data.parts[hemi] - chance
for hemi in hemispheres_to_analyze:
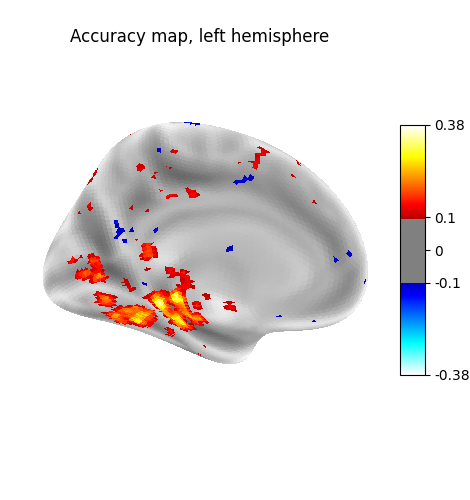
plot_surf_stat_map(
stat_map=score_img,
view="ventral",
hemi=hemi,
threshold=0.1,
bg_map=fsaverage_data,
title=f"Accuracy map, {hemi} hemisphere",
cmap="bwr",
)
show()
/home/runner/work/nilearn/nilearn/examples/02_decoding/plot_haxby_searchlight_surface.py:135: UserWarning:
You are using the 'agg' matplotlib backend that is non-interactive.
No figure will be plotted when calling matplotlib.pyplot.show() or nilearn.plotting.show().
You can fix this by installing a different backend: for example via
pip install PyQt6
References¶
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 7.372 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 1013 MB