Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
8.10.7. nilearn.plotting.plot_epi¶
- nilearn.plotting.plot_epi(epi_img=None, cut_coords=None, output_file=None, display_mode='ortho', figure=None, axes=None, title=None, annotate=True, draw_cross=True, black_bg=True, cmap=<matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap object>, vmin=None, vmax=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
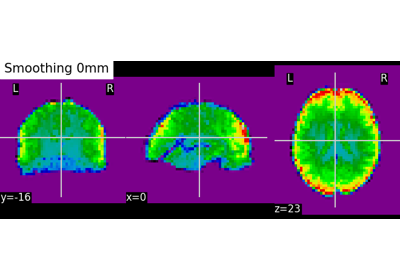
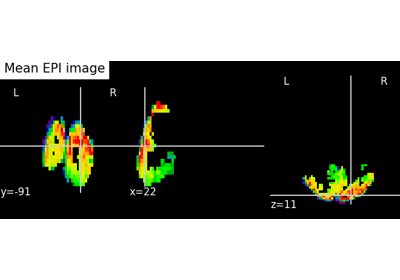
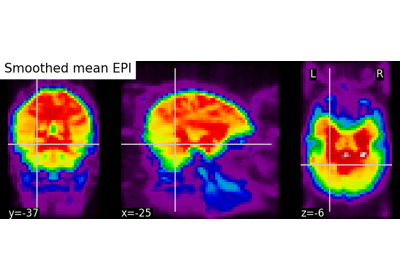
Plot cuts of an EPI image (by default 3 cuts: Frontal, Axial, and Lateral)
- Parameters
- epi_imga nifti-image like object or a filename, optional
The EPI (T2*) image.
- cut_coordsNone, a tuple of floats, or an integer, optional
The MNI coordinates of the point where the cut is performed If display_mode is ‘ortho’ or ‘tiled’, this should be a 3-tuple: (x, y, z) For display_mode == ‘x’, ‘y’, or ‘z’, then these are the coordinates of each cut in the corresponding direction. If None is given, the cuts is calculated automaticaly. If display_mode is ‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’, cut_coords can be an integer, in which case it specifies the number of cuts to perform. If display_mode is ‘mosaic’, and the number of cuts is the same for all directions, cut_coords can be specified as an integer. It can also be a length 3 tuple specifying the number of cuts for every direction if these are different.
- output_filestring, or None, optional
The name of an image file to export the plot to. Valid extensions are .png, .pdf, .svg. If output_file is not None, the plot is saved to a file, and the display is closed.
- display_mode{‘ortho’, ‘tiled’, ‘mosaic’, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’, ‘yx’, ‘xz’, ‘yz’}, optional
Choose the direction of the cuts: ‘x’ - sagittal, ‘y’ - coronal, ‘z’ - axial, ‘ortho’ - three cuts are performed in orthogonal directions, ‘tiled’ - three cuts are performed and arranged in a 2x2 grid. ‘mosaic’ - three cuts are performed along multiple rows and columns. Default=’ortho’.
- figureinteger or matplotlib figure, optional
Matplotlib figure used or its number. If None is given, a new figure is created.
- axesmatplotlib axes or 4 tuple of float: (xmin, ymin, width, height), optional
The axes, or the coordinates, in matplotlib figure space, of the axes used to display the plot. If None, the complete figure is used.
- titlestring, optional
The title displayed on the figure.
- annotateboolean, optional
If annotate is True, positions and left/right annotation are added to the plot. Default=True.
- draw_crossboolean, optional
If draw_cross is True, a cross is drawn on the plot to indicate the cut plosition. Default=True.
- black_bgboolean, optional
If True, the background of the image is set to be black. If you wish to save figures with a black background, you will need to pass “facecolor=’k’, edgecolor=’k’” to matplotlib.pyplot.savefig. Default=True.
- cmapmatplotlib colormap, optional
The colormap for specified image. Default=plt.cm.nipy_spectral.
- thresholda number, None, or ‘auto’, optional
If None is given, the image is not thresholded. If a number is given, it is used to threshold the image: values below the threshold (in absolute value) are plotted as transparent. If auto is given, the threshold is determined magically by analysis of the image.
- vminfloat, optional
Lower bound for plotting, passed to matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.
- vmaxfloat, optional
Upper bound for plotting, passed to matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.
Notes
Arrays should be passed in numpy convention: (x, y, z) ordered.