Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
9.4.2. Computing a connectome with sparse inverse covariance¶
This example constructs a functional connectome using the sparse inverse covariance.
We use the MSDL atlas of functional regions in movie watching, and the nilearn.maskers.NiftiMapsMasker to extract time series.
Note that the inverse covariance (or precision) contains values that can be linked to negated partial correlations, so we negated it for display.
As the MSDL atlas comes with (x, y, z) MNI coordinates for the different regions, we can visualize the matrix as a graph of interaction in a brain. To avoid having too dense a graph, we represent only the 20% edges with the highest values.
Note
If you are using Nilearn with a version older than 0.9.0, then you should either upgrade your version or import maskers from the input_data module instead of the maskers module.
That is, you should manually replace in the following example all occurrences of:
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
with:
from nilearn.input_data import NiftiMasker
9.4.2.1. Retrieve the atlas and the data¶
from nilearn import datasets
atlas = datasets.fetch_atlas_msdl()
# Loading atlas image stored in 'maps'
atlas_filename = atlas['maps']
# Loading atlas data stored in 'labels'
labels = atlas['labels']
# Loading the functional datasets
data = datasets.fetch_development_fmri(n_subjects=1)
# print basic information on the dataset
print('First subject functional nifti images (4D) are at: %s' %
data.func[0]) # 4D data
Out:
First subject functional nifti images (4D) are at: /home/nicolas/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz
9.4.2.2. Extract time series¶
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMapsMasker
masker = NiftiMapsMasker(maps_img=atlas_filename, standardize=True,
memory='nilearn_cache', verbose=5)
time_series = masker.fit_transform(data.func[0],
confounds=data.confounds)
Out:
[NiftiMapsMasker.fit_transform] loading regions from /home/nicolas/nilearn_data/msdl_atlas/MSDL_rois/msdl_rois.nii
Resampling maps
/home/nicolas/GitRepos/nilearn-fork/nilearn/_utils/cache_mixin.py:304: UserWarning:
memory_level is currently set to 0 but a Memory object has been provided. Setting memory_level to 1.
[Memory]0.0s, 0.0min : Loading resample_img...
________________________________________resample_img cache loaded - 0.0s, 0.0min
[Memory]0.1s, 0.0min : Loading _filter_and_extract...
__________________________________filter_and_extract cache loaded - 0.0s, 0.0min
9.4.2.3. Compute the sparse inverse covariance¶
try:
from sklearn.covariance import GraphicalLassoCV
except ImportError:
# for Scitkit-Learn < v0.20.0
from sklearn.covariance import GraphLassoCV as GraphicalLassoCV
estimator = GraphicalLassoCV()
estimator.fit(time_series)
Out:
GraphicalLassoCV()
9.4.2.4. Display the connectome matrix¶
from nilearn import plotting
# Display the covariance
# The covariance can be found at estimator.covariance_
plotting.plot_matrix(estimator.covariance_, labels=labels,
figure=(9, 7), vmax=1, vmin=-1,
title='Covariance')
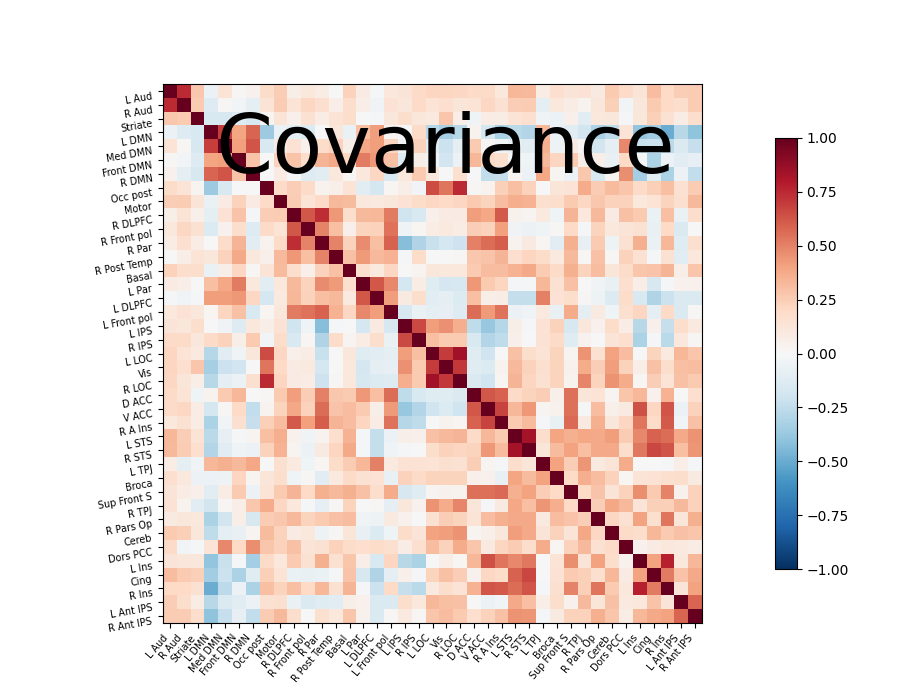
Out:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7fa503455790>
9.4.2.5. And now display the corresponding graph¶
coords = atlas.region_coords
plotting.plot_connectome(estimator.covariance_, coords,
title='Covariance')
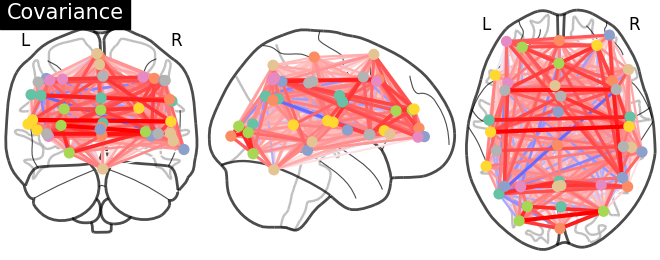
Out:
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fa4fbe877f0>
9.4.2.6. Display the sparse inverse covariance¶
we negate it to get partial correlations
plotting.plot_matrix(-estimator.precision_, labels=labels,
figure=(9, 7), vmax=1, vmin=-1,
title='Sparse inverse covariance')
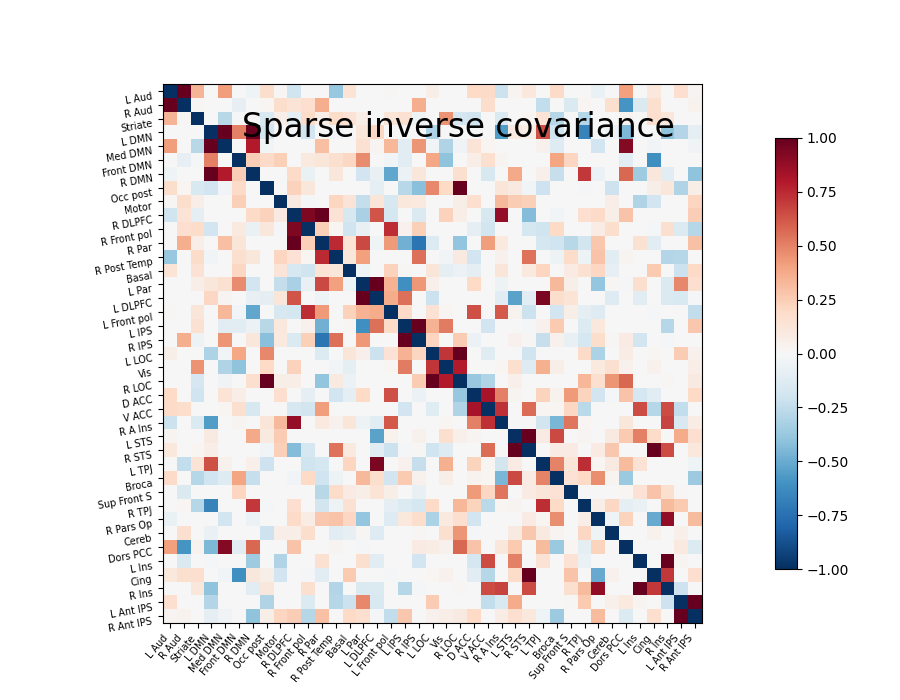
Out:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x7fa4ffaa86d0>
9.4.2.7. And now display the corresponding graph¶
plotting.plot_connectome(-estimator.precision_, coords,
title='Sparse inverse covariance')
plotting.show()
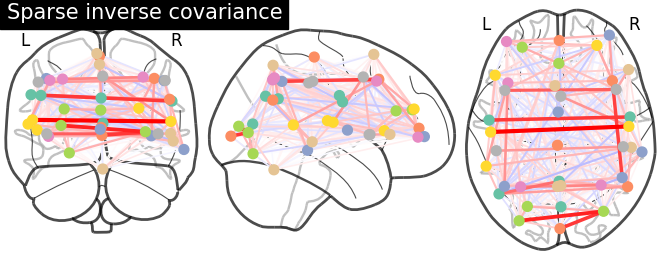
9.4.2.8. 3D visualization in a web browser¶
An alternative to nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome is to use nilearn.plotting.view_connectome that gives more interactive visualizations in a web browser. See 3D Plots of connectomes for more details.
view = plotting.view_connectome(-estimator.precision_, coords)
# In a Jupyter notebook, if ``view`` is the output of a cell, it will
# be displayed below the cell
view
# uncomment this to open the plot in a web browser:
# view.open_in_browser()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 14.608 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 431 MB
