Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
9.2.17. Loading and plotting of a cortical surface atlas¶
The Destrieux parcellation (Destrieux et al, 2010) in fsaverage5 space as distributed with Freesurfer is used as the chosen atlas.
The nilearn.plotting.plot_surf_roi function is used to plot the parcellation on the pial surface.
See Plotting brain images for more details.
9.2.17.1. References¶
Destrieux et al, (2010). Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. NeuroImage, 53, 1. URL http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.010.
9.2.17.2. Data fetcher¶
# Retrieve destrieux parcellation in fsaverage5 space from nilearn
from nilearn import datasets
destrieux_atlas = datasets.fetch_atlas_surf_destrieux()
# The parcellation is already loaded into memory
parcellation = destrieux_atlas['map_left']
# Retrieve fsaverage5 surface dataset for the plotting background. It contains
# the surface template as pial and inflated version and a sulcal depth maps
# which is used for shading
fsaverage = datasets.fetch_surf_fsaverage()
# The fsaverage dataset contains file names pointing to the file locations
print('Fsaverage5 pial surface of left hemisphere is at: %s' %
fsaverage['pial_left'])
print('Fsaverage5 inflated surface of left hemisphere is at: %s' %
fsaverage['infl_left'])
print('Fsaverage5 sulcal depth map of left hemisphere is at: %s' %
fsaverage['sulc_left'])
Out:
Fsaverage5 pial surface of left hemisphere is at: /home/nicolas/GitRepos/nilearn-fork/nilearn/datasets/data/fsaverage5/pial.left.gii.gz
Fsaverage5 inflated surface of left hemisphere is at: /home/nicolas/GitRepos/nilearn-fork/nilearn/datasets/data/fsaverage5/pial_inflated.left.gii.gz
Fsaverage5 sulcal depth map of left hemisphere is at: /home/nicolas/GitRepos/nilearn-fork/nilearn/datasets/data/fsaverage5/sulc.left.gii.gz
9.2.17.3. Visualization¶
# Display Destrieux parcellation on fsaverage5 pial surface using nilearn
from nilearn import plotting
plotting.plot_surf_roi(fsaverage['pial_left'], roi_map=parcellation,
hemi='left', view='lateral',
bg_map=fsaverage['sulc_left'], bg_on_data=True,
darkness=.5)
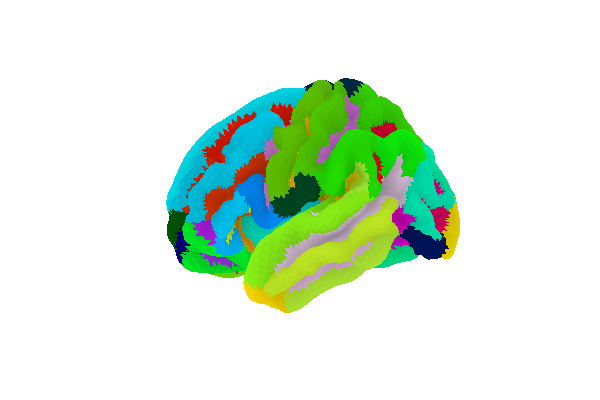
Out:
<Figure size 600x400 with 1 Axes>
Display Destrieux parcellation on inflated fsaverage5 surface
plotting.plot_surf_roi(fsaverage['infl_left'], roi_map=parcellation,
hemi='left', view='lateral',
bg_map=fsaverage['sulc_left'], bg_on_data=True,
darkness=.5)
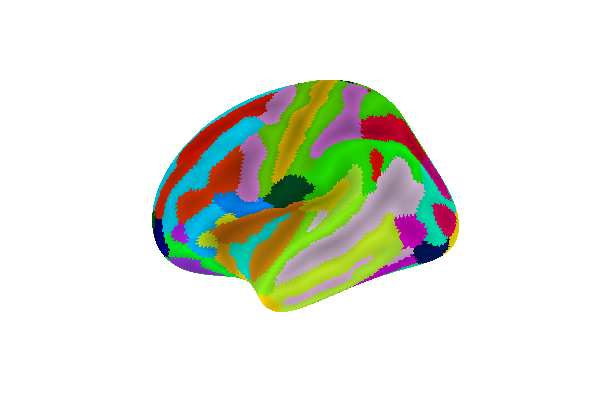
Out:
<Figure size 600x400 with 1 Axes>
Display Destrieux parcellation with different views: posterior
plotting.plot_surf_roi(fsaverage['infl_left'], roi_map=parcellation,
hemi='left', view='posterior',
bg_map=fsaverage['sulc_left'], bg_on_data=True,
darkness=.5)
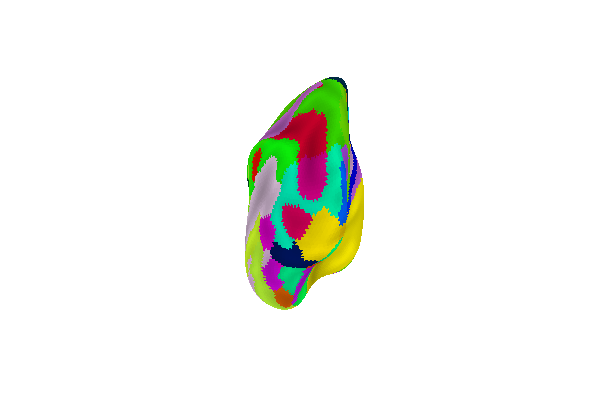
Out:
<Figure size 600x400 with 1 Axes>
Display Destrieux parcellation with different views: ventral
plotting.plot_surf_roi(fsaverage['infl_left'], roi_map=parcellation,
hemi='left', view='ventral',
bg_map=fsaverage['sulc_left'], bg_on_data=True,
darkness=.5)
plotting.show()
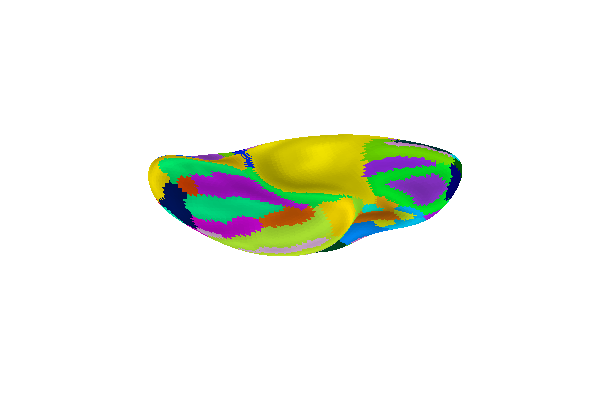
Display connectome from surface parcellation
The following code extracts 3D coordinates of surface parcels (a.k.a. labels in the Freesurfer naming convention). To do so we load the pial surface of fsaverage subject, get the vertices contained in each parcel and compute the mean location to obtain the coordinates.
import numpy as np
from nilearn import surface
atlas = destrieux_atlas
coordinates = []
labels = destrieux_atlas['labels']
for hemi in ['left', 'right']:
vert = destrieux_atlas['map_%s' % hemi]
rr, _ = surface.load_surf_mesh(fsaverage['pial_%s' % hemi])
for k, label in enumerate(labels):
if "Unknown" not in str(label): # Omit the Unknown label.
# Compute mean location of vertices in label of index k
coordinates.append(np.mean(rr[vert == k], axis=0))
coordinates = np.array(coordinates) # 3D coordinates of parcels
# We now make a synthetic connectivity matrix that connects labels
# between left and right hemispheres.
n_parcels = len(coordinates)
corr = np.zeros((n_parcels, n_parcels))
n_parcels_hemi = n_parcels // 2
corr[np.arange(n_parcels_hemi), np.arange(n_parcels_hemi) + n_parcels_hemi] = 1
corr = corr + corr.T
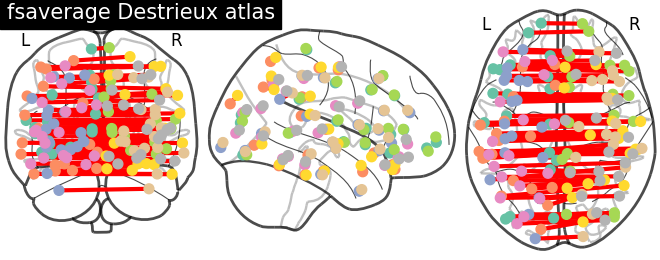
plotting.plot_connectome(corr, coordinates,
edge_threshold="90%",
title='fsaverage Destrieux atlas')
plotting.show()
9.2.17.4. 3D visualization in a web browser¶
An alternative to nilearn.plotting.plot_surf_roi is to use nilearn.plotting.view_surf for more interactive visualizations in a web browser. See 3D Plots of statistical maps or atlases on the cortical surface for more details.
view = plotting.view_surf(fsaverage.infl_left, parcellation,
cmap='gist_ncar', symmetric_cmap=False)
# In a Jupyter notebook, if ``view`` is the output of a cell, it will
# be displayed below the cell
view
# uncomment this to open the plot in a web browser:
# view.open_in_browser()
you can also use nilearn.plotting.view_connectome to open an interactive view of the connectome.
view = plotting.view_connectome(corr, coordinates, edge_threshold='90%')
# uncomment this to open the plot in a web browser:
# view.open_in_browser()
view
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.786 seconds)
