Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
8.6.1. nilearn.input_data.NiftiMasker¶
- class
nilearn.input_data.NiftiMasker(mask_img=None, sessions=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, detrend=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='background', mask_args=None, sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory_level=1, memory=Memory(location=None), verbose=0, reports=True)¶ Applying a mask to extract time-series from Niimg-like objects.
NiftiMasker is useful when preprocessing (detrending, standardization, resampling, etc.) of in-mask voxels is necessary. Use case: working with time series of resting-state or task maps.
Parameters: mask_img : Niimg-like object, optional
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Mask for the data. If not given, a mask is computed in the fit step. Optional parameters (mask_args and mask_strategy) can be set to fine tune the mask extraction. If the mask and the images have different resolutions, the images are resampled to the mask resolution. If target_shape and/or target_affine are provided, the mask is resampled first. After this, the images are resampled to the resampled mask.
sessions : numpy array, optional
Add a session level to the preprocessing. Each session will be detrended independently. Must be a 1D array of n_samples elements.
smoothing_fwhm : float, optional
If smoothing_fwhm is not None, it gives the full-width half maximum in millimeters of the spatial smoothing to apply to the signal.
standardize : {‘zscore’, ‘psc’, True, False}, default is ‘zscore’
Strategy to standardize the signal. ‘zscore’: the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. ‘psc’: Timeseries are shifted to zero mean value and scaled to percent signal change (as compared to original mean signal). True : the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. False : Do not standardize the data.
detrend : boolean, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean.low_pass : None or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean.high_pass : None or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean.t_r : float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean.target_affine : 3x3 or 4x4 matrix, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
target_shape : 3-tuple of integers, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
mask_strategy : {‘background’, ‘epi’ or ‘template’}, optional
The strategy used to compute the mask: use ‘background’ if your images present a clear homogeneous background, ‘epi’ if they are raw EPI images, or you could use ‘template’ which will extract the gray matter part of your data by resampling the MNI152 brain mask for your data’s field of view. Depending on this value, the mask will be computed from masking.compute_background_mask, masking.compute_epi_mask or masking.compute_brain_mask. Default is ‘background’.
mask_args : dict, optional
If mask is None, these are additional parameters passed to masking.compute_background_mask or masking.compute_epi_mask to fine-tune mask computation. Please see the related documentation for details.
sample_mask : Any type compatible with numpy-array indexing
Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension. This complements 3D masking by the mask_img argument. This masking step is applied before data preprocessing at the beginning of NiftiMasker.transform. This is useful to perform data subselection as part of a scikit-learn pipeline.
dtype : {dtype, “auto”}
Data type toward which the data should be converted. If “auto”, the data will be converted to int32 if dtype is discrete and float32 if it is continuous.
memory : instance of joblib.Memory or string
Used to cache the masking process. By default, no caching is done. If a string is given, it is the path to the caching directory.
memory_level : integer, optional
Rough estimator of the amount of memory used by caching. Higher value means more memory for caching.
verbose : integer, optional
Indicate the level of verbosity. By default, nothing is printed
See also
nilearn.masking.compute_background_mask,nilearn.masking.compute_epi_mask,nilearn.image.resample_img,nilearn.masking.apply_mask,nilearn.signal.cleanAttributes
`mask_img_` (nibabel.Nifti1Image) The mask of the data, or the computed one. `affine_` (4x4 numpy array) Affine of the transformed image. __init__(mask_img=None, sessions=None, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, detrend=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='background', mask_args=None, sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory_level=1, memory=Memory(location=None), verbose=0, reports=True)¶Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
fit(imgs=None, y=None)¶Compute the mask corresponding to the data
Parameters: imgs: list of Niimg-like objects
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Data on which the mask must be calculated. If this is a list, the affine is considered the same for all.
fit_transform(X, y=None, confounds=None, **fit_params)¶Fit to data, then transform it
Parameters: X : Niimg-like object
y : numpy array of shape [n_samples]
Target values.
confounds: list of confounds, optional
List of confounds (2D arrays or filenames pointing to CSV files). Must be of same length than imgs_list.
Returns: X_new : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new]
Transformed array.
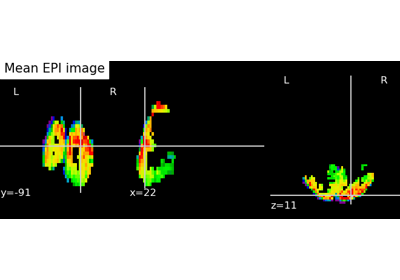
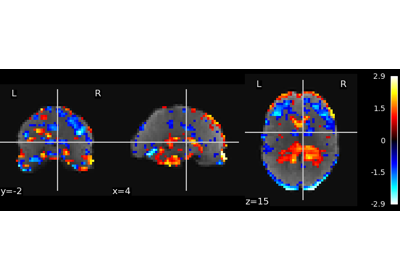
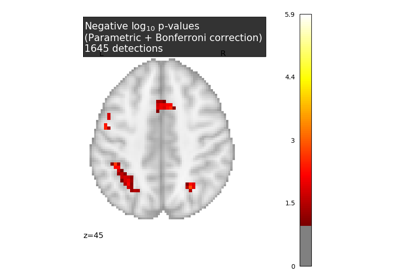
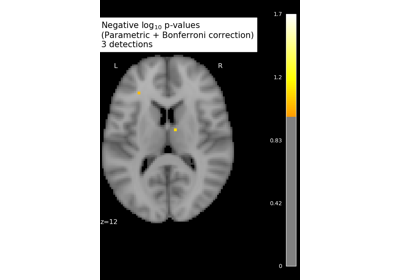
generate_report()¶
get_params(deep=True)¶Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep : bool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
inverse_transform(X)¶Transform the 2D data matrix back to an image in brain space.
set_params(**params)¶Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Parameters: **params : dict
Estimator parameters.
Returns: self : object
Estimator instance.
transform(imgs, confounds=None)¶Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
Parameters: imgs: 3D/4D Niimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Images to process. It must boil down to a 4D image with scans number as last dimension.
confounds: CSV file or array-like, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)
Returns: region_signals: 2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each element. shape: (number of scans, number of elements)
transform_single_imgs(imgs, confounds=None, copy=True)¶Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
Parameters: imgs: 3D/4D Niimg-like object
See http://nilearn.github.io/manipulating_images/input_output.html Images to process. It must boil down to a 4D image with scans number as last dimension.
confounds: CSV file or array-like or pandas DataFrame, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details:
nilearn.signal.clean. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)Returns: region_signals: 2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each voxel inside the mask. shape: (number of scans, number of voxels)