6.3. Extracting functional brain networks: ICA and related#
6.3.1. Multi-subject ICA: CanICA#
6.3.1.1. Objective#
ICA is a useful approach for finding independent sources from fMRI images. ICA and similar techniques can be therefore used to define regions or networks that share similar BOLD signal across time. The CanICA incorporates information both within-subjects and across subjects to arrive at consensus components.
6.3.1.2. Fitting CanICA model with nilearn#
CanICA is a ready-to-use object that can be applied to multi-subject Nifti data, for instance presented as filenames, and will perform a multi-subject ICA decomposition following the CanICA model. As with every object in nilearn, we give its parameters at construction, and then fit it on the data. For examples of this process, see here: Deriving spatial maps from group fMRI data using ICA and Dictionary Learning
Once an ICA object has been fit to an fMRI dataset, the individual components can be accessed as a 4D Nifti object using the components_img_ attribute.
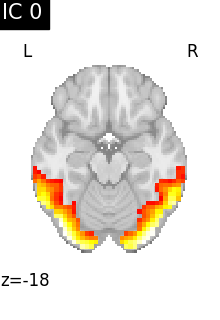
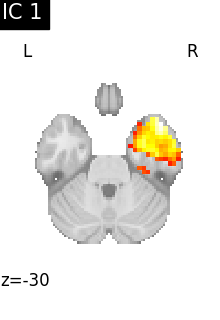
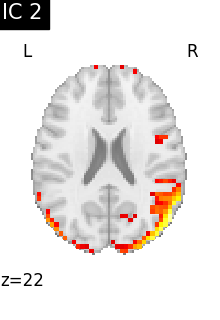
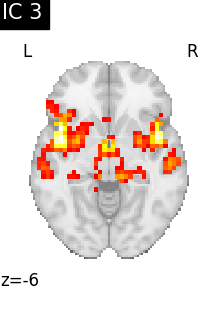
6.3.1.3. Visualizing results#
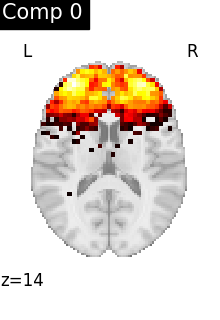
We can visualize each component outlined over the brain:
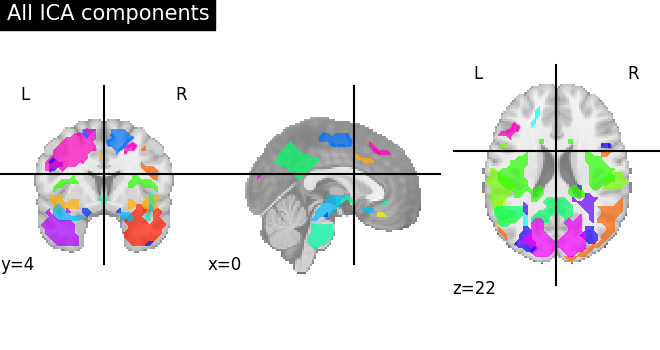
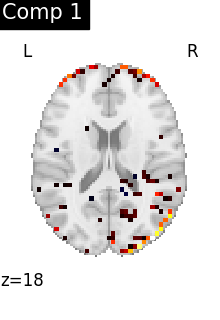
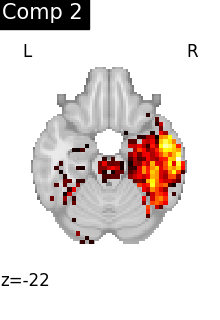
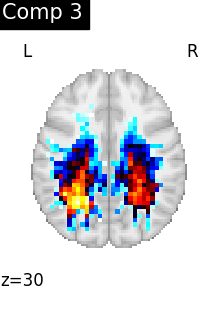
We can also plot the map for different components separately:
See also
The full code can be found as an example: Deriving spatial maps from group fMRI data using ICA and Dictionary Learning
Note
Note that as the ICA components are not ordered, the two components displayed on your computer might not match those of the documentation. For a fair representation, you should display all components and investigate which one resemble those displayed above.
6.3.1.4. Interpreting such components#
ICA, and related algorithms, extract patterns that coactivate in the signal. As a result, it finds functional networks, but also patterns of non neural activity, ie confounding signals. Both are visible in the plots of the components.
6.3.2. An alternative to ICA: Dictionary learning#
Recent work has shown that Dictionary learning based techniques outperform ICA in term of stability and constitutes a better first step in a statistical analysis pipeline. Dictionary learning in neuro-imaging seeks to extract a few representative temporal elements along with their sparse spatial loadings, which constitute good extracted maps.
DictLearning is a ready-to-use class with the same interface as CanICA. Sparsity of output map is controlled by a parameter alpha: using a larger alpha yields sparser maps.
We can fit both estimators to compare them. 4D plotting (using nilearn.plotting.plot_prob_atlas) offers an efficient way to compare both resulting outputs.
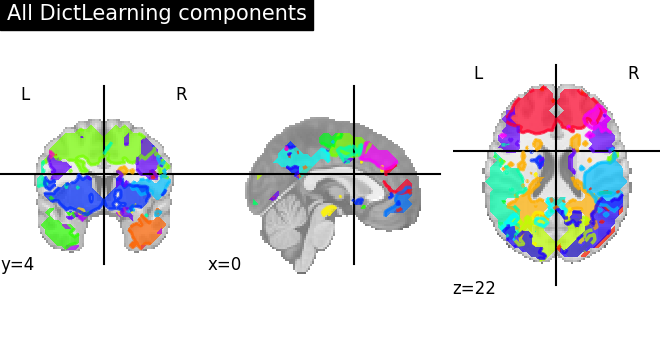

Maps obtained with Dictionary learning are often easier to exploit as they are more contrasted than ICA maps, with blobs usually better defined. Typically, smoothing can be lower than when doing ICA.
While Dictionary learning computation time is comparable to CanICA, obtained atlases have been shown to outperform ICA in a variety of classification tasks.
See also
The full code can be found as an example: Deriving spatial maps from group fMRI data using ICA and Dictionary Learning
See also
Learn how to extract fMRI data from regions created with Dictionary learning with this example: Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes