Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.plotting.plot_glass_brain#
- nilearn.plotting.plot_glass_brain(stat_map_img, output_file=None, display_mode='ortho', colorbar=False, cbar_tick_format='%.2g', figure=None, axes=None, title=None, threshold='auto', annotate=True, black_bg=False, cmap=None, alpha=0.7, vmin=None, vmax=None, plot_abs=True, symmetric_cbar='auto', resampling_interpolation='continuous', radiological=False, **kwargs)[source]#
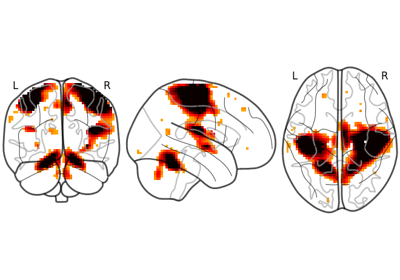
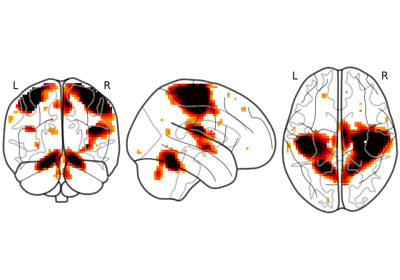
Plot 2d projections of an ROI/mask image (by default 3 projections: Frontal, Axial, and Lateral). The brain glass schematics are added on top of the image.
The plotted image should be in MNI space for this function to work properly.
Only glass brain can be plotted by switching stat_map_img to None.
- Parameters:
- stat_map_imgNiimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. The statistical map image. It needs to be in MNI space in order to align with the brain schematics.
- output_file
str, or None, optional The name of an image file to export the plot to. Valid extensions are .png, .pdf, .svg. If output_file is not None, the plot is saved to a file, and the display is closed.
- display_modestring, optional
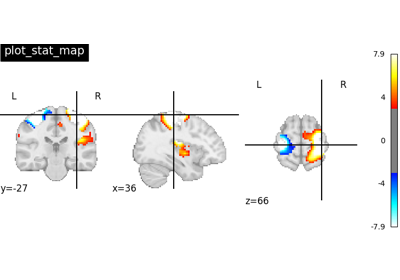
Choose the direction of the cuts: ‘x’ - sagittal, ‘y’ - coronal, ‘z’ - axial, ‘l’ - sagittal left hemisphere only, ‘r’ - sagittal right hemisphere only, ‘ortho’ - three cuts are performed in orthogonal directions. Possible values are: ‘ortho’, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’, ‘xz’, ‘yx’, ‘yz’, ‘l’, ‘r’, ‘lr’, ‘lzr’, ‘lyr’, ‘lzry’, ‘lyrz’. Default=’ortho’.
- colorbar
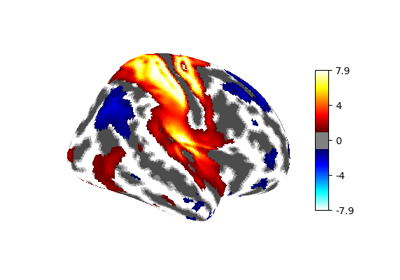
bool, optional If True, display a colorbar on the right of the plots. Default=False.
- cbar_tick_format: str, optional
Controls how to format the tick labels of the colorbar. Ex: use “%i” to display as integers. Default is ‘%.2g’ for scientific notation.
- figure
int, ormatplotlib.figure.Figure, or None, optional Matplotlib figure used or its number. If None is given, a new figure is created.
- axes
matplotlib.axes.Axes, or 4 tupleoffloat: (xmin, ymin, width, height), default=None The axes, or the coordinates, in matplotlib figure space, of the axes used to display the plot. If None, the complete figure is used.
- title
str, or None, default=None The title displayed on the figure.
- thresholda number, None, or ‘auto’, optional
If None is given, the image is not thresholded. If a number is given, it is used to threshold the image: values below the threshold (in absolute value) are plotted as transparent. If “auto” is given, the threshold is determined magically by analysis of the image. Default=’auto’.
- annotate
bool, default=True If annotate is True, positions and left/right annotation are added to the plot.
- black_bg
bool, or “auto”, optional If True, the background of the image is set to be black. If you wish to save figures with a black background, you will need to pass facecolor=”k”, edgecolor=”k” to
matplotlib.pyplot.savefig. Default=False.- cmap
matplotlib.colors.Colormap, orstr, optional The colormap to use. Either a string which is a name of a matplotlib colormap, or a matplotlib colormap object. Default=None.
- alphafloat between 0 and 1, optional
Alpha transparency for the brain schematics. Default=0.7.
- vmin
float, optional Lower bound of the colormap. If None, the min of the image is used. Passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.- vmax
float, optional Upper bound of the colormap. If None, the max of the image is used. Passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.- plot_absboolean, optional
If set to True (default) maximum intensity projection of the absolute value will be used (rendering positive and negative values in the same manner). If set to false the sign of the maximum intensity will be represented with different colors. See Glass brain plotting in nilearn (all options) # noqa for examples. Default=True.
- symmetric_cbar
bool, or “auto”, optional Specifies whether the colorbar should range from -vmax to vmax or from vmin to vmax. Setting to “auto” will select the latter if the range of the whole image is either positive or negative.
Note
The colormap will always range from -vmax to vmax.
Default=’auto’.
- resampling_interpolation
str, optional Interpolation to use when resampling the image to the destination space. Can be:
“continuous”: use 3rd-order spline interpolation
“nearest”: use nearest-neighbor mapping.
Note
“nearest” is faster but can be noisier in some cases.
Default=’continuous’.
- radiological
bool, default=False Invert x axis and R L labels to plot sections as a radiological view. If False (default), the left hemisphere is on the left of a coronal image. If True, left hemisphere is on the right.
Notes
Arrays should be passed in numpy convention: (x, y, z) ordered.
Examples using nilearn.plotting.plot_glass_brain#
First level analysis of a complete BIDS dataset from openneuro
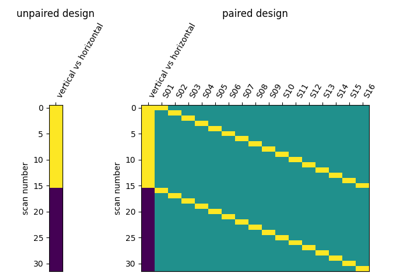
Second-level fMRI model: two-sample test, unpaired and paired
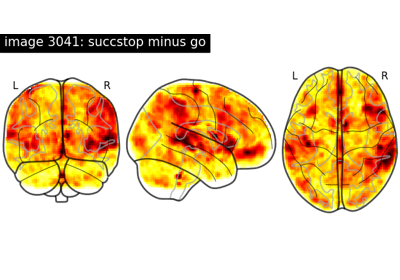
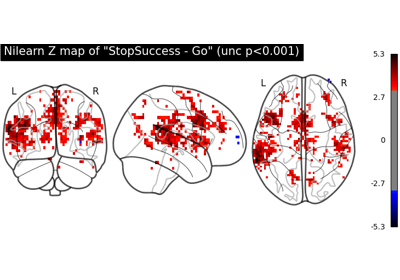
NeuroVault meta-analysis of stop-go paradigm studies
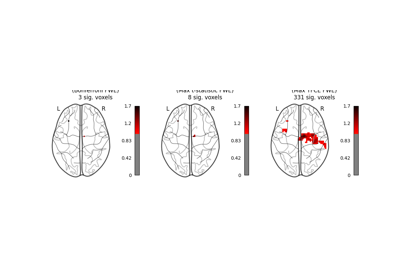
Massively univariate analysis of a motor task from the Localizer dataset