Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.decomposition.DictLearning#
- class nilearn.decomposition.DictLearning(n_components=20, n_epochs=1, alpha=10, reduction_ratio='auto', dict_init=None, random_state=None, batch_size=20, method='cd', mask=None, smoothing_fwhm=4, standardize=True, detrend=True, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='epi', mask_args=None, n_jobs=1, verbose=0, memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0)[source]#
Perform a map learning algorithm based on spatial component sparsity, over a CanICA initialization.
This yields more stable maps than CanICA.
See [1].
New in version 0.2.
- Parameters:
- maskNiimg-like object or MultiNiftiMasker instance, optional
Mask to be used on data. If an instance of masker is passed, then its mask will be used. If no mask is given, it will be computed automatically by a MultiNiftiMasker with default parameters.
- n_componentsint, optional
Number of components to extract. Default=20.
- batch_sizeint, optional
The number of samples to take in each batch. Default=20.
- n_epochsfloat, optional
Number of epochs the algorithm should run on the data. Default=1.
- alphafloat, optional
Sparsity controlling parameter. Default=10.
- dict_initNiimg-like object, optional
Initial estimation of dictionary maps. Would be computed from CanICA if not provided.
- reduction_ratio‘auto’ or float between 0. and 1., optional
Between 0. or 1. : controls data reduction in the temporal domain. 1. means no reduction, < 1. calls for an SVD based reduction.
if set to ‘auto’, estimator will set the number of components per reduced session to be n_components. Default=’auto’.
- method{‘cd’, ‘lars’}, optional
Coding method used by sklearn backend. Below are the possible values. lars: uses the least angle regression method to solve the lasso problem (linear_model.lars_path) cd: uses the coordinate descent method to compute the Lasso solution (linear_model.Lasso). Lars will be faster if the estimated components are sparse. Default=’cd’.
- random_stateint or RandomState, optional
Pseudo number generator state used for random sampling.
- smoothing_fwhm
float, optional. If smoothing_fwhm is not None, it gives the full-width at half maximum in millimeters of the spatial smoothing to apply to the signal. Default=4mm.
- standardizeboolean, optional
If standardize is True, the time-series are centered and normed: their variance is put to 1 in the time dimension. Default=True.
- detrendboolean, optional
If detrend is True, the time-series will be detrended before components extraction. Default=True.
- target_affine3x3 or 4x4 matrix, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
- target_shape3-tuple of integers, optional
This parameter is passed to image.resample_img. Please see the related documentation for details.
- low_passNone or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details.
- high_passNone or float, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details.
- t_rfloat, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details.
- mask_strategy{“background”, “epi”, “whole-brain-template”,”gm-template”, “wm-template”}, optional
The strategy used to compute the mask:
“background”: Use this option if your images present a clear homogeneous background.
“epi”: Use this option if your images are raw EPI images
“whole-brain-template”: This will extract the whole-brain part of your data by resampling the MNI152 brain mask for your data’s field of view.
Note
This option is equivalent to the previous ‘template’ option which is now deprecated.
“gm-template”: This will extract the gray matter part of your data by resampling the corresponding MNI152 template for your data’s field of view.
New in version 0.8.1.
“wm-template”: This will extract the white matter part of your data by resampling the corresponding MNI152 template for your data’s field of view.
New in version 0.8.1.
Note
Depending on this value, the mask will be computed from
nilearn.masking.compute_background_mask,nilearn.masking.compute_epi_mask, ornilearn.masking.compute_brain_mask.Default=’epi’.
- mask_argsdict, optional
If mask is None, these are additional parameters passed to masking.compute_background_mask or masking.compute_epi_mask to fine-tune mask computation. Please see the related documentation for details.
- memoryinstance of joblib.Memory or string, optional
Used to cache the masking process. By default, no caching is done. If a string is given, it is the path to the caching directory.
- memory_levelinteger, optional
Rough estimator of the amount of memory used by caching. Higher value means more memory for caching. Default=0.
- n_jobsinteger, optional
The number of CPUs to use to do the computation. -1 means ‘all CPUs’, -2 ‘all CPUs but one’, and so on. Default=1.
- verboseinteger, optional
Indicate the level of verbosity. By default, nothing is printed. Default=0.
References
- Attributes:
- `components_`2D numpy array (n_components x n-voxels)
Masked dictionary components extracted from the input images.
Note
Use attribute components_img_ rather than manually unmasking components_ with masker_ attribute.
- `components_img_`4D Nifti image
4D image giving the extracted components. Each 3D image is a component.
New in version 0.4.1.
- `masker_`instance of MultiNiftiMasker
Masker used to filter and mask data as first step. If an instance of MultiNiftiMasker is given in mask parameter, this is a copy of it. Otherwise, a masker is created using the value of mask and other NiftiMasker related parameters as initialization.
- `mask_img_`Niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. The mask of the data. If no mask was given at masker creation, contains the automatically computed mask.
- __init__(n_components=20, n_epochs=1, alpha=10, reduction_ratio='auto', dict_init=None, random_state=None, batch_size=20, method='cd', mask=None, smoothing_fwhm=4, standardize=True, detrend=True, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, target_affine=None, target_shape=None, mask_strategy='epi', mask_args=None, n_jobs=1, verbose=0, memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0)[source]#
- fit(imgs, y=None, confounds=None)[source]#
Compute the mask and the components across subjects.
- Parameters:
- imgslist of Niimg-like objects
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Data on which the mask is calculated. If this is a list, the affine is considered the same for all.
- confoundslist of CSV file paths, numpy.ndarrays
or pandas DataFrames, optional. This parameter is passed to nilearn.signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. Should match with the list of imgs given.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself. Contains attributes listed at the object level.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)#
Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to X and y with optional parameters fit_params and returns a transformed version of X.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns:
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
- get_metadata_routing()#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- inverse_transform(loadings)[source]#
Use provided loadings to compute corresponding linear component combination in whole-brain voxel space.
- Parameters:
- loadingslist of numpy array (n_samples x n_components)
Component signals to transform back into voxel signals
- Returns:
- reconstructed_imgslist of nibabel.Nifti1Image
For each loading, reconstructed Nifti1Image
- score(imgs, confounds=None, per_component=False)[source]#
Score function based on explained variance on imgs.
Should only be used by DecompositionEstimator derived classes
- Parameters:
- imgsiterable of Niimg-like objects
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Data to be scored
- confoundsCSV file path or numpy.ndarray
or pandas DataFrame, optional This parameter is passed to nilearn.signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- per_componentbool, optional
Specify whether the explained variance ratio is desired for each map or for the global set of components. Default=False.
- Returns:
- scorefloat
Holds the score for each subjects. Score is two dimensional if per_component is True. First dimension is squeezed if the number of subjects is one
- set_fit_request(*, confounds='$UNCHANGED$', imgs='$UNCHANGED$')#
Request metadata passed to the
fitmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed tofitif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it tofit.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- confoundsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
confoundsparameter infit.- imgsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
imgsparameter infit.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_inverse_transform_request(*, loadings='$UNCHANGED$')#
Request metadata passed to the
inverse_transformmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toinverse_transformif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toinverse_transform.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- loadingsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
loadingsparameter ininverse_transform.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_output(*, transform=None)#
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters:
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of transform and fit_transform.
“default”: Default output format of a transformer
“pandas”: DataFrame output
None: Transform configuration is unchanged
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_score_request(*, confounds='$UNCHANGED$', imgs='$UNCHANGED$', per_component='$UNCHANGED$')#
Request metadata passed to the
scoremethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed toscoreif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it toscore.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- confoundsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
confoundsparameter inscore.- imgsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
imgsparameter inscore.- per_componentstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
per_componentparameter inscore.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- set_transform_request(*, confounds='$UNCHANGED$', imgs='$UNCHANGED$')#
Request metadata passed to the
transformmethod.Note that this method is only relevant if
enable_metadata_routing=True(seesklearn.set_config). Please see User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.The options for each parameter are:
True: metadata is requested, and passed totransformif provided. The request is ignored if metadata is not provided.False: metadata is not requested and the meta-estimator will not pass it totransform.None: metadata is not requested, and the meta-estimator will raise an error if the user provides it.str: metadata should be passed to the meta-estimator with this given alias instead of the original name.
The default (
sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED) retains the existing request. This allows you to change the request for some parameters and not others.New in version 1.3.
Note
This method is only relevant if this estimator is used as a sub-estimator of a meta-estimator, e.g. used inside a
Pipeline. Otherwise it has no effect.- Parameters:
- confoundsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
confoundsparameter intransform.- imgsstr, True, False, or None, default=sklearn.utils.metadata_routing.UNCHANGED
Metadata routing for
imgsparameter intransform.
- Returns:
- selfobject
The updated object.
- transform(imgs, confounds=None)[source]#
Project the data into a reduced representation.
- Parameters:
- imgsiterable of Niimg-like objects
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Data to be projected
- confoundsCSV file path or numpy.ndarray
or pandas DataFrame, optional This parameter is passed to nilearn.signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- Returns:
- loadingslist of 2D ndarray,
For each subject, each sample, loadings for each decomposition components shape: number of subjects * (number of scans, number of regions)
Examples using nilearn.decomposition.DictLearning#
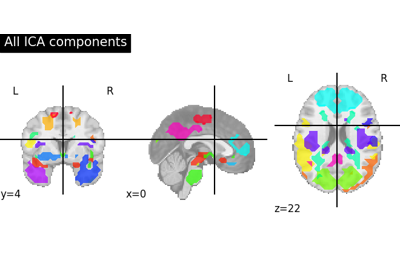
Deriving spatial maps from group fMRI data using ICA and Dictionary Learning
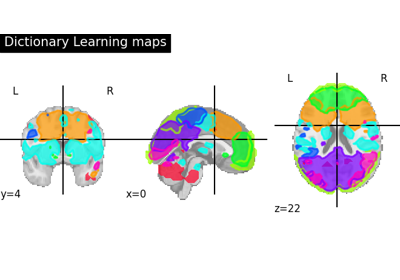
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes