Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Extract signals on spheres and plot a connectome#
This example shows how to extract signals from spherical regions. We show how to build spheres around user-defined coordinates, as well as centered on coordinates from the Power-264 atlas [1], and the Dosenbach-160 atlas [2].
Note
If you are using Nilearn with a version older than 0.9.0, then you should either upgrade your version or import maskers from the input_data module instead of the maskers module.
That is, you should manually replace in the following example all occurrences of:
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
with:
from nilearn.input_data import NiftiMasker
References
[1] Power, Jonathan D., et al. “Functional network organization of the human brain.” Neuron 72.4 (2011): 665-678.
[2] Dosenbach N.U., Nardos B., et al. “Prediction of individual brain maturity using fMRI.”, 2010, Science 329, 1358-1361.
We estimate connectomes using two different methods: sparse inverse covariance and partial_correlation, to recover the functional brain networks structure.
We’ll start by extracting signals from Default Mode Network regions and computing a connectome from them.
Retrieve the brain development fmri dataset#
We are going to use a subject from the development functional connectivity dataset.
from nilearn import datasets
dataset = datasets.fetch_development_fmri(n_subjects=10)
# print basic information on the dataset
print(f"First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: {dataset.func[0]}")
First subject functional nifti image (4D) is at: /home/remi/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz
Coordinates of Default Mode Network#
dmn_coords = [(0, -52, 18), (-46, -68, 32), (46, -68, 32), (1, 50, -5)]
labels = [
"Posterior Cingulate Cortex",
"Left Temporoparietal junction",
"Right Temporoparietal junction",
"Medial prefrontal cortex",
]
Extracts signal from sphere around DMN seeds#
We can compute the mean signal within spheres of a fixed radius around a sequence of (x, y, z) coordinates with the object nilearn.maskers.NiftiSpheresMasker. The resulting signal is then prepared by the masker object: Detrended, band-pass filtered and standardized to 1 variance.
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiSpheresMasker
masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
dmn_coords,
radius=8,
detrend=True,
standardize="zscore_sample",
standardize_confounds="zscore_sample",
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=2,
memory="nilearn_cache",
memory_level=1,
verbose=2,
clean__butterworth__padtype="even", # kwarg to modify Butterworth filter
)
# Additionally, we pass confound information to ensure our extracted
# signal is cleaned from confounds.
func_filename = dataset.func[0]
confounds_filename = dataset.confounds[0]
time_series = masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=[confounds_filename]
)
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling nilearn.maskers.base_masker._filter_and_extract...
_filter_and_extract('/home/remi/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz',
<nilearn.maskers.nifti_spheres_masker._ExtractionFunctor object at 0x7fd1b7a83c90>,
{ 'allow_overlap': False,
'clean_kwargs': {'butterworth__padtype': 'even'},
'detrend': True,
'dtype': None,
'high_pass': 0.01,
'high_variance_confounds': False,
'low_pass': 0.1,
'mask_img': None,
'radius': 8,
'seeds': [(0, -52, 18), (-46, -68, 32), (46, -68, 32), (1, 50, -5)],
'smoothing_fwhm': None,
'standardize': 'zscore_sample',
'standardize_confounds': 'zscore_sample',
't_r': 2}, confounds=[ '/home/remi/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_desc-reducedConfounds_regressors.tsv'], sample_mask=None, dtype=None, memory=Memory(location=nilearn_cache/joblib), memory_level=1, verbose=2)
[NiftiSpheresMasker.transform_single_imgs] Loading data from /home/remi/nilearn_data/development_fmri/development_fmri/sub-pixar123_task-pixar_space-MNI152NLin2009cAsym_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz
[NiftiSpheresMasker.transform_single_imgs] Extracting region signals
[NiftiSpheresMasker.transform_single_imgs] Cleaning extracted signals
_______________________________________________filter_and_extract - 1.9s, 0.0min
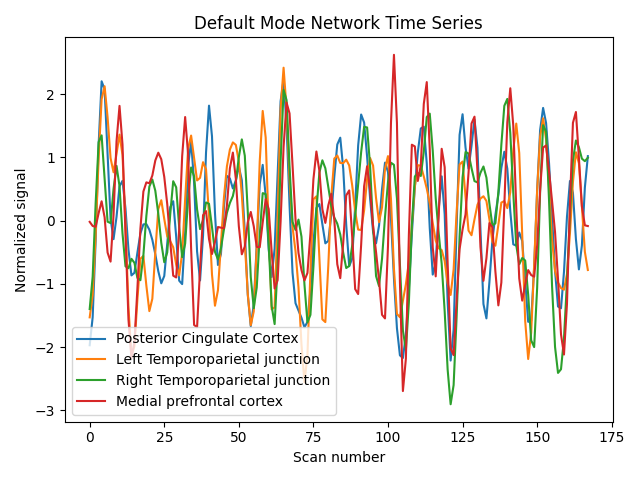
Display time series#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
for time_serie, label in zip(time_series.T, labels):
plt.plot(time_serie, label=label)
plt.title("Default Mode Network Time Series")
plt.xlabel("Scan number")
plt.ylabel("Normalized signal")
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
Compute partial correlation matrix#
Using object nilearn.connectome.ConnectivityMeasure: Its default covariance estimator is Ledoit-Wolf, allowing to obtain accurate partial correlations.
from nilearn.connectome import ConnectivityMeasure
connectivity_measure = ConnectivityMeasure(
kind="partial correlation",
standardize="zscore_sample",
)
partial_correlation_matrix = connectivity_measure.fit_transform([time_series])[
0
]
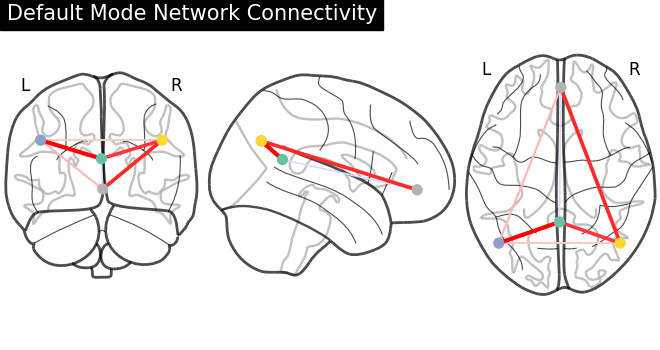
Display connectome#
We display the graph of connections with :func: nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome.
from nilearn import plotting
plotting.plot_connectome(
partial_correlation_matrix,
dmn_coords,
title="Default Mode Network Connectivity",
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fd1b5445f50>
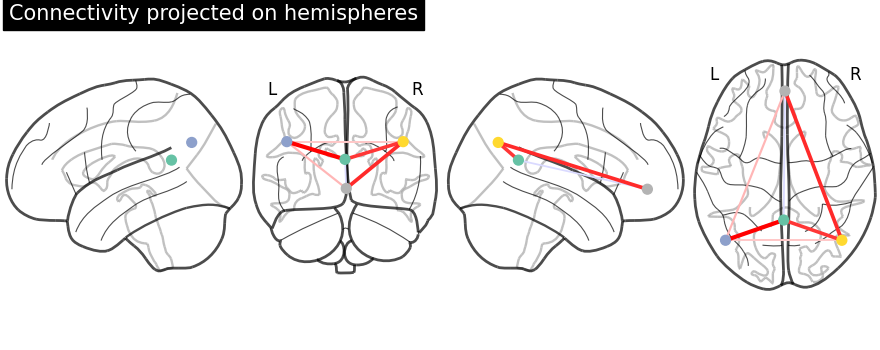
Display connectome with hemispheric projections. Notice (0, -52, 18) is included in both hemispheres since x == 0.
plotting.plot_connectome(
partial_correlation_matrix,
dmn_coords,
title="Connectivity projected on hemispheres",
display_mode="lyrz",
)
plotting.show()
3D visualization in a web browser#
An alternative to nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome is to use nilearn.plotting.view_connectome, which gives more interactive visualizations in a web browser. See 3D Plots of connectomes for more details.
view = plotting.view_connectome(partial_correlation_matrix, dmn_coords)
# In a Jupyter notebook, if ``view`` is the output of a cell, it will
# be displayed below the cell
view
# uncomment this to open the plot in a web browser:
# view.open_in_browser()
Extract signals on spheres from an atlas#
Next, instead of supplying our own coordinates, we will use coordinates generated at the center of mass of regions from two different atlases. This time, we’ll use a different correlation measure.
First we fetch the coordinates of the Power atlas
power = datasets.fetch_coords_power_2011(legacy_format=False)
print(f"Power atlas comes with {power.keys()}.")
Power atlas comes with dict_keys(['rois', 'description']).
Note
You can retrieve the coordinates for any atlas, including atlases not included in nilearn, using nilearn.plotting.find_parcellation_cut_coords.
Compute within spheres averaged time-series#
We collect the regions coordinates in a numpy array
import numpy as np
coords = np.vstack((power.rois["x"], power.rois["y"], power.rois["z"])).T
print(f"Stacked power coordinates in array of shape {coords.shape}.")
Stacked power coordinates in array of shape (264, 3).
and define spheres masker, with small enough radius to avoid regions overlap.
spheres_masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
seeds=coords,
smoothing_fwhm=6,
radius=5.0,
detrend=True,
standardize="zscore_sample",
standardize_confounds="zscore_sample",
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=2,
)
timeseries = spheres_masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=confounds_filename
)
Estimate correlations#
We start by estimating the signal covariance matrix. Here the number of ROIs exceeds the number of samples,
print(f"time series has {timeseries.shape[0]} samples")
time series has 168 samples
in which situation the graphical lasso sparse inverse covariance estimator captures well the covariance structure.
try:
from sklearn.covariance import GraphicalLassoCV
except ImportError:
# for Scitkit-Learn < v0.20.0
from sklearn.covariance import GraphLassoCV as GraphicalLassoCV
covariance_estimator = GraphicalLassoCV(cv=3, verbose=1)
We just fit our regions signals into the GraphicalLassoCV object
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 1 out of 4: 6s
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 2 out of 4: 29s
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 3 out of 4: 68s
[GraphicalLassoCV] Done refinement 4 out of 4: 107s
/home/remi/github/nilearn/env/lib/python3.11/site-packages/numpy/core/_methods.py:173: RuntimeWarning:
invalid value encountered in subtract
and get the ROI-to-ROI covariance matrix.
matrix = covariance_estimator.covariance_
print(f"Covariance matrix has shape {matrix.shape}.")
Covariance matrix has shape (264, 264).
Plot matrix, graph, and strength#
We use :func: nilearn.plotting.plot_matrix to visualize our correlation matrix and display the graph of connections with nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome.
from nilearn import plotting
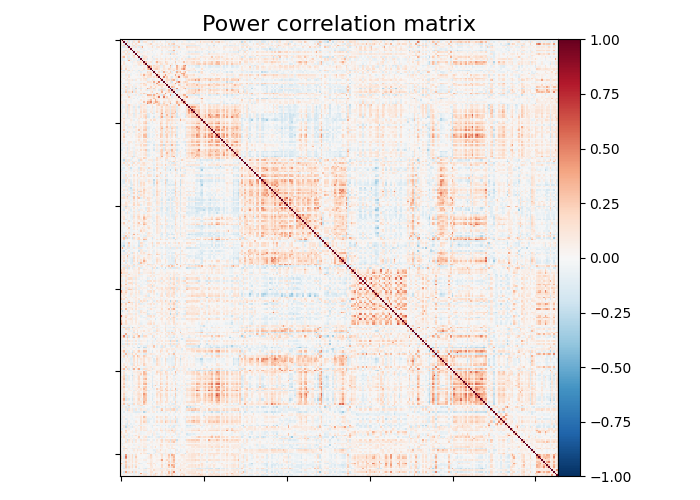
plotting.plot_matrix(
matrix,
vmin=-1.0,
vmax=1.0,
colorbar=True,
title="Power correlation matrix",
)
# Tweak edge_threshold to keep only the strongest connections.
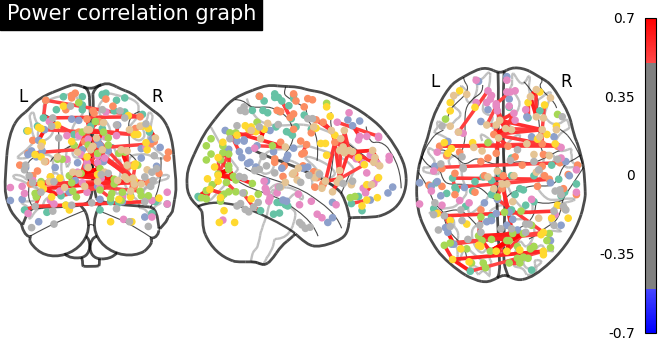
plotting.plot_connectome(
matrix,
coords,
title="Power correlation graph",
edge_threshold="99.8%",
node_size=20,
colorbar=True,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fd1e3366c90>
Note
Note the 1. on the matrix diagonal: These are the signals variances, set to 1. by the spheres_masker. Hence the covariance of the signal is a correlation matrix.
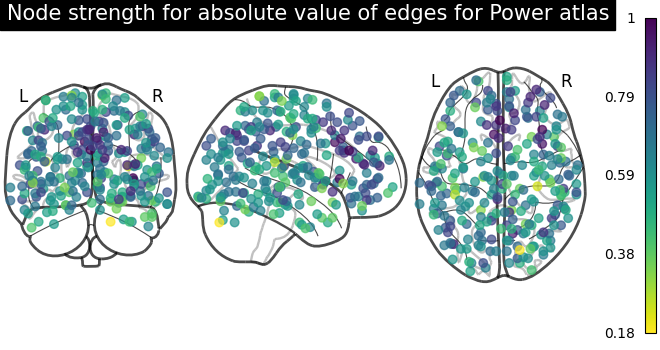
Sometimes, the information in the correlation matrix is overwhelming and aggregating edge strength from the graph would help. Use the function nilearn.plotting.plot_markers to visualize this information.
# calculate normalized, absolute strength for each node
node_strength = np.sum(np.abs(matrix), axis=0)
node_strength /= np.max(node_strength)
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength,
coords,
title="Node strength for absolute value of edges for Power atlas",
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fd1c10a1510>
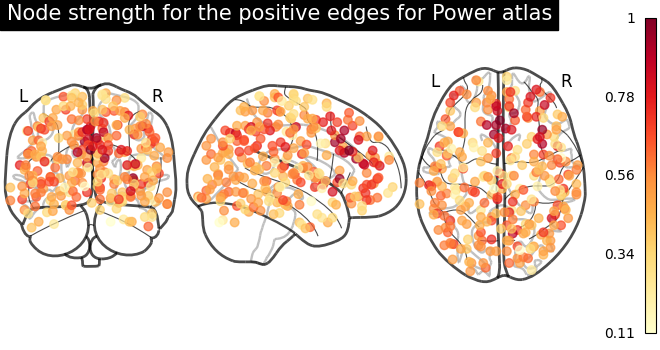
From the correlation matrix, we observe that there is a positive and negative structure. We could make two different plots, one for the positive and one for the negative structure.
from matplotlib.pyplot import cm
# clip connectivity matrix to preserve positive and negative edges
positive_edges = np.clip(matrix, 0, matrix.max())
negative_edges = np.clip(matrix, matrix.min(), 0)
# calculate strength for positive edges
node_strength_positive = np.sum(np.abs(positive_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_positive /= np.max(node_strength_positive)
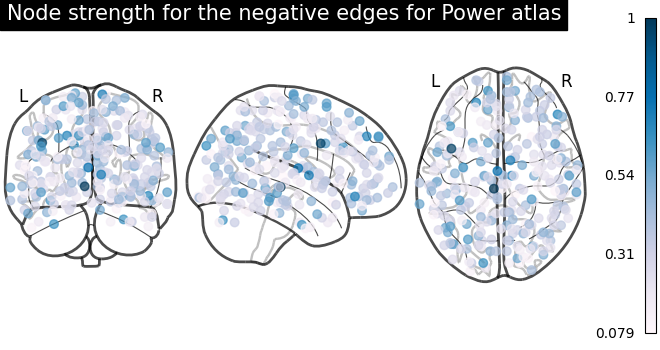
# calculate strength for negative edges
node_strength_negative = np.sum(np.abs(negative_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_negative /= np.max(node_strength_negative)
# plot nodes' strength for positive edges
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength_positive,
coords,
title="Node strength for the positive edges for Power atlas",
node_cmap=cm.YlOrRd,
)
# plot nodes' strength for negative edges
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength_negative,
coords,
title="Node strength for the negative edges for Power atlas",
node_cmap=cm.PuBu,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fd1ed3b8d50>
Connectome extracted from Dosenbach’s atlas#
We repeat the same steps for Dosenbach’s atlas.
dosenbach = datasets.fetch_coords_dosenbach_2010(legacy_format=False)
coords = np.vstack(
(
dosenbach.rois["x"],
dosenbach.rois["y"],
dosenbach.rois["z"],
)
).T
spheres_masker = NiftiSpheresMasker(
seeds=coords,
smoothing_fwhm=6,
radius=4.5,
detrend=True,
standardize="zscore_sample",
standardize_confounds="zscore_sample",
low_pass=0.1,
high_pass=0.01,
t_r=2,
)
timeseries = spheres_masker.fit_transform(
func_filename, confounds=confounds_filename
)
covariance_estimator = GraphicalLassoCV()
covariance_estimator.fit(timeseries)
matrix = covariance_estimator.covariance_
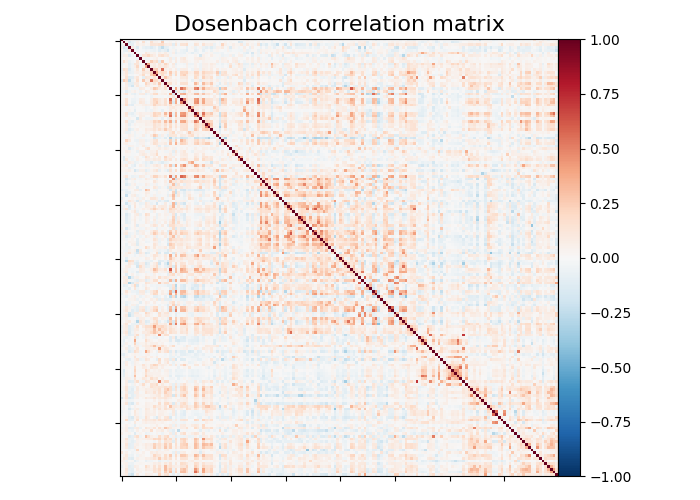
plotting.plot_matrix(
matrix,
vmin=-1.0,
vmax=1.0,
colorbar=True,
title="Dosenbach correlation matrix",
)
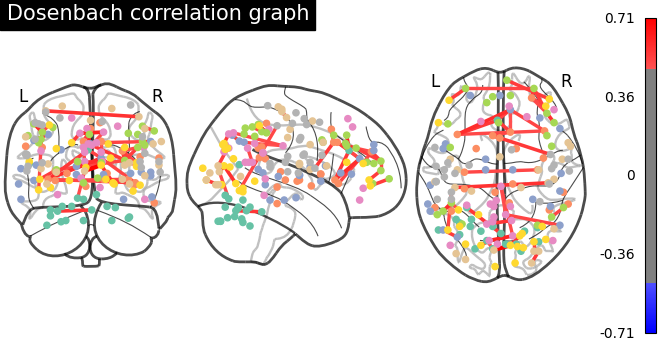
plotting.plot_connectome(
matrix,
coords,
title="Dosenbach correlation graph",
edge_threshold="99.7%",
node_size=20,
colorbar=True,
)
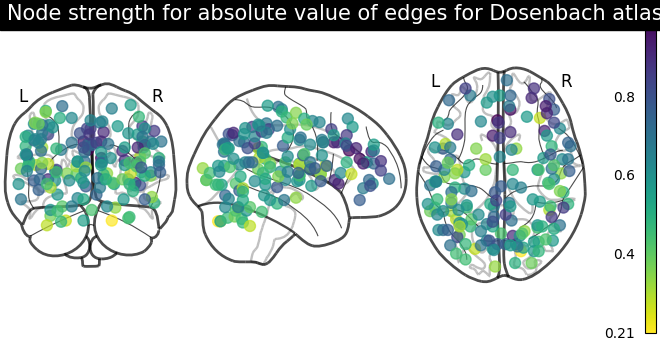
# calculate average strength for each node
node_strength = np.sum(np.abs(matrix), axis=0)
node_strength /= np.max(node_strength)
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength,
coords,
title="Node strength for absolute value of edges for Dosenbach atlas",
)
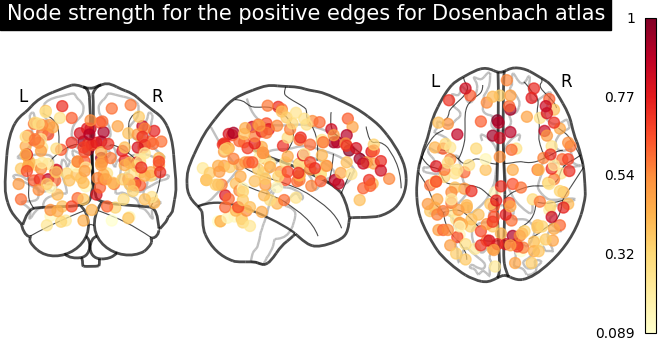
# clip connectivity matrix to preserve positive and negative edges
positive_edges = np.clip(matrix, 0, matrix.max())
negative_edges = np.clip(matrix, matrix.min(), 0)
# calculate strength for positive and edges
node_strength_positive = np.sum(np.abs(positive_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_positive /= np.max(node_strength_positive)
node_strength_negative = np.sum(np.abs(negative_edges), axis=0)
node_strength_negative /= np.max(node_strength_negative)
# plot nodes' strength for positive edges
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength_positive,
coords,
title="Node strength for the positive edges for Dosenbach atlas",
node_cmap=cm.YlOrRd,
)
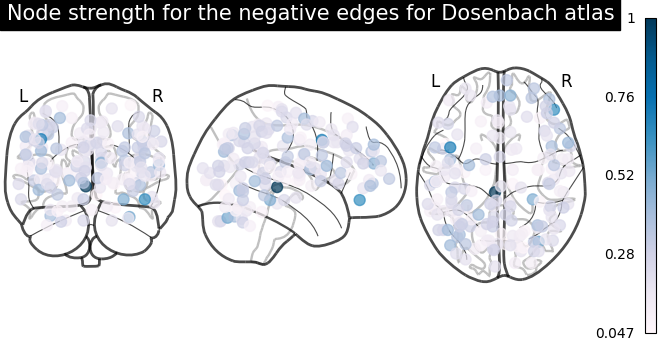
# plot nodes' strength for negative edges
plotting.plot_markers(
node_strength_negative,
coords,
title="Node strength for the negative edges for Dosenbach atlas",
node_cmap=cm.PuBu,
)
/home/remi/github/nilearn/env/lib/python3.11/site-packages/numpy/core/_methods.py:173: RuntimeWarning:
invalid value encountered in subtract
<nilearn.plotting.displays._projectors.OrthoProjector object at 0x7fd1efd40850>
We can easily identify the Dosenbach’s networks from the matrix blocks.
print(f"Dosenbach networks names are {np.unique(dosenbach.networks)}")
plotting.show()
Dosenbach networks names are ['cerebellum' 'cingulo-opercular' 'default' 'fronto-parietal' 'occipital'
'sensorimotor']
References#
See Also#
Total running time of the script: (4 minutes 26.208 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 576 MB