Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the function signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome#
- nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome(adjacency_matrix, node_coords, node_color='auto', node_size=50, edge_cmap=<matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap object>, edge_vmin=None, edge_vmax=None, edge_threshold=None, output_file=None, display_mode='ortho', figure=None, axes=None, title=None, annotate=True, black_bg=False, alpha=0.7, edge_kwargs=None, node_kwargs=None, colorbar=False)[source]#
Plot connectome on top of the brain glass schematics.
The plotted image should be in MNI space for this function to work properly.
In the case of ‘l’ and ‘r’ directions (for hemispheric projections), markers in the coordinate x == 0 are included in both hemispheres.
- Parameters
- adjacency_matrixnumpy array of shape (n, n)
Represents the link strengths of the graph. The matrix can be symmetric which will result in an undirected graph, or not symmetric which will result in a directed graph.
- node_coordsnumpy array_like of shape (n, 3)
3d coordinates of the graph nodes in world space.
- node_colorcolor or sequence of colors or ‘auto’, optional
Color(s) of the nodes. If string is given, all nodes are plotted with same color given in string.
- node_sizescalar or array_like, optional
Size(s) of the nodes in points^2. Default=50.
- edge_cmapcolormap, optional
Colormap used for representing the strength of the edges. Default=cm.bwr.
- edge_vmin, edge_vmaxfloat, optional
If not None, either or both of these values will be used to as the minimum and maximum values to color edges. If None are supplied the maximum absolute value within the given threshold will be used as minimum (multiplied by -1) and maximum coloring levels.
- edge_thresholdstr or number, optional
If it is a number only the edges with a value greater than edge_threshold will be shown. If it is a string it must finish with a percent sign, e.g. “25.3%”, and only the edges with a abs(value) above the given percentile will be shown.
- output_file
str, or None, optional The name of an image file to export the plot to. Valid extensions are .png, .pdf, .svg. If
output_fileis not None, the plot is saved to a file, and the display is closed.- display_modestring, optional
Choose the direction of the cuts: ‘x’ - sagittal, ‘y’ - coronal, ‘z’ - axial, ‘l’ - sagittal left hemisphere only, ‘r’ - sagittal right hemisphere only, ‘ortho’ - three cuts are performed in orthogonal directions. Possible values are: ‘ortho’, ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’, ‘xz’, ‘yx’, ‘yz’, ‘l’, ‘r’, ‘lr’, ‘lzr’, ‘lyr’, ‘lzry’, ‘lyrz’. Default=’ortho’.
- figure
int, ormatplotlib.figure.Figure, or None, optional Matplotlib figure used or its number. If
Noneis given, a new figure is created.- axes
matplotlib.axes.Axes, or 4 tupleoffloat: (xmin, ymin, width, height), optional The axes, or the coordinates, in matplotlib figure space, of the axes used to display the plot. If
None, the complete figure is used.- title
str, or None, optional The title displayed on the figure. Default=None.
- annotate
bool, optional If
annotateisTrue, positions and left/right annotation are added to the plot. Default=True.- black_bg
bool, or ‘auto’, optional If
True, the background of the image is set to be black. If you wish to save figures with a black background, you will need to pass facecolor=’k’, edgecolor=’k’ tomatplotlib.pyplot.savefig. Default=False.- alphafloat between 0 and 1, optional
Alpha transparency for the brain schematics. Default=0.7.
- edge_kwargsdict, optional
Will be passed as kwargs for each edge matlotlib Line2D.
- node_kwargsdict, optional
Will be passed as kwargs to the plt.scatter call that plots all the nodes in one go.
- colorbar
bool, optional If
True, display a colorbar on the right of the plots. Default=False.
See also
nilearn.plotting.find_parcellation_cut_coordsExtraction of node coords on brain parcellations.
nilearn.plotting.find_probabilistic_atlas_cut_coordsExtraction of node coords on brain probabilistic atlases.
Examples using nilearn.plotting.plot_connectome#
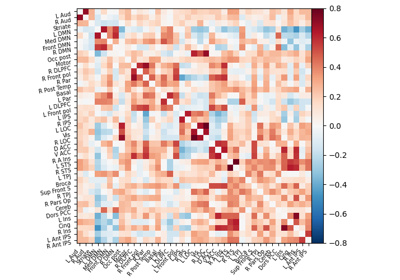
Extracting signals of a probabilistic atlas of functional regions
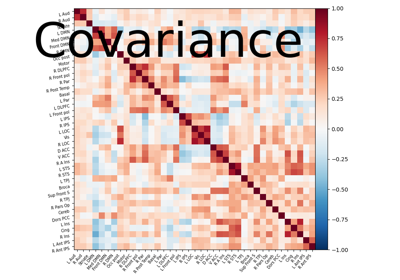
Computing a connectome with sparse inverse covariance
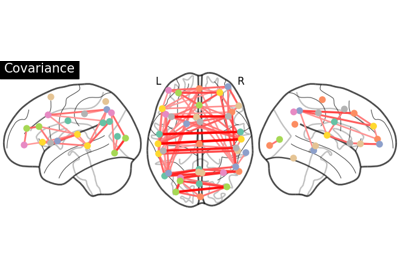
Group Sparse inverse covariance for multi-subject connectome
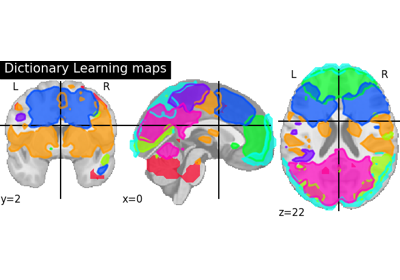
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes
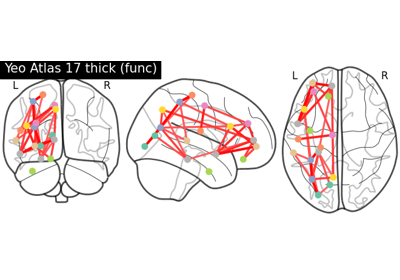
Comparing connectomes on different reference atlases
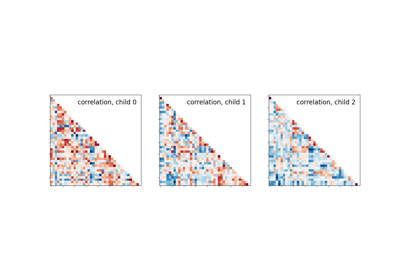
Classification of age groups using functional connectivity