Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.maskers.NiftiMapsMasker#
- class nilearn.maskers.NiftiMapsMasker(maps_img, mask_img=None, allow_overlap=True, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, standardize_confounds=True, high_variance_confounds=False, detrend=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, dtype=None, resampling_target='data', memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0, verbose=0, reports=True)[source]#
Class for masking of Niimg-like objects.
NiftiMapsMasker is useful when data from overlapping volumes should be extracted (contrarily to
nilearn.maskers.NiftiLabelsMasker). Use case: Summarize brain signals from large-scale networks obtained by prior PCA or ICA.Note that, Inf or NaN present in the given input images are automatically put to zero rather than considered as missing data.
- Parameters
- maps_img4D niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Set of continuous maps. One representative time course per map is extracted using least square regression.
- mask_img3D niimg-like object, optional
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Mask to apply to regions before extracting signals.
- allow_overlap
bool, optional If False, an error is raised if the maps overlaps (ie at least two maps have a non-zero value for the same voxel). Default=True.
- smoothing_fwhm
float, optional. If
smoothing_fwhmis notNone, it gives the full-width at half maximum in millimeters of the spatial smoothing to apply to the signal.- standardize{False, True, ‘zscore’, ‘psc’}, optional
Strategy to standardize the signal. ‘zscore’: the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. ‘psc’: Timeseries are shifted to zero mean value and scaled to percent signal change (as compared to original mean signal). True : the signal is z-scored. Timeseries are shifted to zero mean and scaled to unit variance. False : Do not standardize the data. Default=False.
- standardize_confounds
bool, optional If standardize_confounds is True, the confounds are z-scored: their mean is put to 0 and their variance to 1 in the time dimension. Default=True.
- high_variance_confounds
bool, optional If True, high variance confounds are computed on provided image with
nilearn.image.high_variance_confoundsand default parameters and regressed out. Default=False.- detrend
bool, optional This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. Default=False.
- low_passNone or
float, optional This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- high_passNone or
float, optional This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- t_r
float, optional This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details
- dtype{dtype, “auto”}, optional
Data type toward which the data should be converted. If “auto”, the data will be converted to int32 if dtype is discrete and float32 if it is continuous.
- resampling_target{“data”, “mask”, “maps”, None}, optional.
Gives which image gives the final shape/size. For example, if resampling_target is “mask” then maps_img and images provided to fit() are resampled to the shape and affine of mask_img. “None” means no resampling: if shapes and affines do not match, a ValueError is raised. Default=”data”.
- memory
joblib.Memoryorstr, optional Used to cache the region extraction process. By default, no caching is done. If a string is given, it is the path to the caching directory.
- memory_level
int, optional Aggressiveness of memory caching. The higher the number, the higher the number of functions that will be cached. Zero means no caching. Default=0.
- verbose
int, optional Indicate the level of verbosity. By default, nothing is printed. Default=0.
- reports
bool, optional If set to True, data is saved in order to produce a report. Default=True.
Notes
If resampling_target is set to “maps”, every 3D image processed by transform() will be resampled to the shape of maps_img. It may lead to a very large memory consumption if the voxel number in maps_img is large.
- Attributes
- maps_img_
nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image The maps mask of the data.
- n_elements_
int The number of overlapping maps in the mask. This is equivalent to the number of volumes in the mask image.
New in version 0.9.2.
- maps_img_
- __init__(maps_img, mask_img=None, allow_overlap=True, smoothing_fwhm=None, standardize=False, standardize_confounds=True, high_variance_confounds=False, detrend=False, low_pass=None, high_pass=None, t_r=None, dtype=None, resampling_target='data', memory=Memory(location=None), memory_level=0, verbose=0, reports=True)[source]#
- generate_report(displayed_maps=10)[source]#
Generate an HTML report for the current
NiftiMapsMaskerobject.Note
This functionality requires to have
Matplotlibinstalled.- Parameters
- displayed_maps
int, orlist, orndarray, or “all”, optional Indicates which maps will be displayed in the HTML report.
If “all”: All maps will be displayed in the report.
masker.generate_report("all")
If a
listorndarray: This indicates the indices of the maps to be displayed in the report. For example, the following code will generate a report with maps 6, 3, and 12, displayed in this specific order:
masker.generate_report([6, 3, 12])
If an
int: This will only display the first n maps, n being the value of the parameter. By default, the report will only contain the first 10 maps. Example to display the first 16 maps:
masker.generate_report(16)
Default=10.
- displayed_maps
- Returns
- reportnilearn.reporting.html_report.HTMLReport
HTML report for the masker.
- fit(imgs=None, y=None)[source]#
Prepare signal extraction from regions.
All parameters are unused, they are for scikit-learn compatibility.
- fit_transform(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None)[source]#
Prepare and perform signal extraction.
- transform_single_imgs(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None)[source]#
Extract signals from a single 4D niimg.
- Parameters
- imgs3D/4D Niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Images to process. If a 3D niimg is provided, a singleton dimension will be added to the output to represent the single scan in the niimg.
- confoundsCSV file or array-like, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)
- sample_maskAny type compatible with numpy-array indexing, optional
shape: (number of scans - number of volumes removed, ) Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension to perform scrubbing (remove volumes with high motion) and/or non-steady-state volumes. This parameter is passed to signal.clean.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- region_signals2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each map. shape: (number of scans, number of maps)
- Warns
- DeprecationWarning
If a 3D niimg input is provided, the current behavior (adding a singleton dimension to produce a 2D array) is deprecated. Starting in version 0.12, a 1D array will be returned for 3D inputs.
- inverse_transform(region_signals)[source]#
Compute voxel signals from region signals
Any mask given at initialization is taken into account.
- Parameters
- region_signals1D/2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each region. If a 1D array is provided, then the shape should be (number of elements,), and a 3D img will be returned. If a 2D array is provided, then the shape should be (number of scans, number of elements), and a 4D img will be returned.
- Returns
- voxel_signalsnibabel.Nifti1Image
Signal for each voxel. shape: that of maps.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- set_output(*, transform=None)#
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of transform and fit_transform.
“default”: Default output format of a transformer
“pandas”: DataFrame output
None: Transform configuration is unchanged
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- transform(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None)[source]#
Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
- Parameters
- imgs3D/4D Niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Images to process. If a 3D niimg is provided, a singleton dimension will be added to the output to represent the single scan in the niimg.
- confoundsCSV file or array-like, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)
- sample_maskAny type compatible with numpy-array indexing, optional
shape: (number of scans - number of volumes removed, ) Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension to perform scrubbing (remove volumes with high motion) and/or non-steady-state volumes. This parameter is passed to signal.clean.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- region_signals2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each element. shape: (number of scans, number of elements)
- Warns
- DeprecationWarning
If a 3D niimg input is provided, the current behavior (adding a singleton dimension to produce a 2D array) is deprecated. Starting in version 0.12, a 1D array will be returned for 3D inputs.
Examples using nilearn.maskers.NiftiMapsMasker#
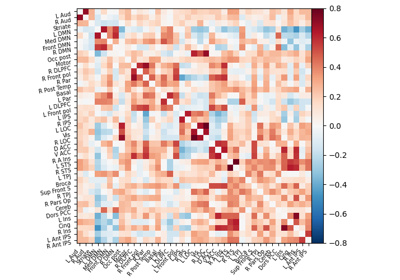
Extracting signals of a probabilistic atlas of functional regions
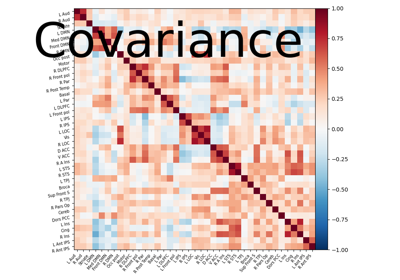
Computing a connectome with sparse inverse covariance
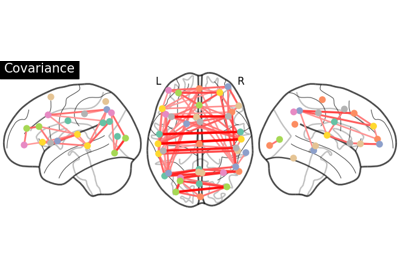
Group Sparse inverse covariance for multi-subject connectome
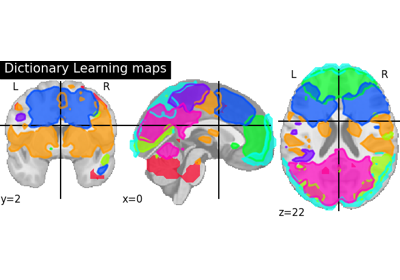
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes
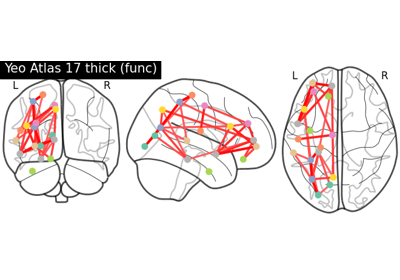
Comparing connectomes on different reference atlases
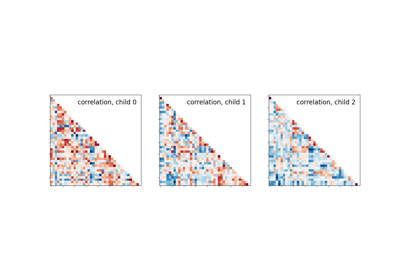
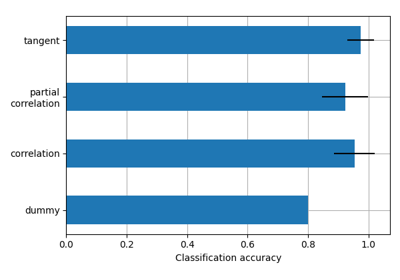
Classification of age groups using functional connectivity
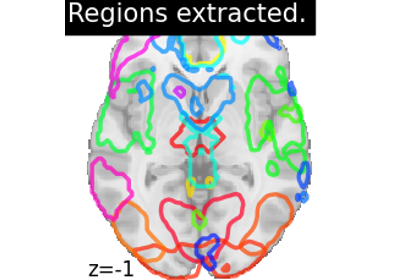
Regions Extraction of Default Mode Networks using Smith Atlas