Note
This page is a reference documentation. It only explains the class signature, and not how to use it. Please refer to the user guide for the big picture.
nilearn.maskers.BaseMasker#
- class nilearn.maskers.BaseMasker[source]#
Base class for NiftiMaskers.
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)#
- abstract transform_single_imgs(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, copy=True)[source]#
Extract signals from a single 4D niimg.
- Parameters
- imgs3D/4D Niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Images to process. If a 3D niimg is provided, a singleton dimension will be added to the output to represent the single scan in the niimg.
- confoundsCSV file or array-like, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)
- sample_maskAny type compatible with numpy-array indexing, optional
shape: (number of scans - number of volumes removed, ) Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension to perform scrubbing (remove volumes with high motion) and/or non-steady-state volumes. This parameter is passed to signal.clean.
New in version 0.8.0.
- copyBoolean, optional
Indicates whether a copy is returned or not. Default=True.
- Returns
- region_signals2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each element. shape: (number of scans, number of elements)
- Warns
- DeprecationWarning
If a 3D niimg input is provided, the current behavior (adding a singleton dimension to produce a 2D array) is deprecated. Starting in version 0.12, a 1D array will be returned for 3D inputs.
- transform(imgs, confounds=None, sample_mask=None)[source]#
Apply mask, spatial and temporal preprocessing
- Parameters
- imgs3D/4D Niimg-like object
See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation. Images to process. If a 3D niimg is provided, a singleton dimension will be added to the output to represent the single scan in the niimg.
- confoundsCSV file or array-like, optional
This parameter is passed to signal.clean. Please see the related documentation for details. shape: (number of scans, number of confounds)
- sample_maskAny type compatible with numpy-array indexing, optional
shape: (number of scans - number of volumes removed, ) Masks the niimgs along time/fourth dimension to perform scrubbing (remove volumes with high motion) and/or non-steady-state volumes. This parameter is passed to signal.clean.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- region_signals2D numpy.ndarray
Signal for each element. shape: (number of scans, number of elements)
- Warns
- DeprecationWarning
If a 3D niimg input is provided, the current behavior (adding a singleton dimension to produce a 2D array) is deprecated. Starting in version 0.12, a 1D array will be returned for 3D inputs.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, confounds=None, sample_mask=None, **fit_params)[source]#
Fit to data, then transform it
- Parameters
- XNiimg-like object
- ynumpy array of shape [n_samples], optional
Target values.
- confoundslist of confounds, optional
List of confounds (2D arrays or filenames pointing to CSV files). Must be of same length than imgs_list.
- sample_masklist of sample_mask, optional
List of sample_mask (1D arrays) if scrubbing motion outliers. Must be of same length than imgs_list.
New in version 0.8.0.
- Returns
- X_newnumpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features_new]
Transformed array.
- inverse_transform(X)[source]#
Transform the 2D data matrix back to an image in brain space.
- Parameters
- X1D/2D
numpy.ndarray Signal for each element in the mask. If a 1D array is provided, then the shape should be (number of elements,), and a 3D img will be returned. If a 2D array is provided, then the shape should be (number of scans, number of elements), and a 4D img will be returned. See Input and output: neuroimaging data representation.
- X1D/2D
- Returns
- imgTransformed image in brain space.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- set_output(*, transform=None)#
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of transform and fit_transform.
“default”: Default output format of a transformer
“pandas”: DataFrame output
None: Transform configuration is unchanged
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using nilearn.maskers.BaseMasker#
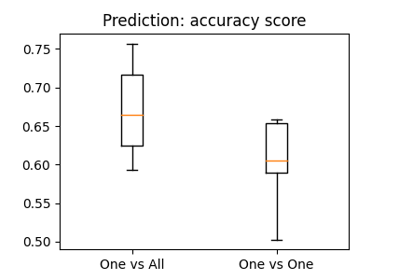
The haxby dataset: different multi-class strategies
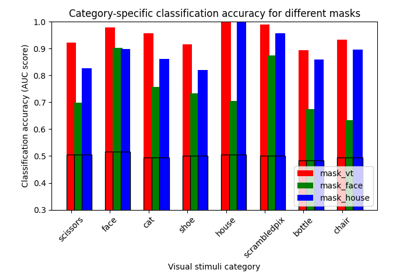
ROI-based decoding analysis in Haxby et al. dataset

Encoding models for visual stimuli from Miyawaki et al. 2008
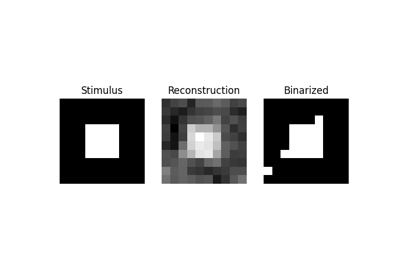
Reconstruction of visual stimuli from Miyawaki et al. 2008
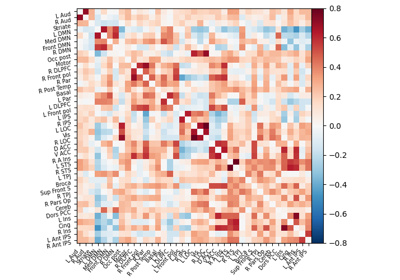
Extracting signals of a probabilistic atlas of functional regions
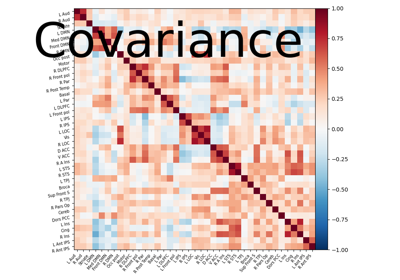
Computing a connectome with sparse inverse covariance
Producing single subject maps of seed-to-voxel correlation
Group Sparse inverse covariance for multi-subject connectome
Regions extraction using dictionary learning and functional connectomes
Comparing connectomes on different reference atlases
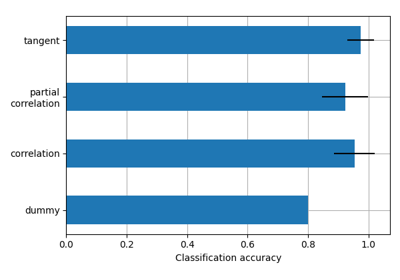
Classification of age groups using functional connectivity
Regions Extraction of Default Mode Networks using Smith Atlas
Extracting signals from brain regions using the NiftiLabelsMasker
Computing a Region of Interest (ROI) mask manually
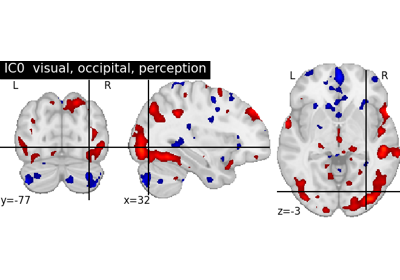
Multivariate decompositions: Independent component analysis of fMRI
Massively univariate analysis of a calculation task from the Localizer dataset
Massively univariate analysis of a motor task from the Localizer dataset

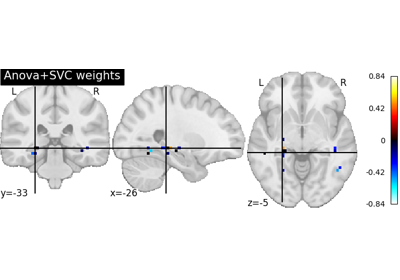
Massively univariate analysis of face vs house recognition
Beta-Series Modeling for Task-Based Functional Connectivity and Decoding