Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Massively univariate analysis of a motor task from the Localizer dataset#
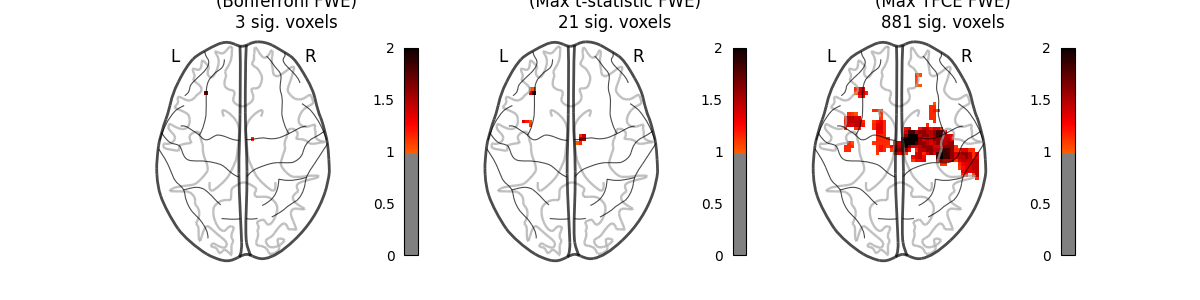
This example shows the results obtained in a massively univariate analysis performed at the inter-subject level with various methods. We use the [left button press (auditory cue)] task from the Localizer dataset and seek association between the contrast values and a variate that measures the speed of pseudo-word reading. No confounding variate is included in the model.
A standard ANOVA is performed. Data smoothed at 5 voxels FWHM are used.
A permuted Ordinary Least Squares algorithm is run at each voxel. Data smoothed at 5 voxels FWHM are used.
Note
If you are using Nilearn with a version older than 0.9.0, then you should either upgrade your version or import maskers from the input_data module instead of the maskers module.
That is, you should manually replace in the following example all occurrences of:
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
with:
from nilearn.input_data import NiftiMasker
# Author: Virgile Fritsch, <virgile.fritsch@inria.fr>, May. 2014
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from nilearn import datasets
from nilearn.maskers import NiftiMasker
from nilearn.mass_univariate import permuted_ols
Load Localizer contrast
n_samples = 94
localizer_dataset = datasets.fetch_localizer_contrasts(
['left button press (auditory cue)'],
n_subjects=n_samples, legacy_format=False
)
# print basic information on the dataset
print('First contrast nifti image (3D) is located at: %s' %
localizer_dataset.cmaps[0])
tested_var = localizer_dataset.ext_vars['pseudo']
# Quality check / Remove subjects with bad tested variate
mask_quality_check = np.where(
np.logical_not(np.isnan(tested_var))
)[0]
n_samples = mask_quality_check.size
contrast_map_filenames = [localizer_dataset.cmaps[i]
for i in mask_quality_check]
tested_var = tested_var[mask_quality_check].values.reshape((-1, 1))
print("Actual number of subjects after quality check: %d" % n_samples)
First contrast nifti image (3D) is located at: /home/yasmin/nilearn/nilearn_data/brainomics_localizer/brainomics_data/S01/cmaps_LeftAuditoryClick.nii.gz
Actual number of subjects after quality check: 89
Mask data
nifti_masker = NiftiMasker(
smoothing_fwhm=5,
memory='nilearn_cache', memory_level=1) # cache options
fmri_masked = nifti_masker.fit_transform(contrast_map_filenames)
Anova (parametric F-scores)
from sklearn.feature_selection import f_regression
_, pvals_anova = f_regression(fmri_masked, tested_var, center=True)
pvals_anova *= fmri_masked.shape[1]
pvals_anova[np.isnan(pvals_anova)] = 1
pvals_anova[pvals_anova > 1] = 1
neg_log_pvals_anova = - np.log10(pvals_anova)
neg_log_pvals_anova_unmasked = nifti_masker.inverse_transform(
neg_log_pvals_anova)
/home/yasmin/miniconda3/envs/nilearn-dev/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sklearn/utils/validation.py:1141: DataConversionWarning:
A column-vector y was passed when a 1d array was expected. Please change the shape of y to (n_samples, ), for example using ravel().
Perform massively univariate analysis with permuted OLS
This method will produce both voxel-level FWE-corrected -log10 p-values and TFCE-based FWE-corrected -log10 p-values.
Note
permuted_ols can support a wide range of analysis designs, depending on the tested_var. For example, if you wished to perform a one-sample test, you could simply provide an array of ones (e.g., np.ones(n_samples)).
ols_outputs = permuted_ols(
tested_var, # this is equivalent to the design matrix, in array form
fmri_masked,
model_intercept=True,
masker=nifti_masker,
tfce=True,
n_perm=200, # 200 for the sake of time. Ideally, this should be 10000.
verbose=1, # display progress bar
n_jobs=1, # can be changed to use more CPUs
output_type='dict',
)
neg_log_pvals_permuted_ols_unmasked = nifti_masker.inverse_transform(
ols_outputs['logp_max_t'][0, :] # select first regressor
)
neg_log_pvals_tfce_unmasked = nifti_masker.inverse_transform(
ols_outputs['logp_max_tfce'][0, :] # select first regressor
)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
Job #1, processed 0/200 permutations (0.00%, 9456.541538238525 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 10/200 permutations (5.00%, 199.97646498680115 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 20/200 permutations (10.00%, 181.61162781715393 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 30/200 permutations (15.00%, 168.55436976750693 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 40/200 permutations (20.00%, 157.76355361938477 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 50/200 permutations (25.00%, 147.55213737487793 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 60/200 permutations (30.00%, 137.26348598798117 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 70/200 permutations (35.00%, 127.26012999670847 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 80/200 permutations (40.00%, 117.36105537414551 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 90/200 permutations (45.00%, 107.31601328319974 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 100/200 permutations (50.00%, 97.25175547599792 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 110/200 permutations (55.00%, 87.64054558493875 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 120/200 permutations (60.00%, 77.7589923540751 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 130/200 permutations (65.00%, 67.94184952515822 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 140/200 permutations (70.00%, 58.147416216986514 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 150/200 permutations (75.00%, 48.44477184613545 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 160/200 permutations (80.00%, 38.746485114097595 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 170/200 permutations (85.00%, 29.04467405992396 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 180/200 permutations (90.00%, 19.370041264428032 seconds remaining)
Job #1, processed 190/200 permutations (95.00%, 9.687544634467676 seconds remaining)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 1 out of 1 | elapsed: 3.2min finished
Visualization
from nilearn import plotting
from nilearn.image import get_data
# Various plotting parameters
z_slice = 12 # plotted slice
threshold = - np.log10(0.1) # 10% corrected
vmax = max(
np.amax(ols_outputs['logp_max_t']),
np.amax(neg_log_pvals_anova),
np.amax(ols_outputs['logp_max_tfce']),
)
images_to_plot = {
"Parametric Test\n(Bonferroni FWE)": neg_log_pvals_anova_unmasked,
"Permutation Test\n(Max t-statistic FWE)": (
neg_log_pvals_permuted_ols_unmasked
),
"Permutation Test\n(Max TFCE FWE)": neg_log_pvals_tfce_unmasked,
}
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 3), ncols=3)
for i_col, (title, img) in enumerate(images_to_plot.items()):
ax = axes[i_col]
n_detections = (get_data(img) > threshold).sum()
new_title = title + f"\n{n_detections} sig. voxels"
plotting.plot_glass_brain(
img,
colorbar=True,
vmax=vmax,
display_mode='z',
plot_abs=False,
cut_coords=[12],
threshold=threshold,
figure=fig,
axes=ax,
)
ax.set_title(new_title)
fig.suptitle(
"Group left button press ($-\\log_{10}$ p-values)",
y=1.3,
fontsize=16,
)
Text(0.5, 1.3, 'Group left button press ($-\\log_{10}$ p-values)')
Total running time of the script: ( 3 minutes 25.132 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 33 MB